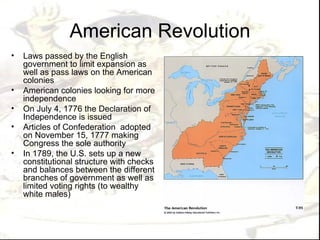
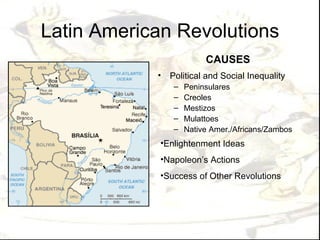
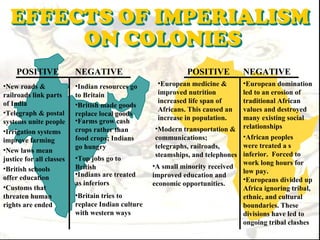
This document provides an overview of the key events and themes of Period 5 (1750-1900) in AP World History. It discusses the major political revolutions that occurred during this time period including the American, French, Haitian, and Latin American revolutions. It also summarizes the key impacts of industrialization and imperialism, the rise of the West's dominance globally, and reactions to imperialism from other civilizations like Japan, Russia, and those in Latin America, South Asia, and Africa.