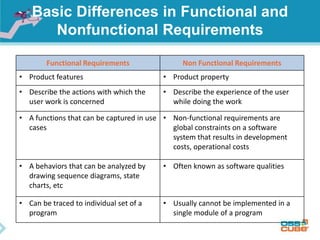
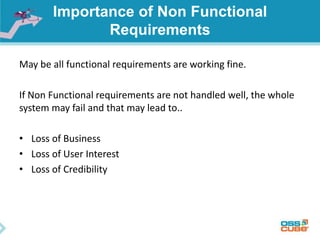
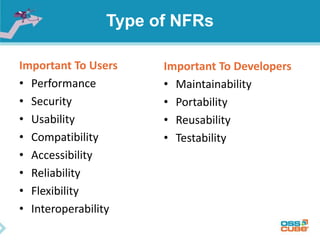
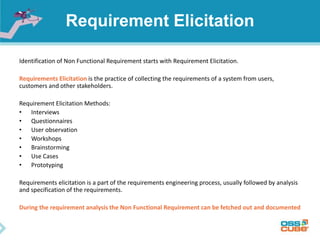
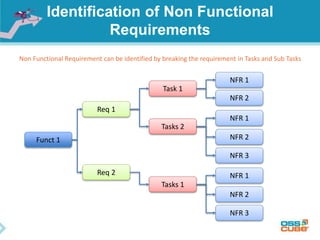
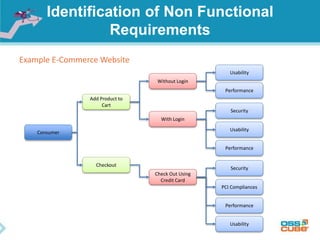
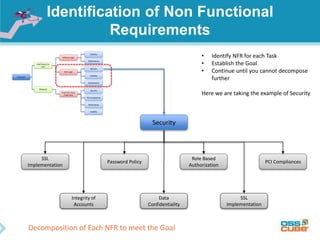
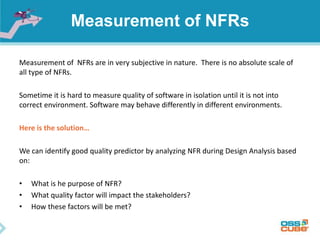
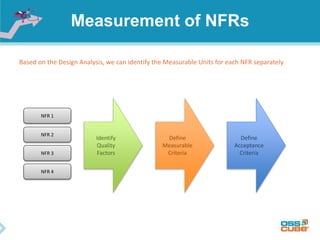
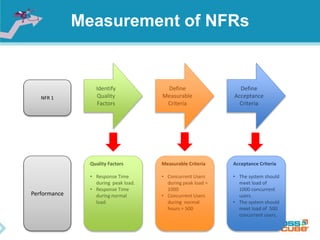
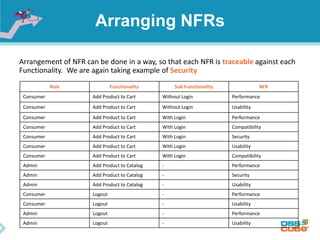
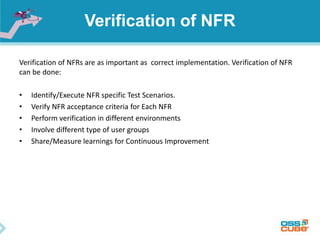
The document discusses the importance of non-functional requirements (NFRs) in software engineering, emphasizing their role in defining how a system performs rather than what it does. It outlines methods for identifying, measuring, and verifying NFRs, as well as the challenges associated with them, while highlighting key types essential to users and developers. Additionally, it provides insights into elicitation techniques, the differences between functional and non-functional requirements, and the negative impacts of inadequate NFR management.