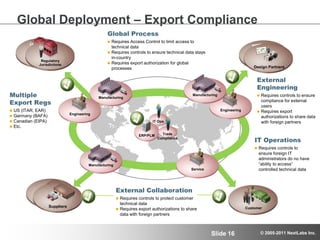
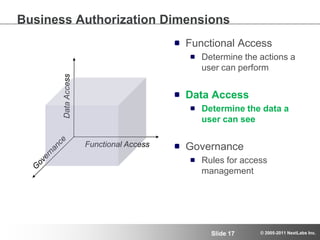
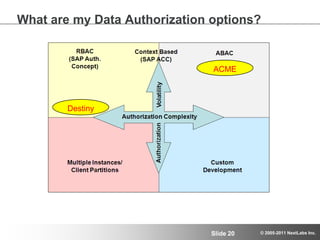
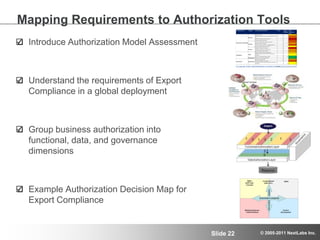
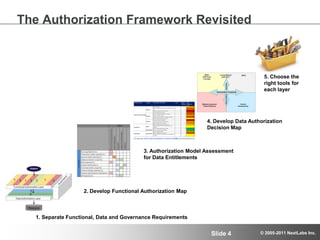
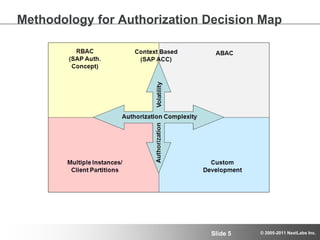
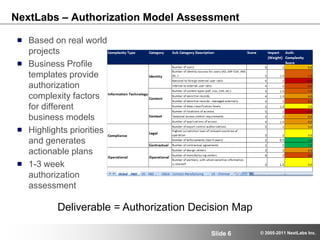
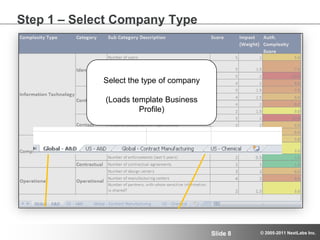
The document discusses advanced authorization methodologies for SAP global deployments, focusing on export compliance requirements. It introduces an authorization decision map and a framework for assessing authorization complexities, volatility, and compliance with global regulations. The framework aims to streamline access to technical data and ensure compliance with various export laws through a structured authorization model.





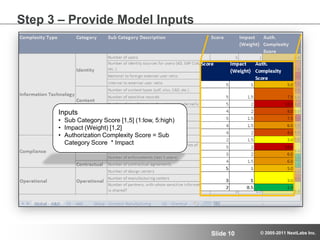
![Subcategory DescriptionStep 3 – Provide Model InputsInputsSub Category Score [1,5] (1:low, 5:high)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sapadvancedauthorizationsep2011webinarpartiiforslideshare-111005155422-phpapp01/85/Part-II-of-III-Advanced-Authorization-for-SAP-Global-Deployments-September-27-2011-12-320.jpg)
![Impact (Weight) [1,2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sapadvancedauthorizationsep2011webinarpartiiforslideshare-111005155422-phpapp01/85/Part-II-of-III-Advanced-Authorization-for-SAP-Global-Deployments-September-27-2011-13-320.jpg)
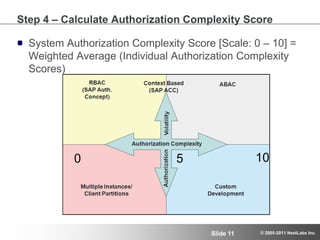
![Authorization Complexity Score = Sub Category Score * ImpactStep 4 – Calculate Authorization Complexity Score System Authorization Complexity Score [Scale: 0 – 10] = Weighted Average (Individual Authorization Complexity Scores)1050](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sapadvancedauthorizationsep2011webinarpartiiforslideshare-111005155422-phpapp01/85/Part-II-of-III-Advanced-Authorization-for-SAP-Global-Deployments-September-27-2011-14-320.jpg)