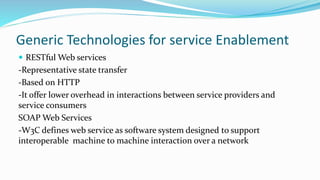
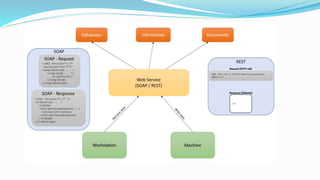
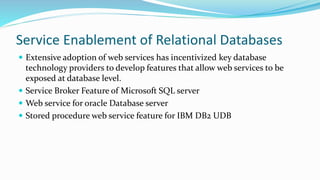
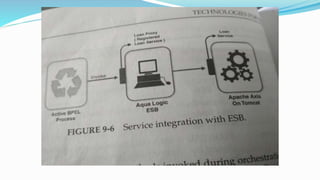
This document discusses technologies for enabling service-oriented architectures (SOAs). It covers generic technologies like RESTful and SOAP web services. Platform-specific technologies for Java (JAX-WS) and .NET (.NET, WCF) are also discussed. Standards like XML, HTTP, SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI that web services are built on are explained. The roles of service providers, consumers and registries are defined. Enterprise service buses and their role in service integration are summarized. Finally, factors to consider in building a business case for SOA like stakeholders' objectives, benefits, cost savings, and return on investment are outlined.















![Cost Savings
The cost saving can be computed as
Development cost savings=[(N*R)/100]*(C*A)
N-number of services that are reusable
R(%)-Degree of reuse
C=Complexity of services(average no of functions or objects points per
service)
A=Average cost per function point or object point](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iii-soatechnologies-210823094335/85/Unit-3-SOA-Technologies-20-320.jpg)

