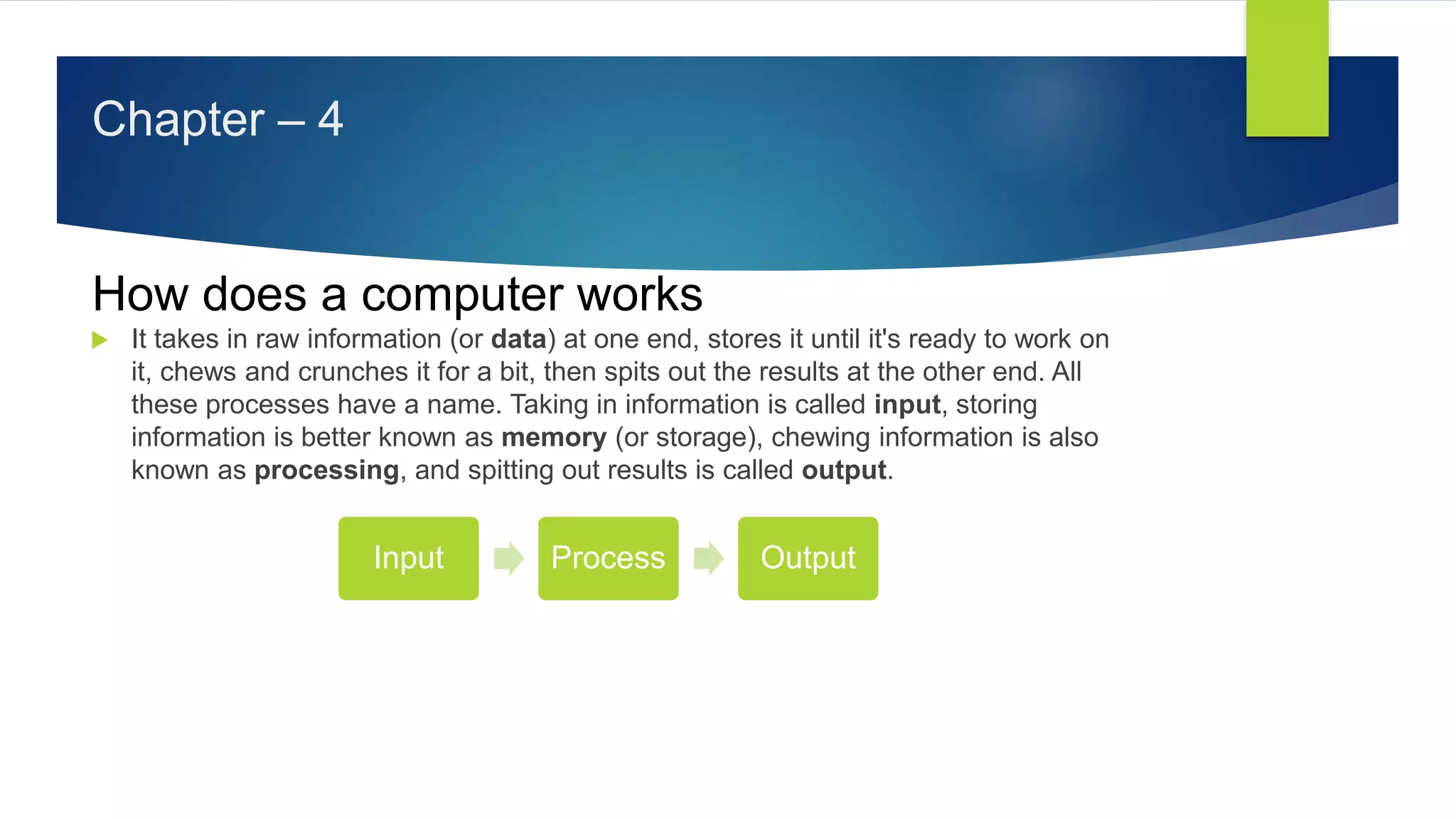
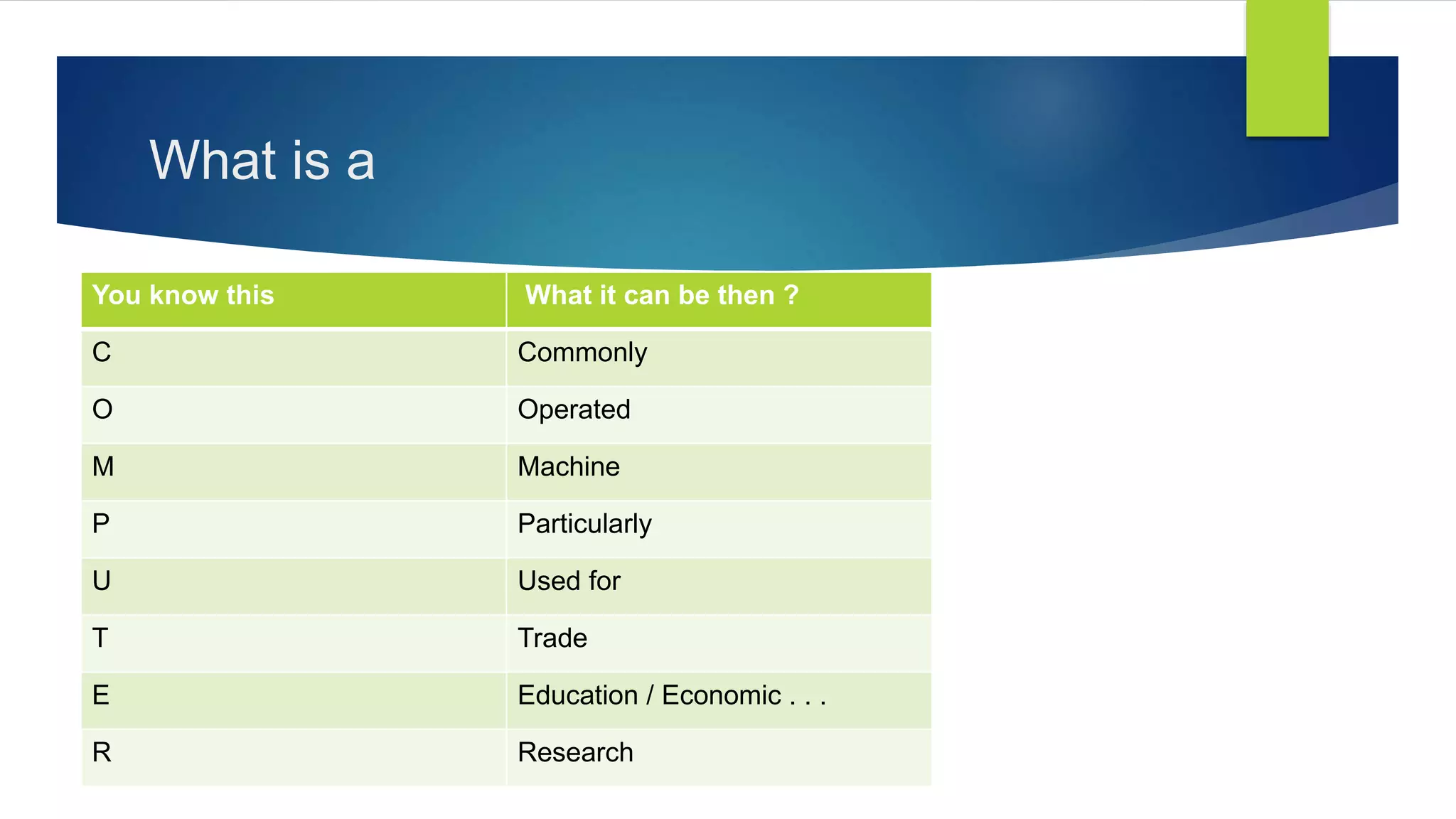
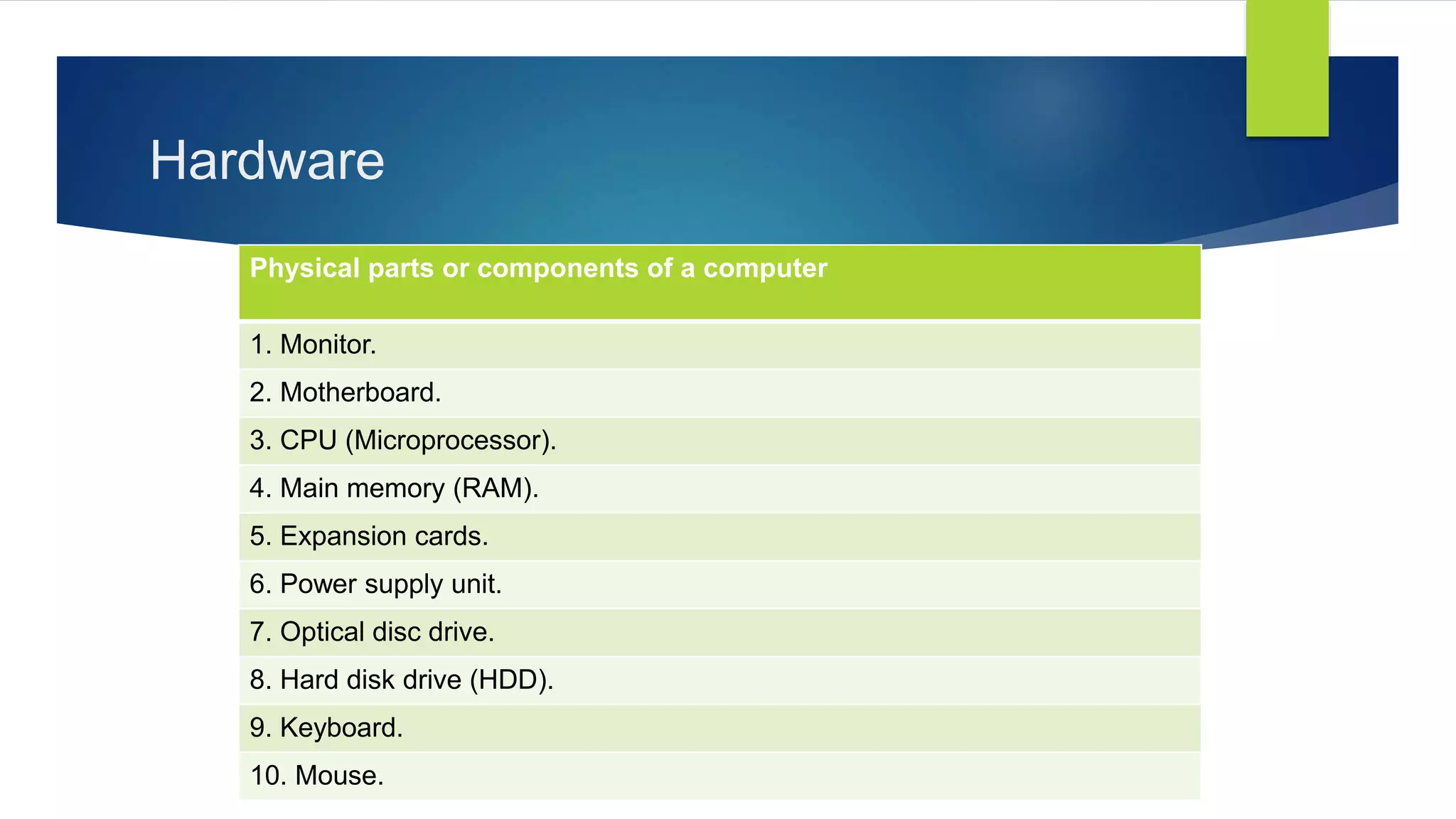
The document outlines the importance and basics of computer education for school students, detailing the definition of a computer, its types, generations, hardware, and software. It explains the fundamental processes of input, processing, and output in computing. Additionally, the text highlights the historical context of computer development and looks forward to future trends in technology.
















![Chapter – 3
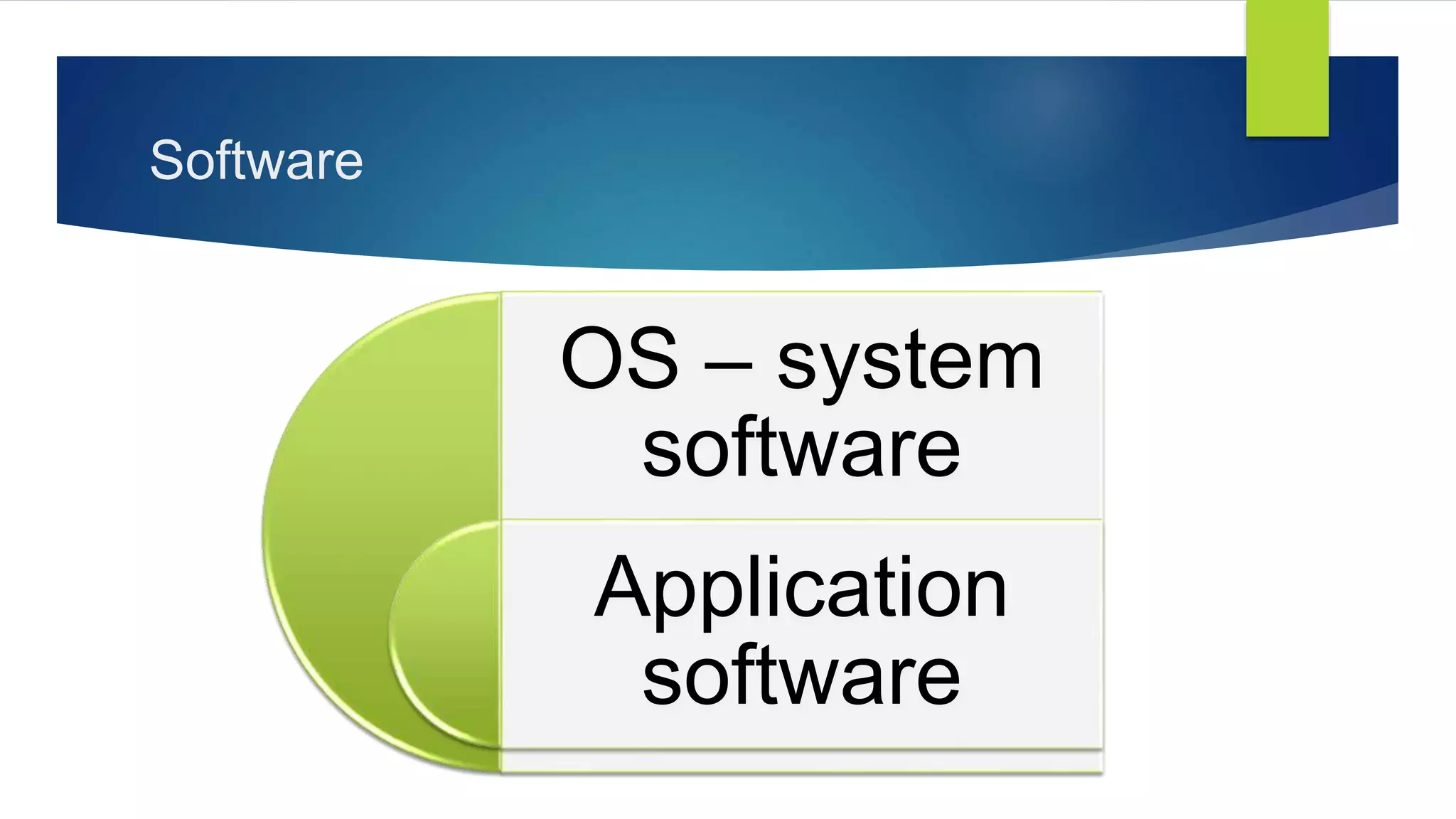
Understanding Software
https://youtu.be/pTdSs8kQqSA
[Play this video]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceandbasicsofcomputereducationforschoolstudents-160629121828/75/Importance-and-basics-of-computer-education-for-school-students-23-2048.jpg)