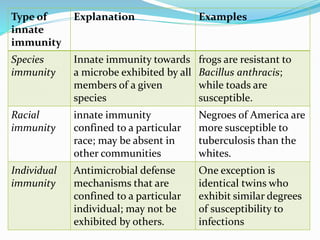
The document defines and compares innate, acquired, active, and passive immunity. It describes the mechanisms of innate immunity like epithelial surfaces and cellular factors. It also explains the types of acquired immunity including natural and artificial active immunity induced by infection or vaccination, as well as natural and artificial passive immunity from maternal antibody transfer or administration of antibodies.