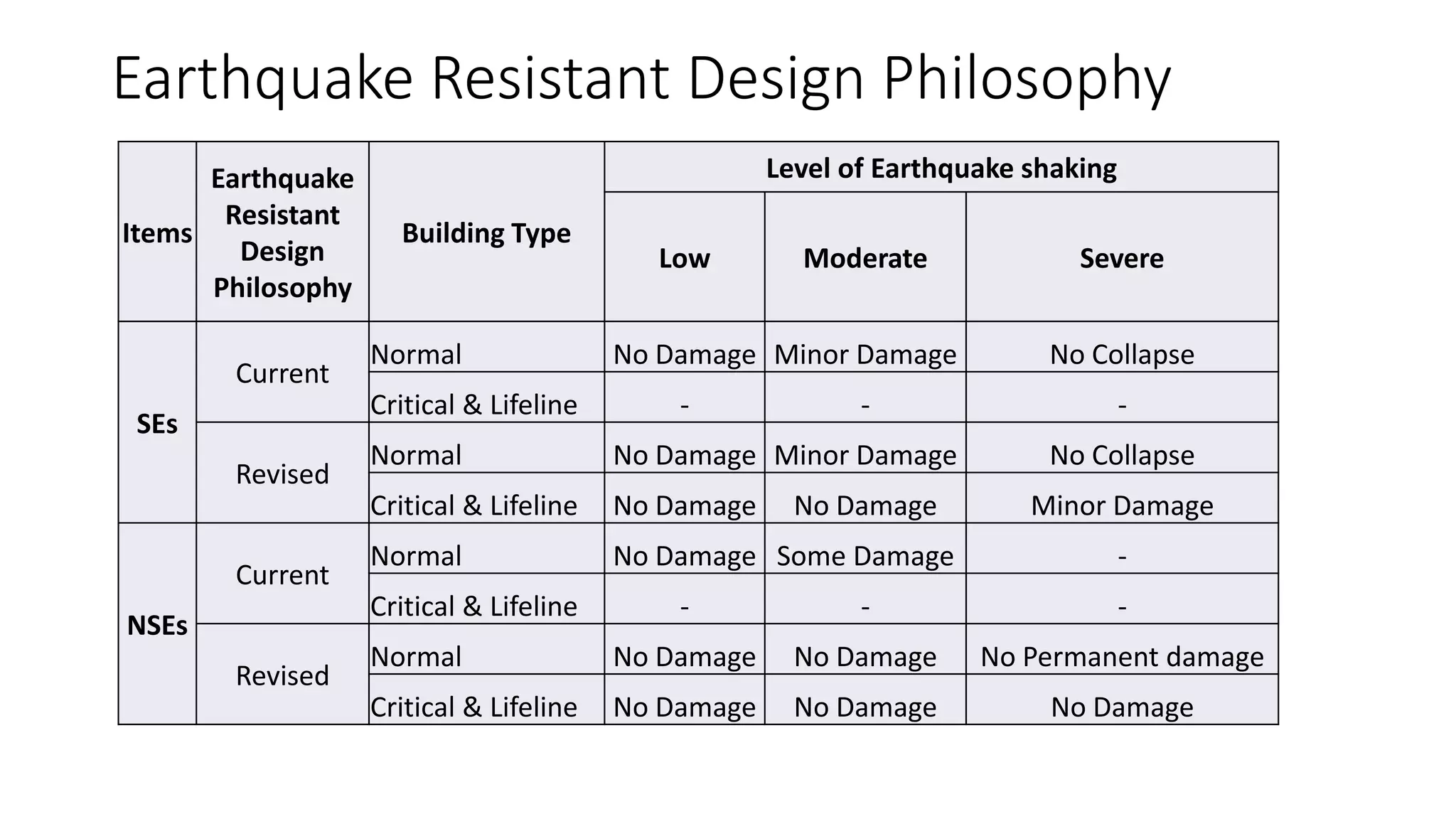
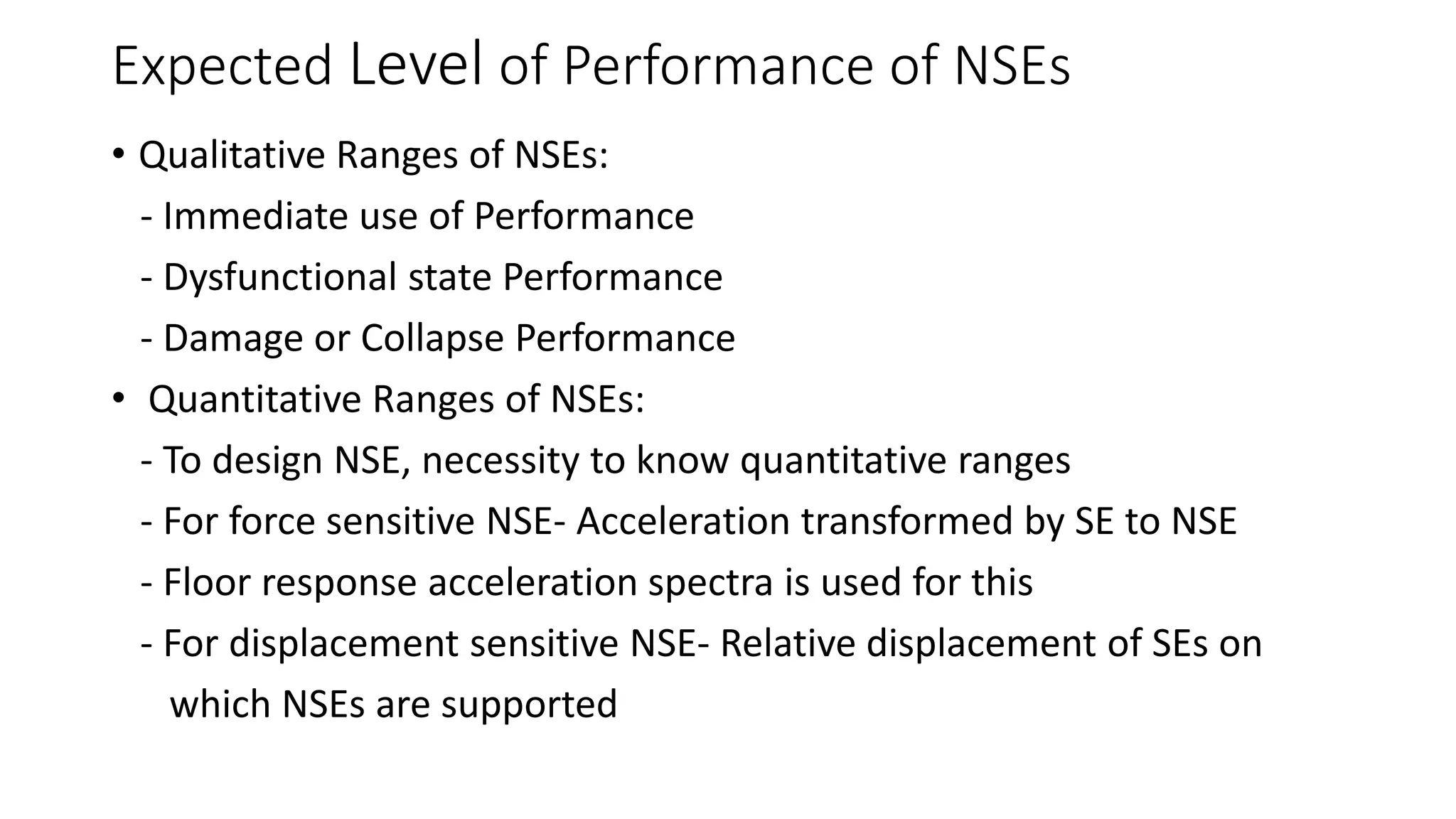
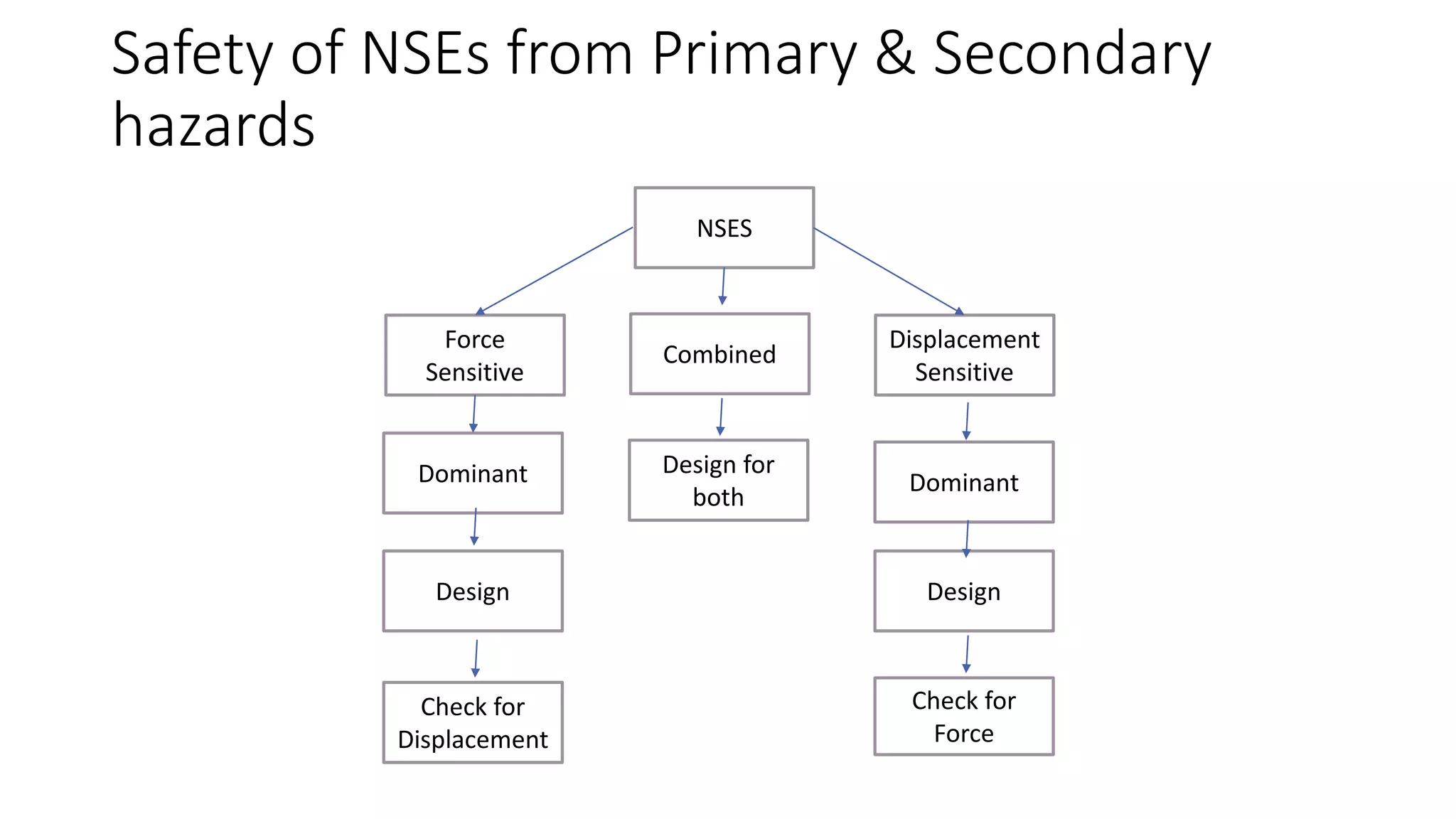
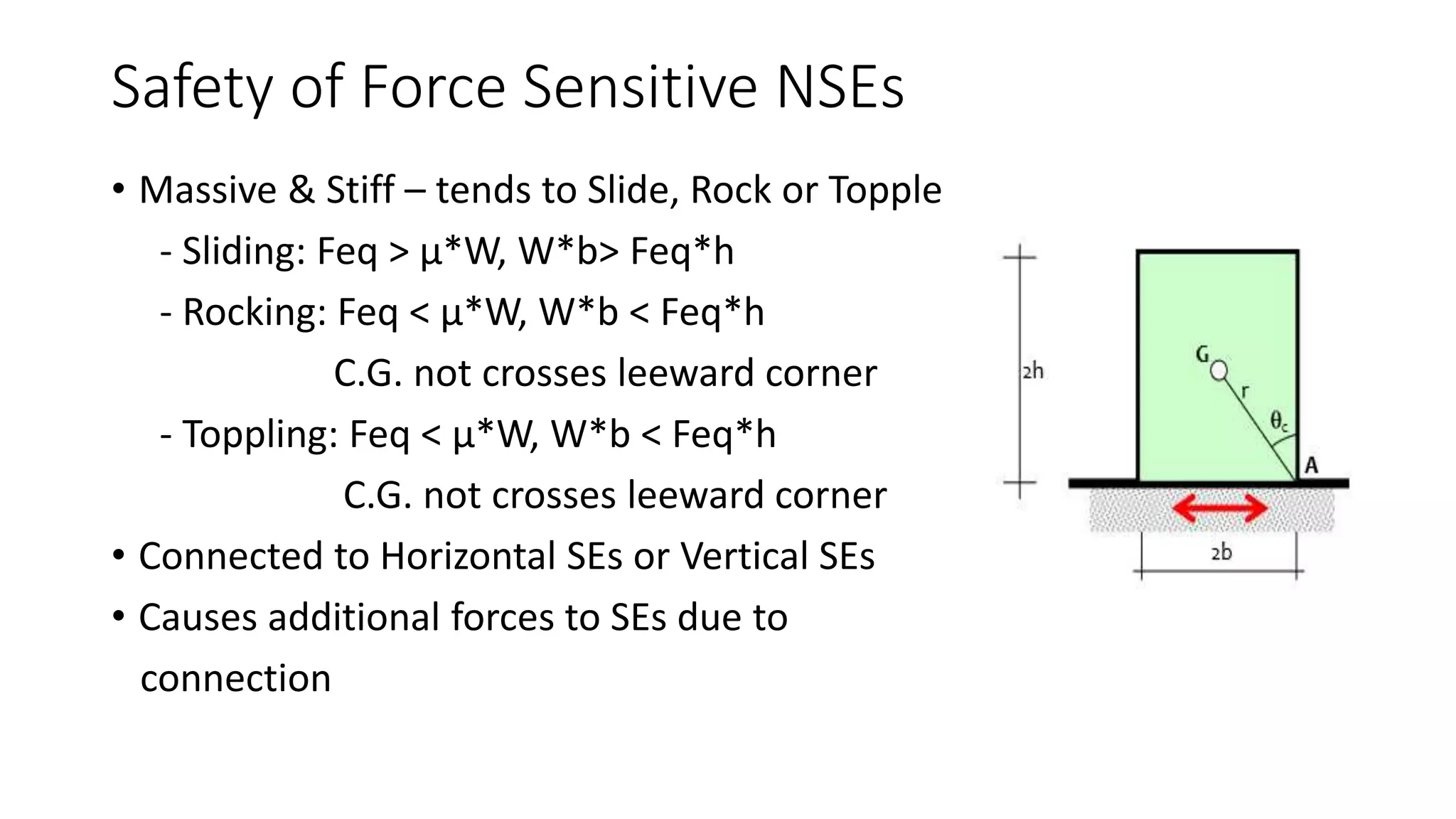
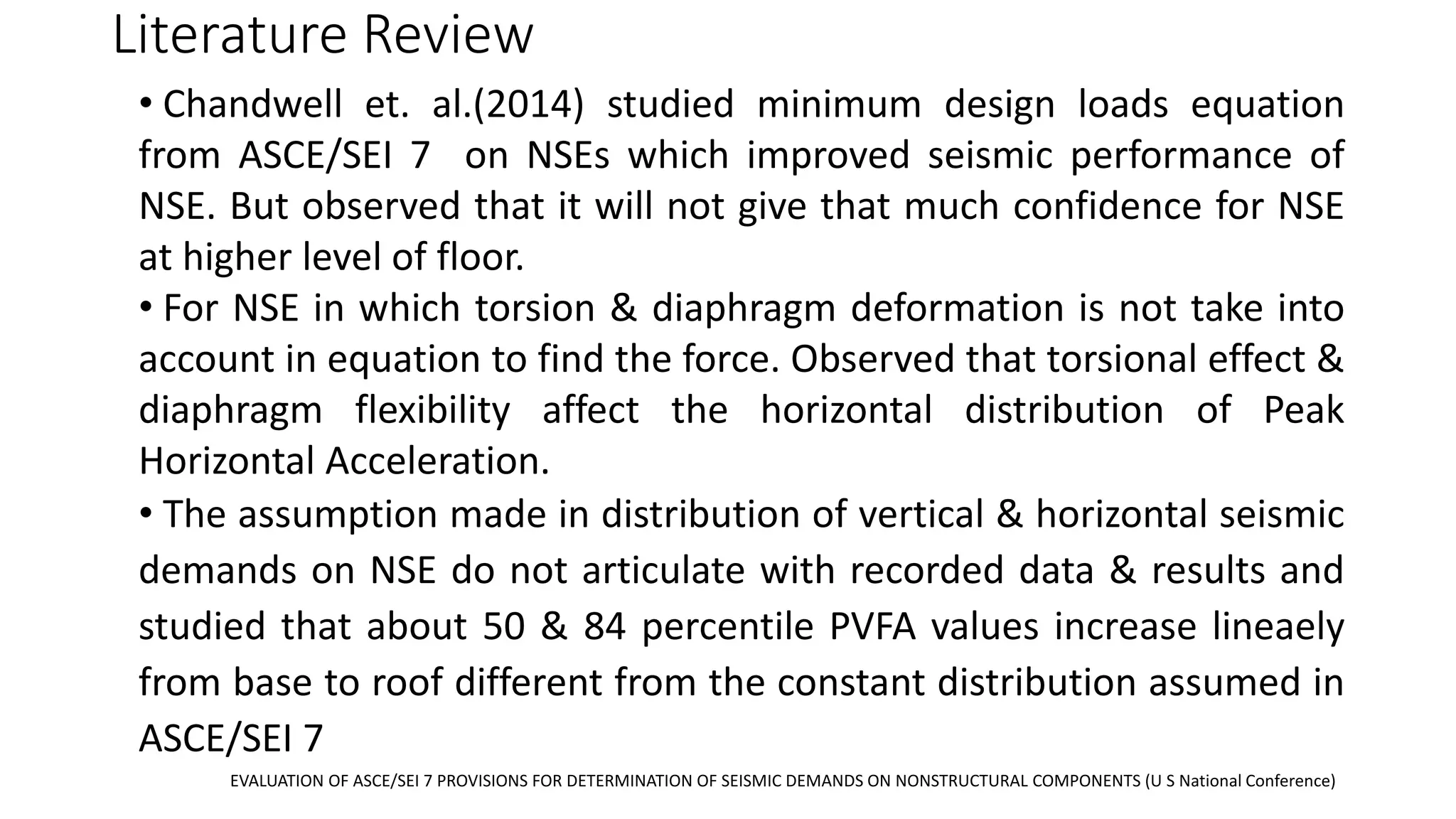
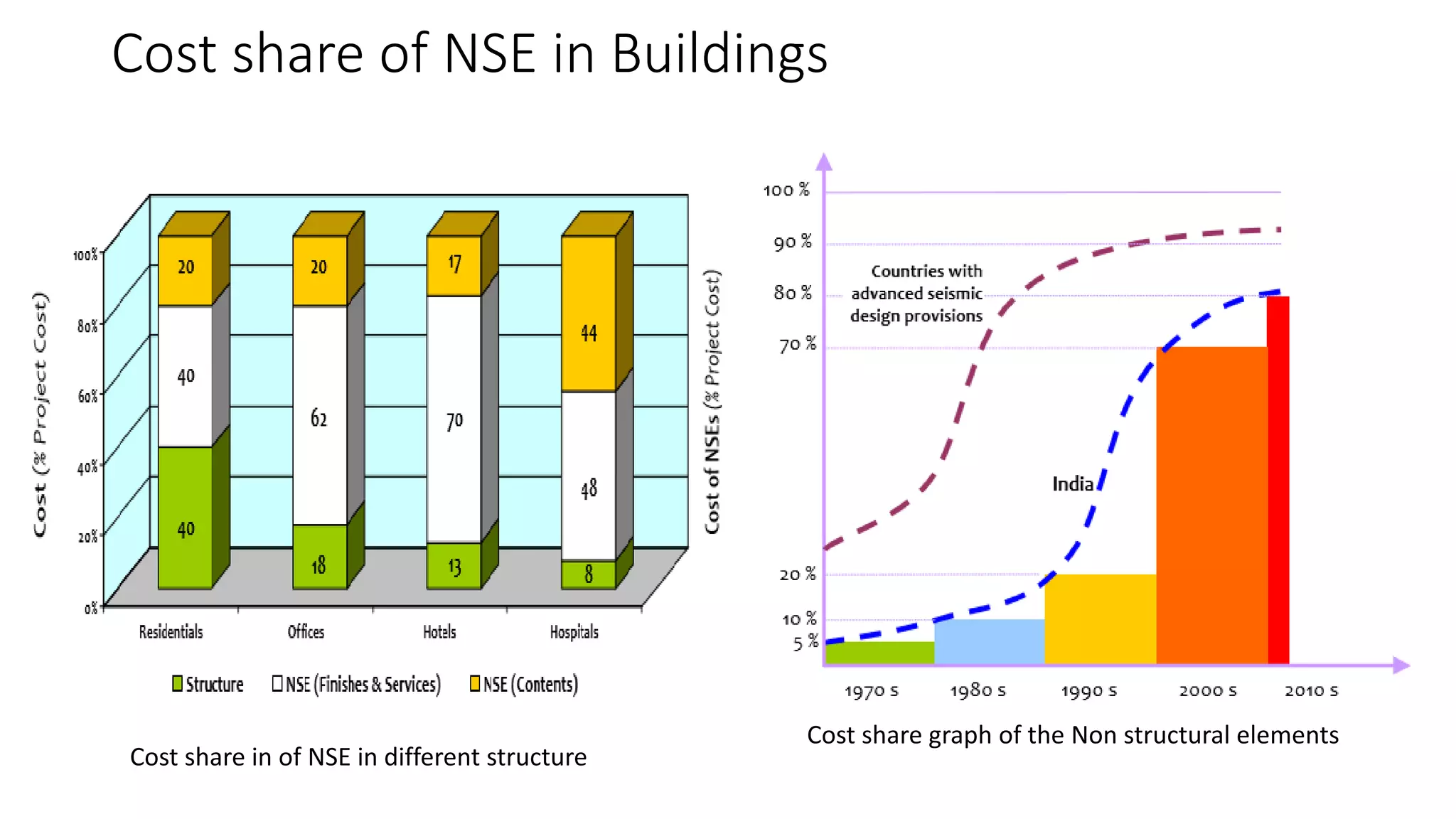
This document discusses the importance of designing non-structural elements (NSEs) for earthquake resistance. NSEs such as furniture, equipment, and components attached to buildings can cause damage or injuries if not properly secured during seismic activity. The document reviews literature showing NSEs have performed poorly in past earthquakes. It discusses challenges in designing NSEs, which can be sensitive to forces or displacements during shaking. Proper design of connections and allowing for relative movement between NSEs and structural elements is needed. The document observes more emphasis should be placed on NSE design given their costs and role in post-earthquake usability and safety.
![Birla Vishvakarma Mahavidyalaya (Engg. College)
[An Autonomous Institution]
Seminar On:
IMPORTANCE OF NON STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS DURING
EARTHQUAKE
Guided by : Dr. Snehal Mevada
Prepared by : Mehul Doshi (16SE818)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceofnseduringeq-170218050958/75/Importance-of-Non-Structural-Elements-during-Earthquake-1-2048.jpg)





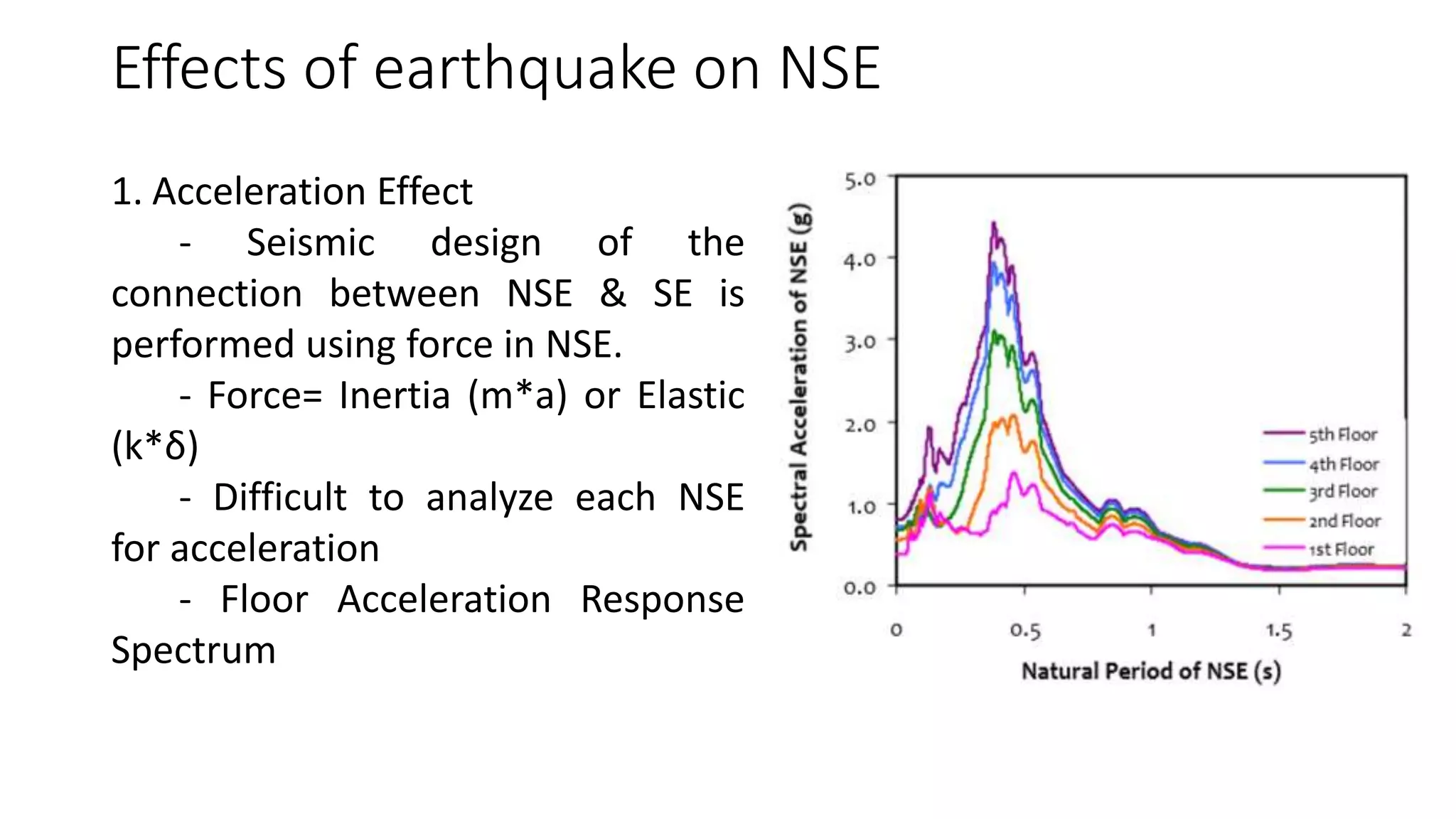

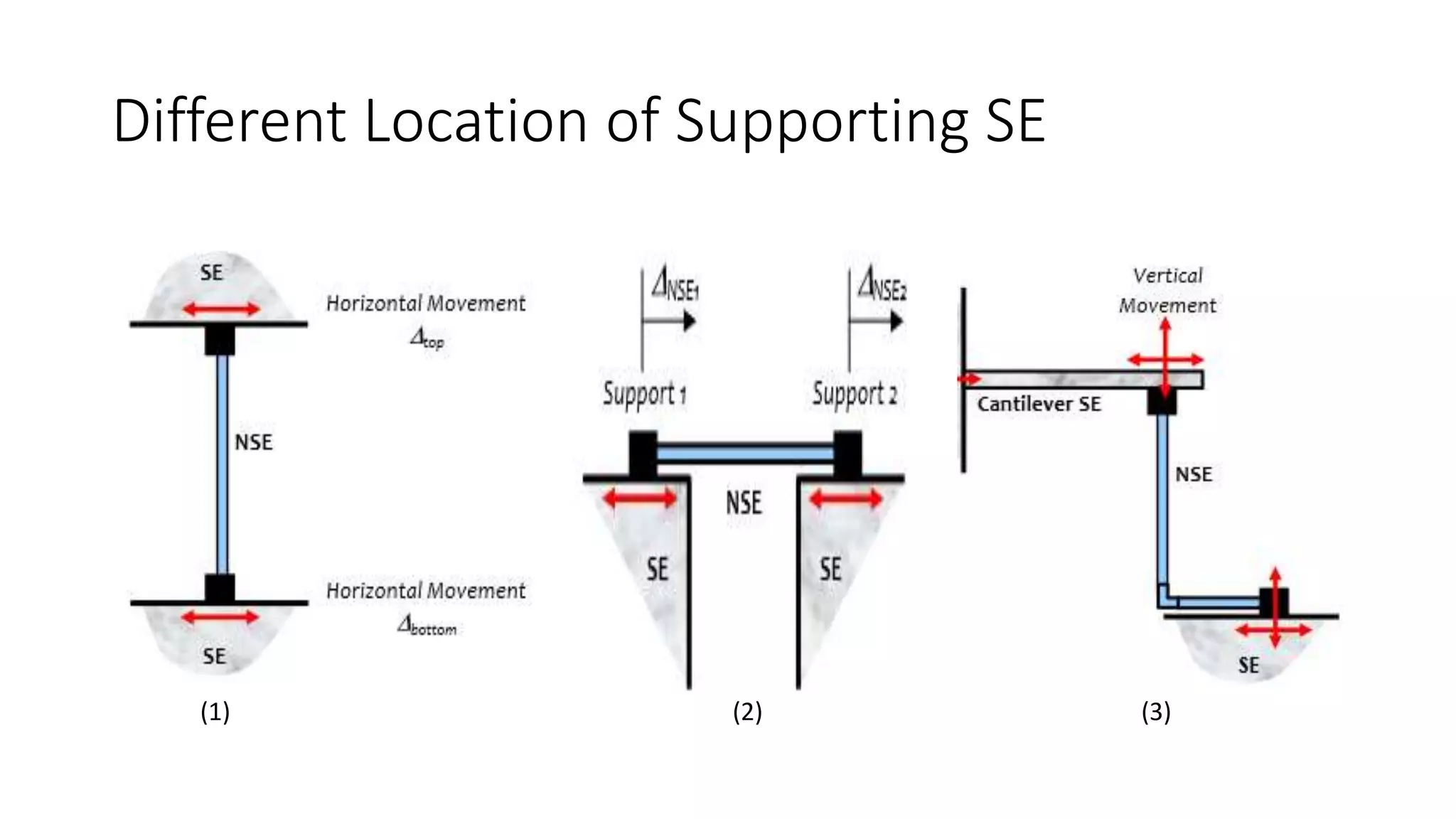
![Effects of earthquake on NSE
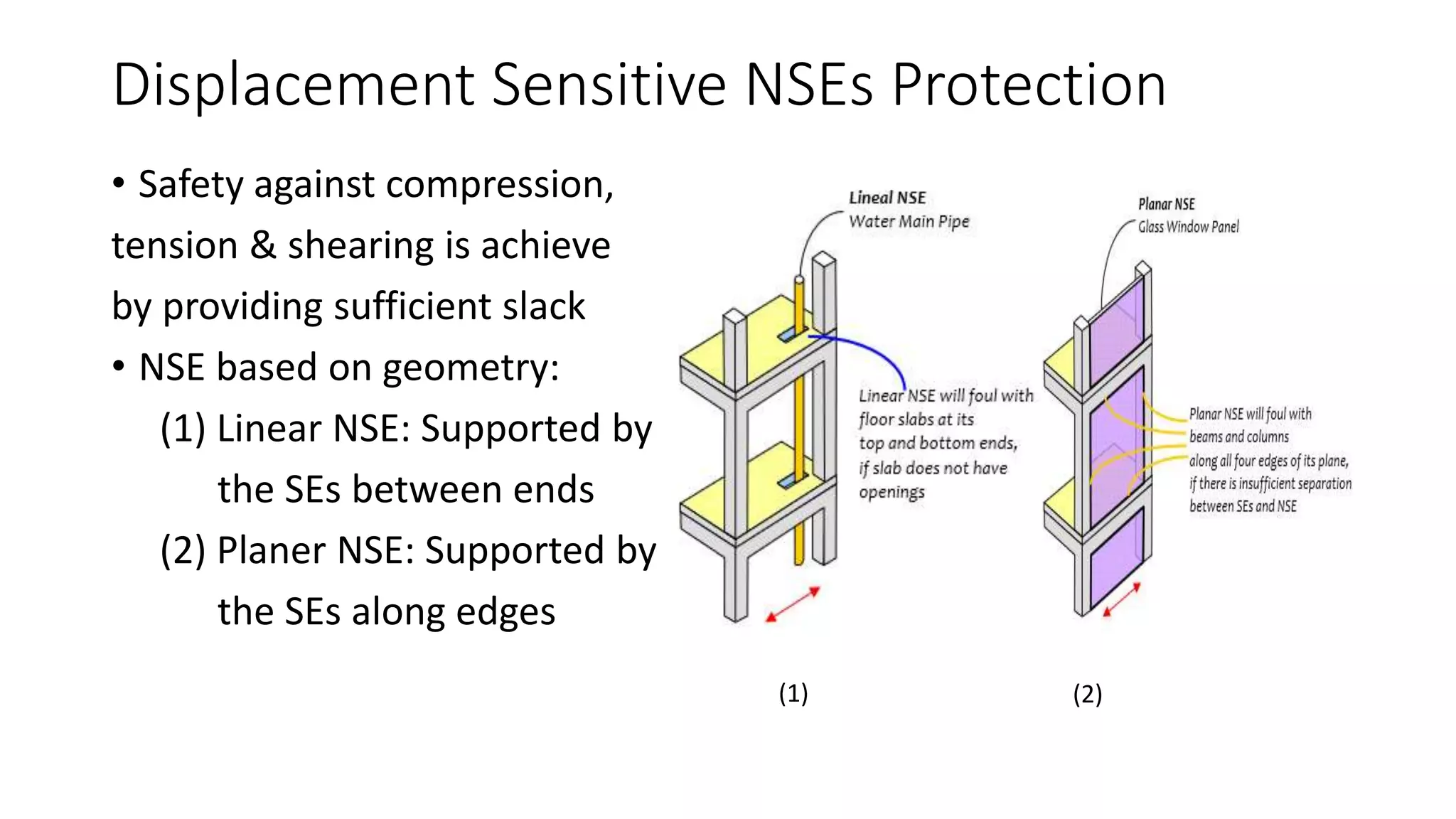
2. Displacement Effect:
- Support point shaking different amount
- Relative movement of the NSE
- Supports are moving out or coming closer then compression or
tension type relative displacement given by Iδ1I + Iδ2I
- One support come closer & other go away then relative
displacement [Iδ1I - Iδ2I ]
- Both these should be < δ(accommodate)
- Every displacement sensitive NSE should be checked at each level](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceofnseduringeq-170218050958/75/Importance-of-Non-Structural-Elements-during-Earthquake-11-2048.jpg)