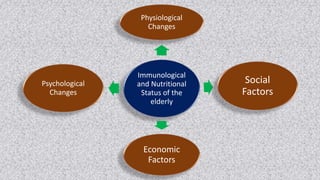
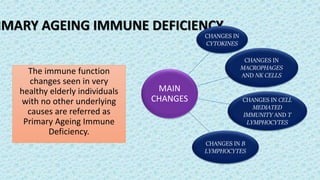
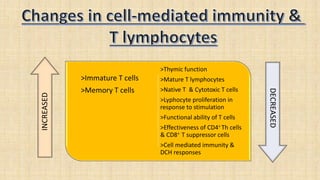
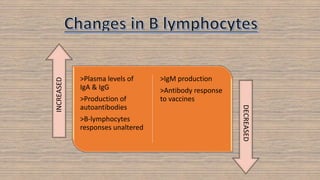
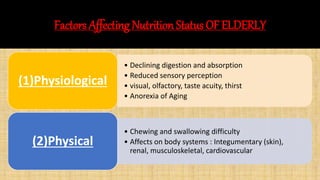
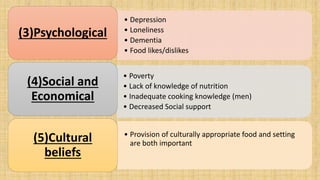
The document discusses the effects of aging on nutrition and immunity. It notes that the proportion of elderly individuals is rising globally and aging is associated with increased illness and health costs. Primary aging immune deficiency refers to normal immune changes seen in healthy elderly individuals. Key immune changes include reductions in T-lymphocytes and cell-mediated immunity as well as alterations in cytokine secretions. Nutritional status is affected by physiological, physical, psychological, social, economic and cultural factors in older adults. Common nutritional deficiencies include vitamins and minerals. Physiological changes like reduced digestion and senses can impair nutrition. Maintaining good nutrition is important for quality of life in the elderly.