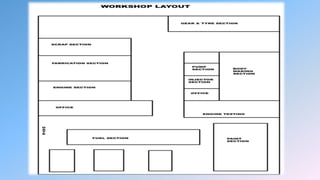
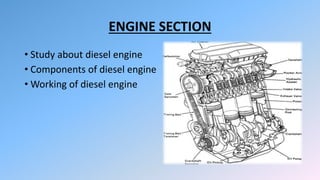
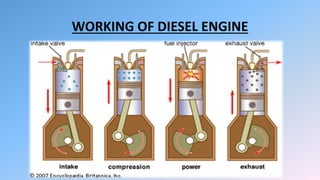
The document provides details about the Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC) and its operations, highlighting its history since 1947, the number of buses, and daily earnings. It also discusses the engine section focused on diesel engines, including descriptions of key components such as the cylinder block, piston, and turbocharger. The principles of diesel engine operation and its various parts are explained comprehensively.