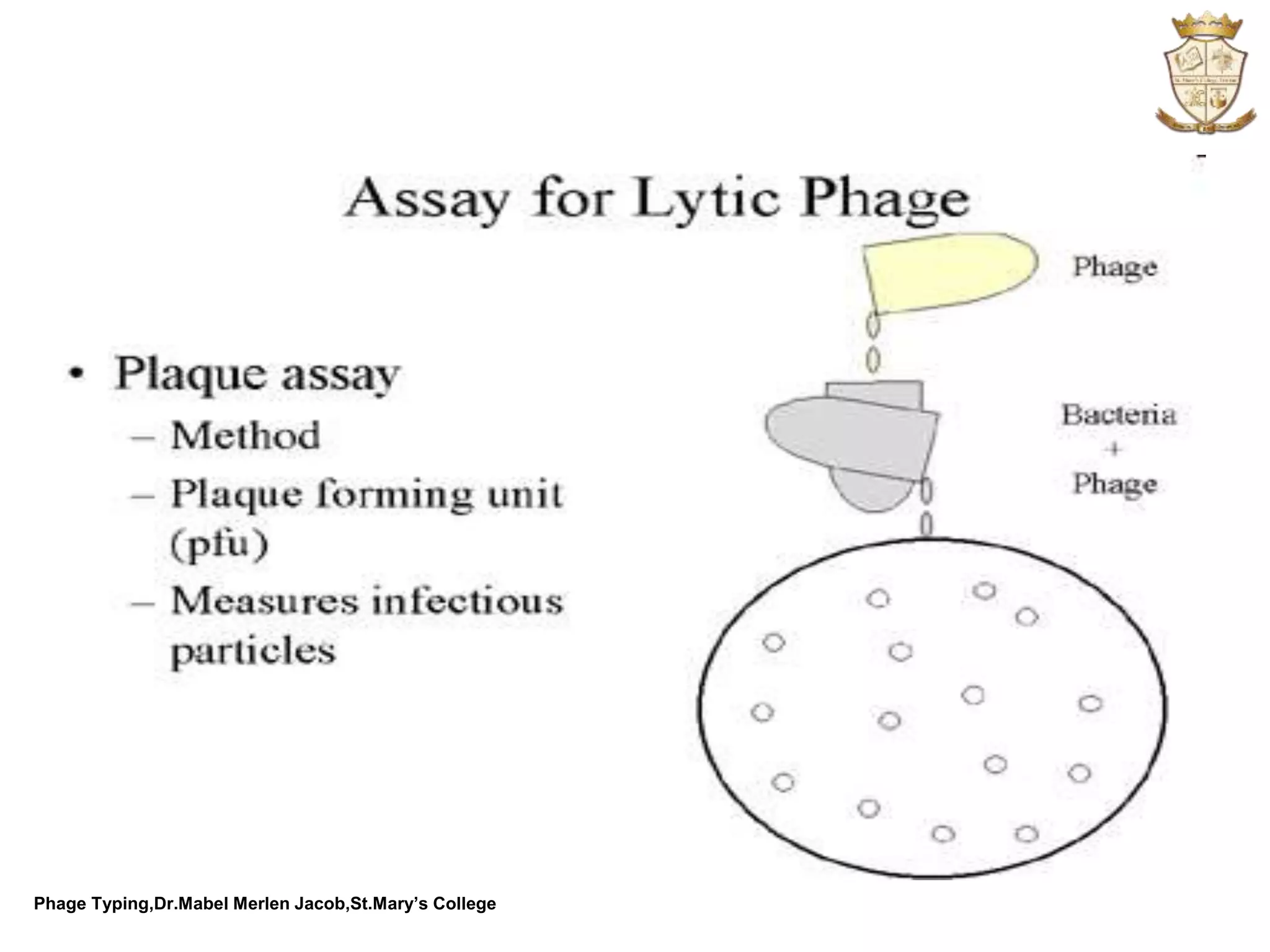
This document discusses phage typing, which is a method used to characterize and detect differences between bacterial strains based on their susceptibility or resistance to various bacteriophages. Phage typing can be used to distinguish between strains that cause disease from harmless strains, and to trace the source of bacterial outbreaks. It involves observing the zones of clearing around spots of different bacteriophages to determine the susceptibility patterns and strain differences. Phage typing is commonly used in epidemiology to identify infectious agents like strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria, or Bacillus anthracis.