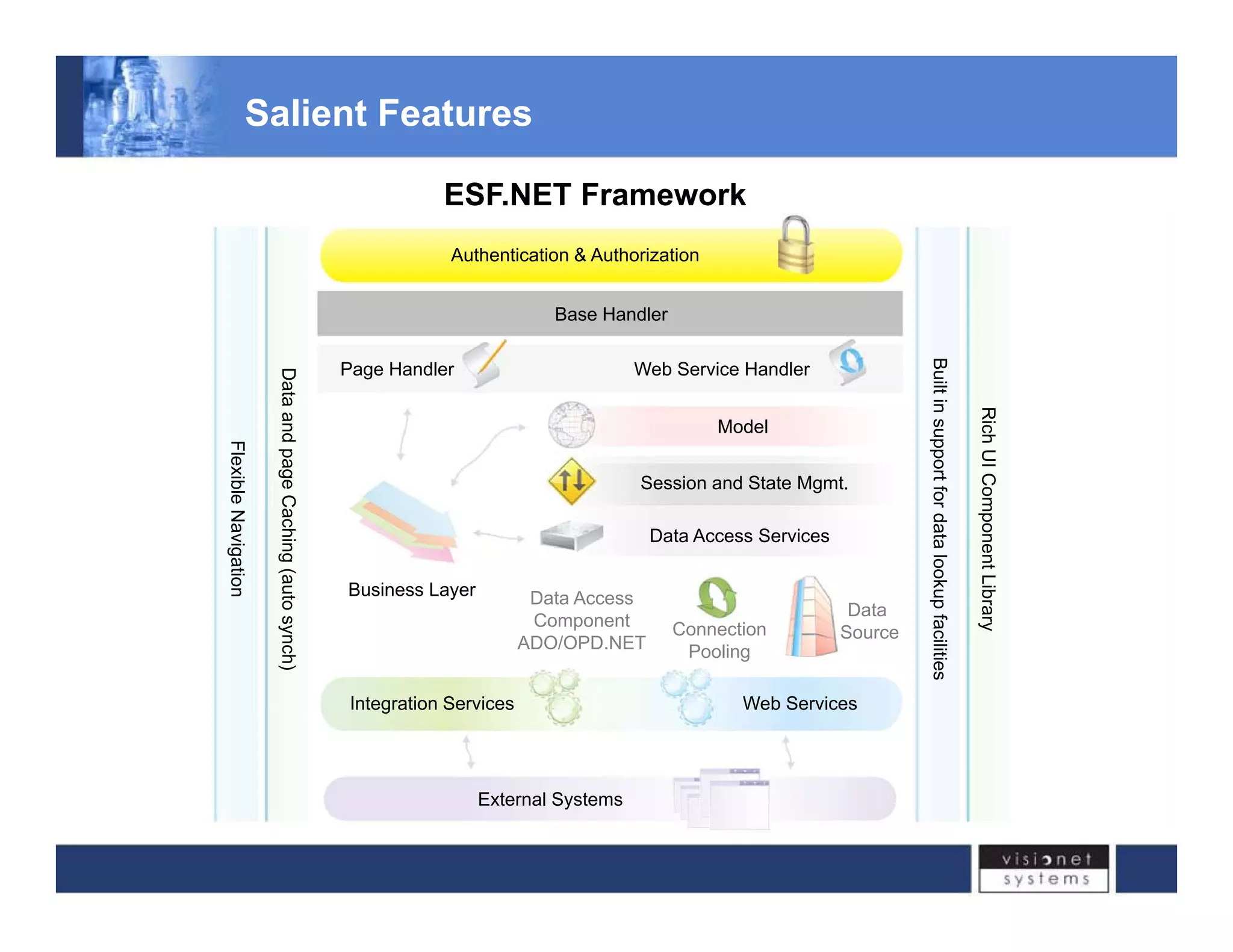
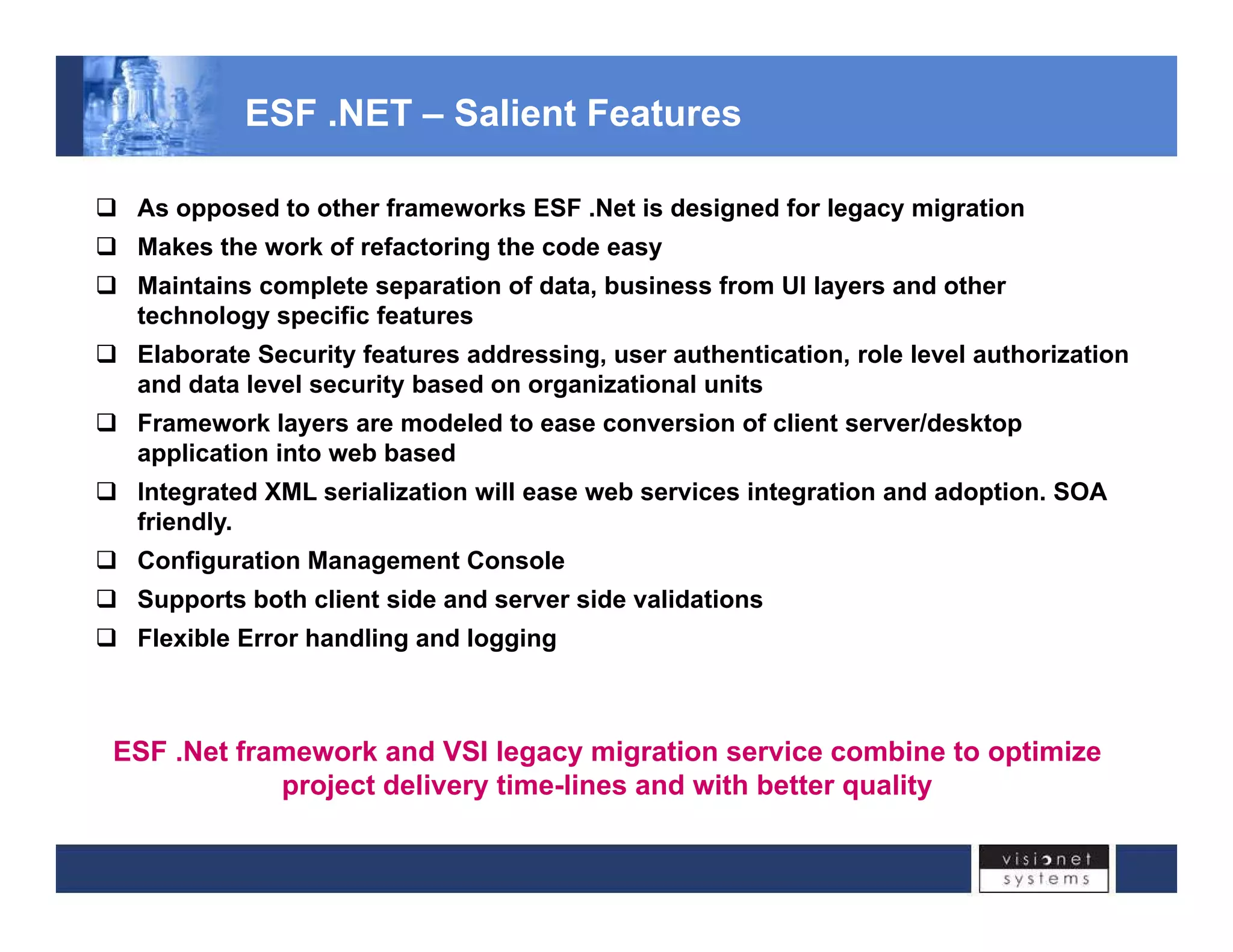
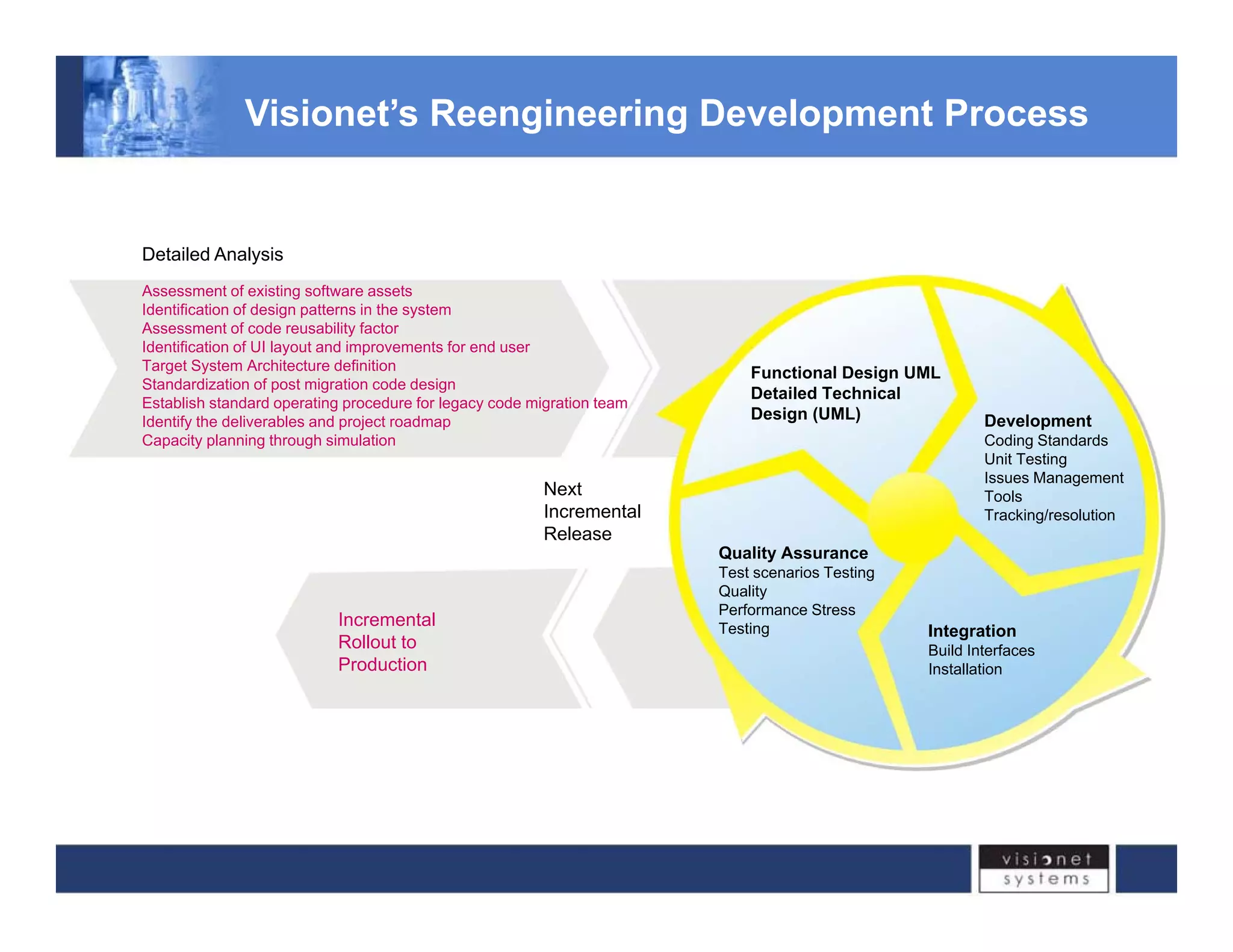
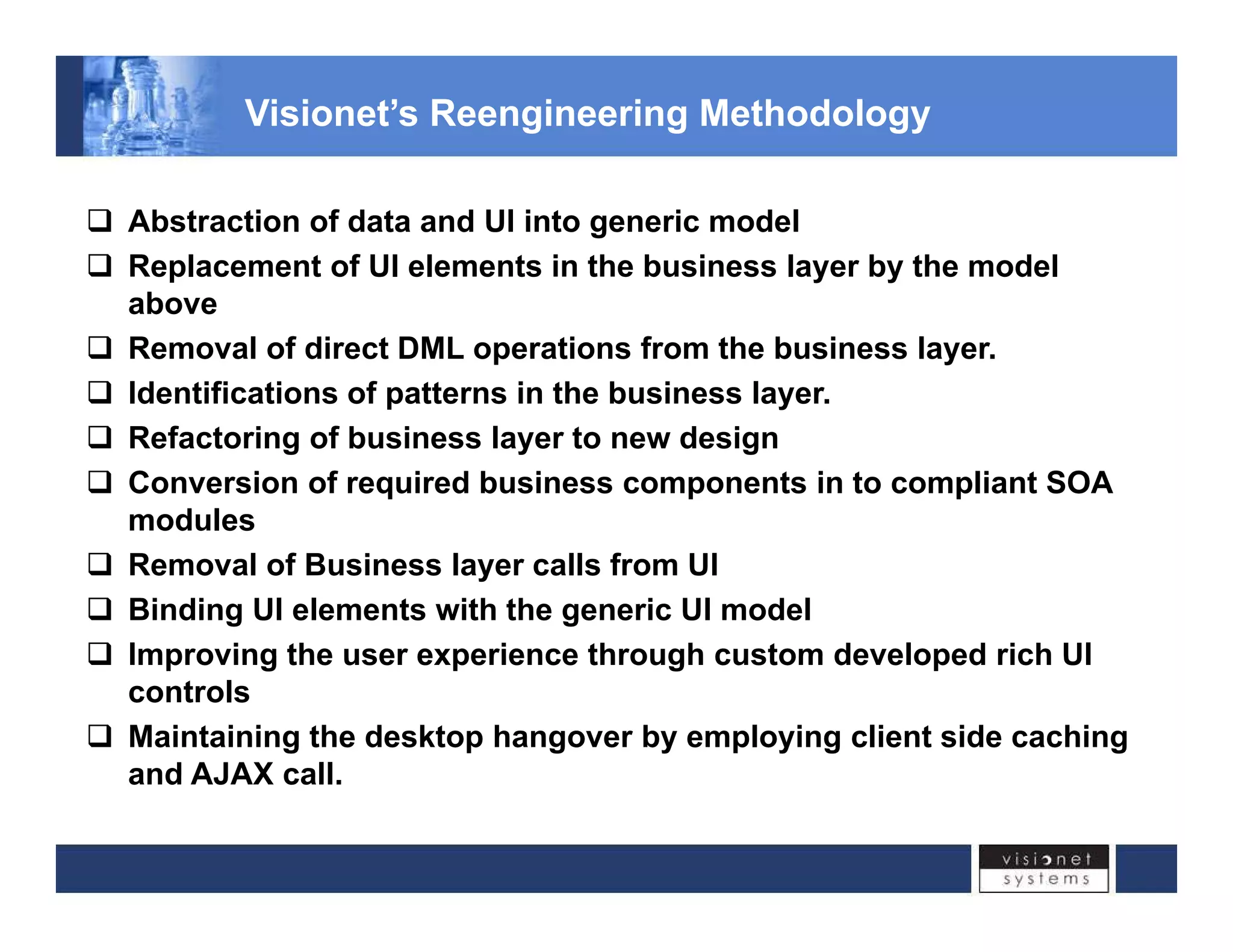
Visionet Systems Inc. addresses challenges associated with legacy application issues in enterprise systems, highlighting the high management costs and lack of flexibility due to monolithic business applications. The document outlines a re-engineering initiative through the esf.net framework, designed for legacy migration, which optimizes project delivery timelines and reduces development costs. Key features of the framework include improved code refactoring, security features, and support for services-oriented architecture, enabling smoother transitions and better integration across applications.