This document discusses immunodeficiency, including:
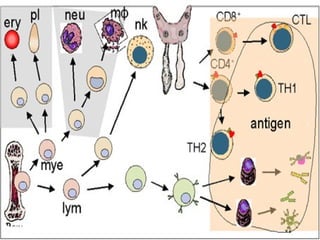
- It defines immunodeficiency and classifies it as either primary or secondary, specific or non-specific. Primary immunodeficiencies are inherited defects in the immune system.
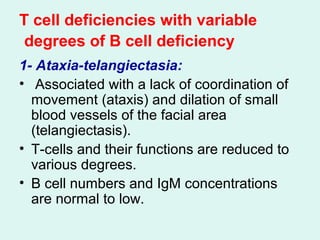
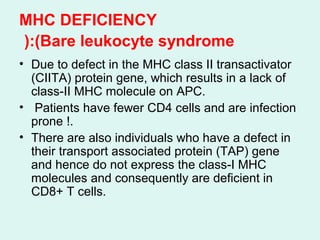
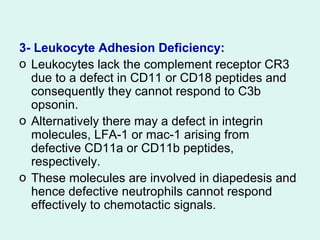
- It describes common examples of primary immunodeficiencies that involve deficiencies of B cells, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia and common variable immunodeficiency, or T cells, such as DiGeorge syndrome.
- Severe combined immunodeficiency is also discussed, which is characterized by an absence of both T and B cell immunity.
- Secondary immunodeficiencies can be caused by drugs like corticosteroids, meth