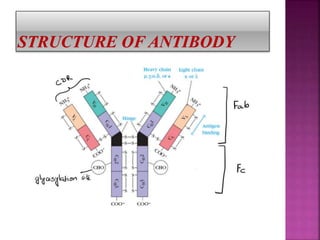
Porter first proposed the 4-chain antibody model in 1959. Antibodies, also called immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by B-lymphocytes in response to antigens. There are five main types of antibodies: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE, which are defined by their heavy chains. Each antibody consists of two light chains and two heavy chains connected by disulfide bonds. The variable region allows antibodies to bind to different antigens, while the constant region defines the antibody class. The five classes have different structures and functions, such as IgM activating the complement system as the first antibody response.


![Five types of antibodies are indentified:
1. Ig G [Ig Gamma]
2. Ig A [Ig alpha]
3. Ig M [Ig mu]
4. Ig D [Ig delta]
5. Ig E [Ig epsilon]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-3-320.jpg)



![1. Immunoglobulin G [IgG]:
IgG is the most abundant
(75-80%) class of
immunoglobulins. IgG is
composed of a single Y –
shaped unit (monomer). IgG
is the only immunoglobulin
that can cross the placenta
and transfer the mother’s
immunity to the developing
foetus.
* They can serve as opsonin &
promote chemostatic activity
of WBCs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-8-320.jpg)
![2. Immunoglobulins A [IgA]:
IgA occurs as a single
(monomer) or double unit
(dimer) held together by J
chain. It is mostly found in the
body secretions Such as saliva,
tears, sweat, milk and walls of
intestine. IgA is the most
predominant antibody is the
colostrum, the initial secretion
from the mother’s breast with
bacterial antigens present on
the body (outer epithelial)
surfaces & remove them. In this
way IgA presents the foreign
substances from entering the
body cells.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-9-320.jpg)
![3. Immunoglobulins M
[IgM]:
IgM is the largest
immunoglobulin composed of 5 Y –
shaped units (IgG type) held
together by a J polypeptide chain.
Thus IgM is a pentamer. Due to its
large size, IgM cannot transverse
blood vessels, hence it is restricted
to the blood streams. IgM is the first
antibody to be produced in response
to an antigen and is the most
effective against envading micro-
organisms.
It may be noted that IgM can
simultaneously combine with 5
antigenic sites due to its pentameric
structure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-10-320.jpg)
![4. Immunoglobulin D [IgD]:
IgD is composed of a single Y-
shaped unit & is present in a low
concentration in the circulation. IgD
molecules are present on the surface
of B cells. There function however ,
is not known for certain. Some
workers believe that IgD may
function as a B- cell receptor.
* When IgD interacts with an antigen
antibody complex is internalised
process & presented via MHC-II
molecule to helper T-cells, for there
destruction & removal from the
body](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-11-320.jpg)
![5. Immunoglobulin E [IgE]:
IgE is a single Y – shaped
monomer. Its is normally present in
minute concentration in blood. IgE
levels are elevated in individuals with
allergies as it is associated with the
body’s allergic responses. The IgE
molecules tightly bind with most cells
which release histamine & cause
allergy.
* Heat labile skin sensitizing antibodies,
therefore also called reagins.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureandfunctionofantibodymolecules-181026140805/85/Structure-and-function-of-antibody-molecules-12-320.jpg)
