The document provides a detailed overview of the history and development of the Indian Railways system. Some key points:
- The first train service in India began in 1851 between Bombay and Thana, and rail networks were established and expanded under British rule.
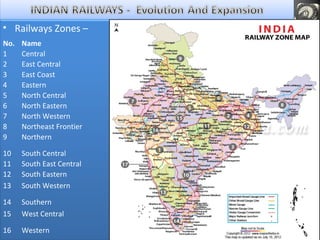
- At independence in 1947, India had over 40 rail systems that were nationalized into one state-owned entity with 16 zones.
- Over time the railways were modernized with the phase out of steam locomotives in 1985, computerization of reservation systems in the late 1980s-1990s, and the opening of difficult routes like the Konkan Railway.
- The railways play a major role in transporting passengers and freight across the large