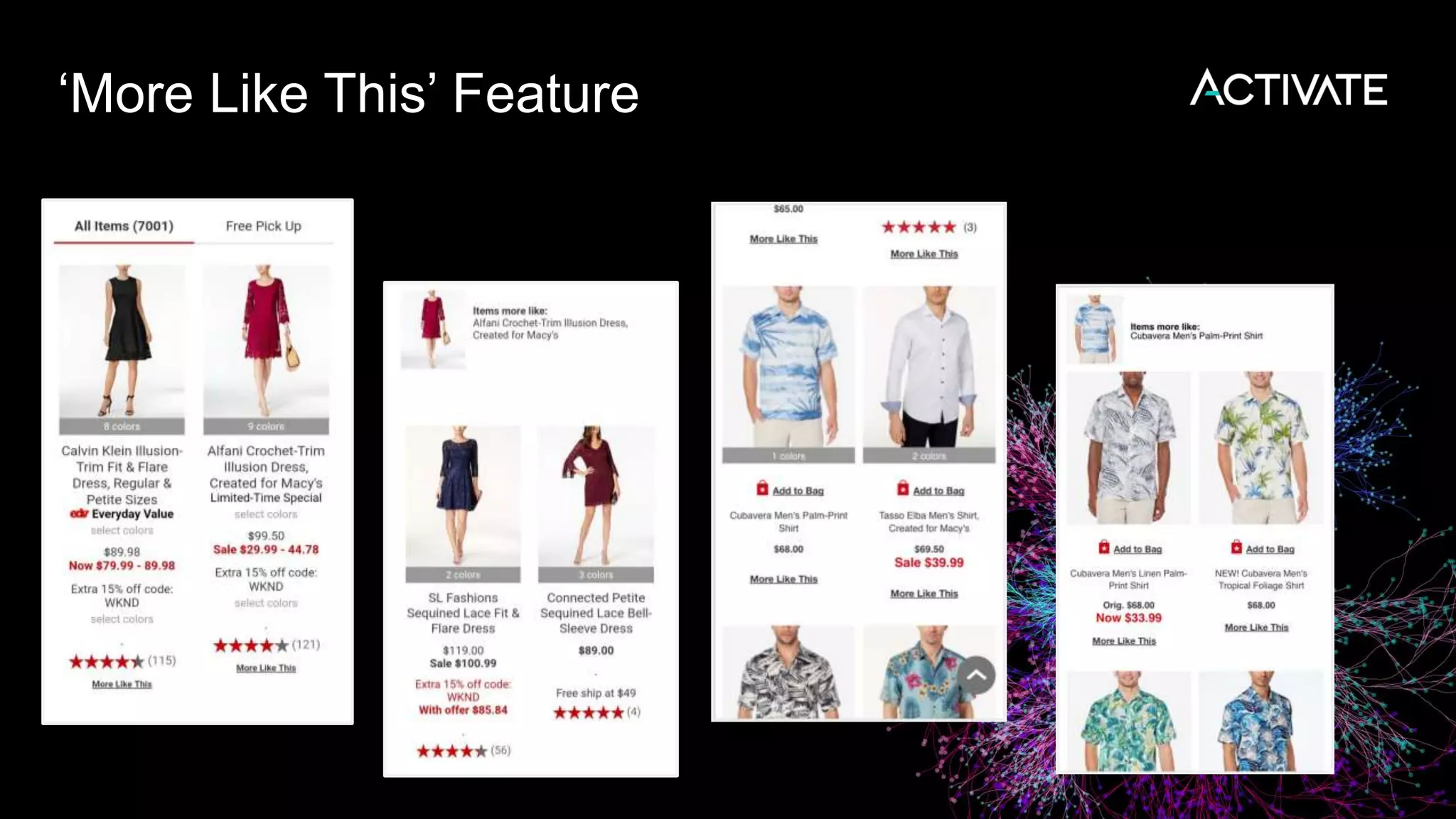
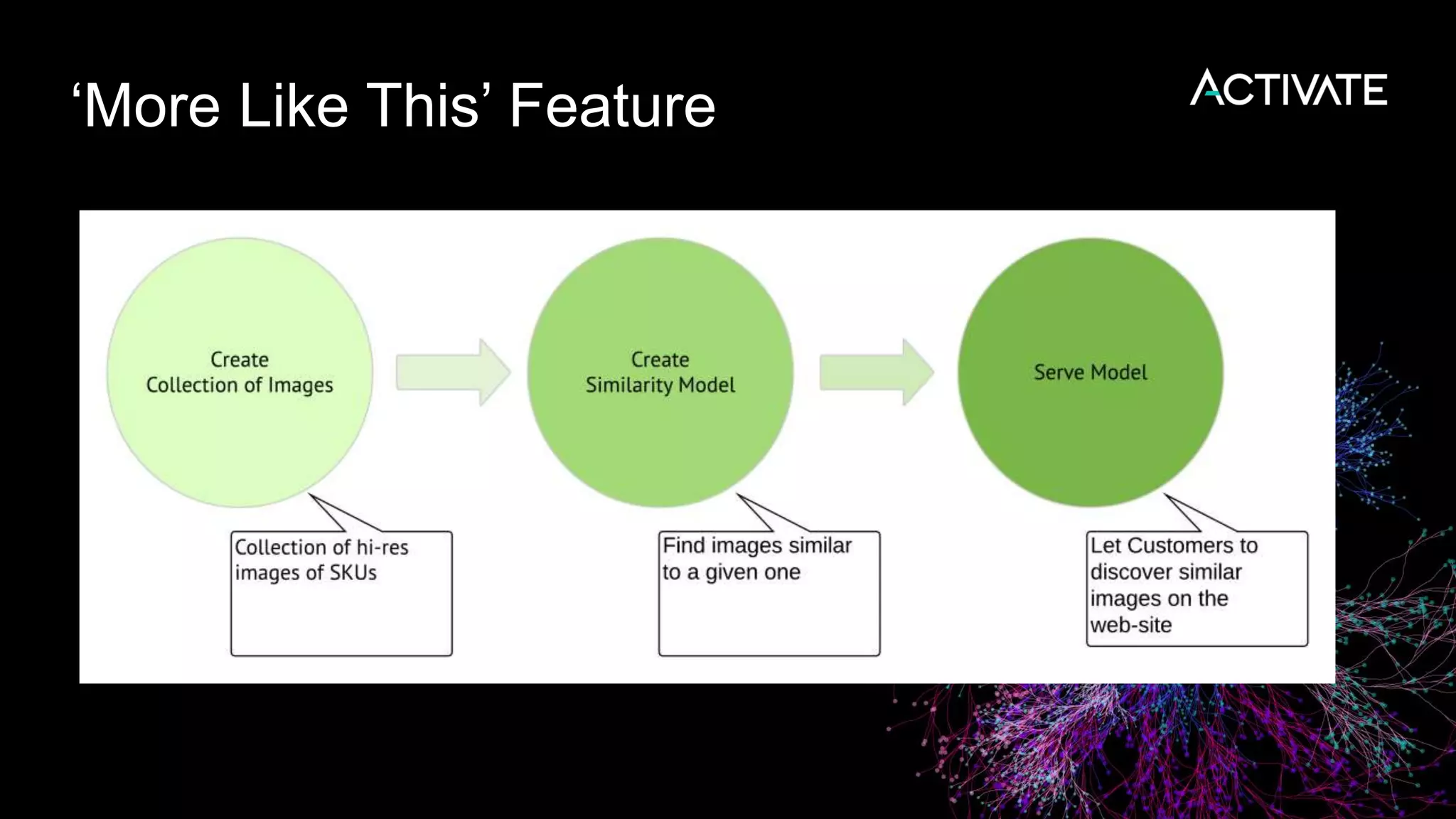
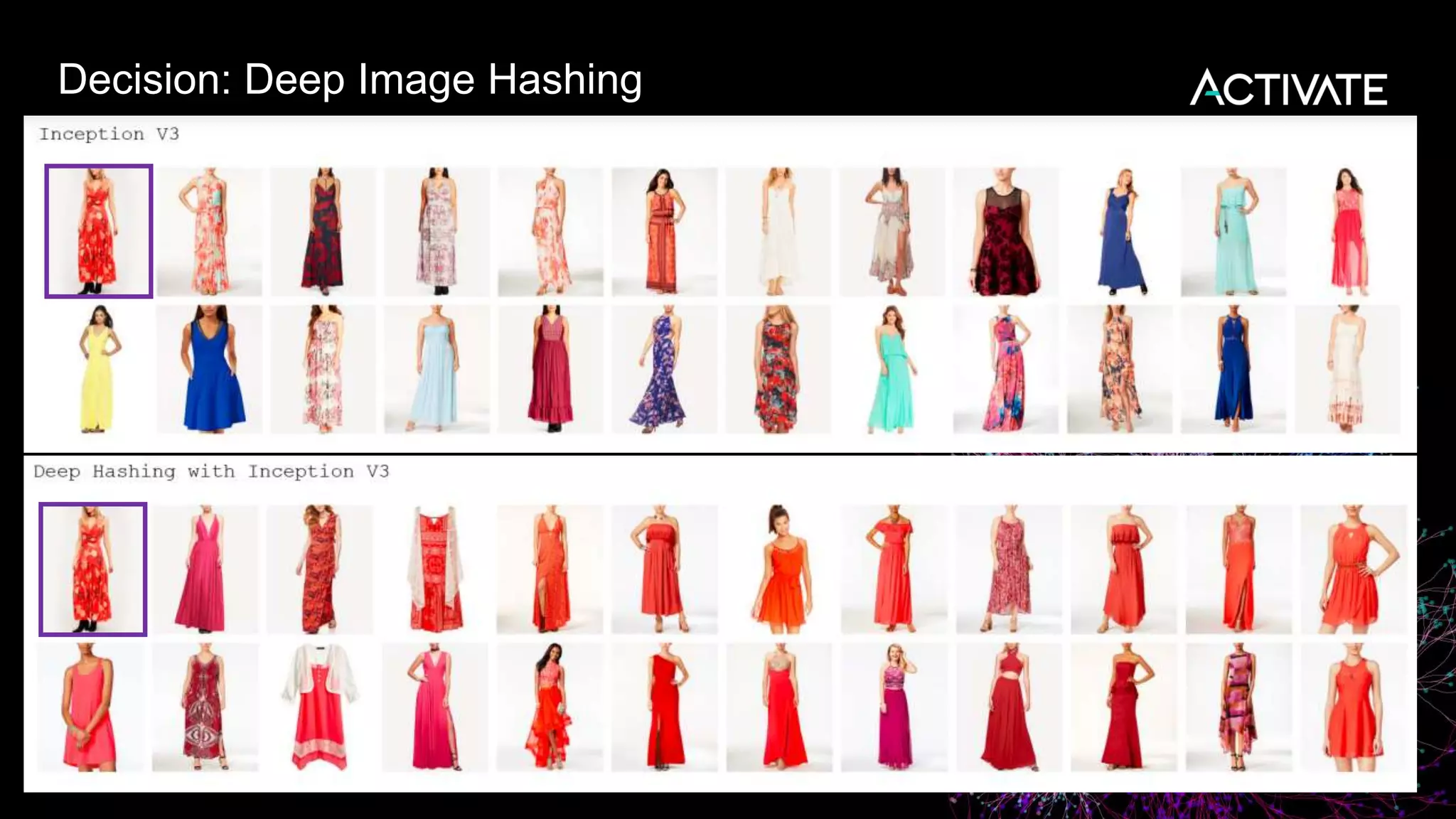
1) Macy's is launching an image-based "More Like This" deep learning feature to provide similar product recommendations to customers on their website.
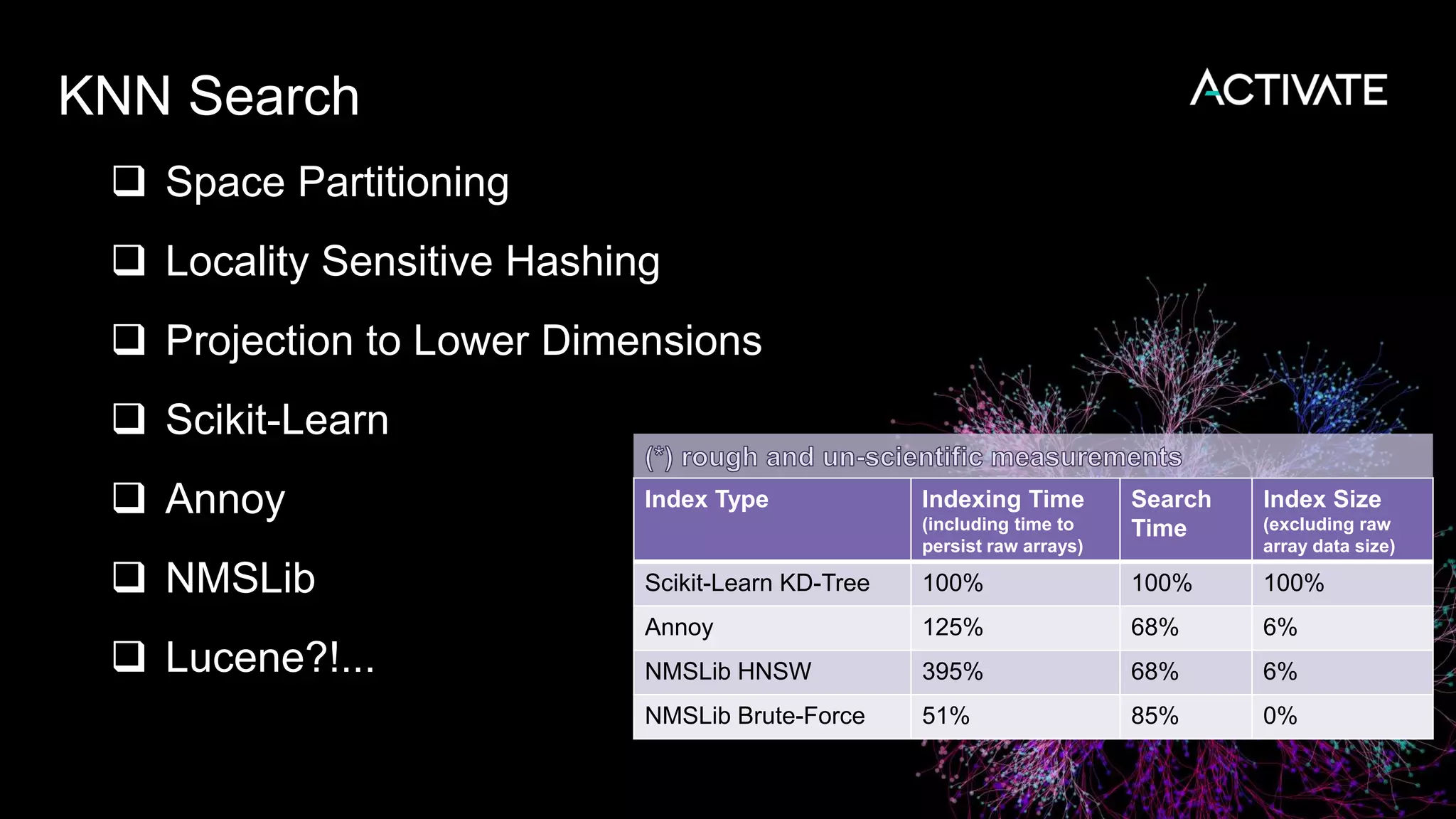
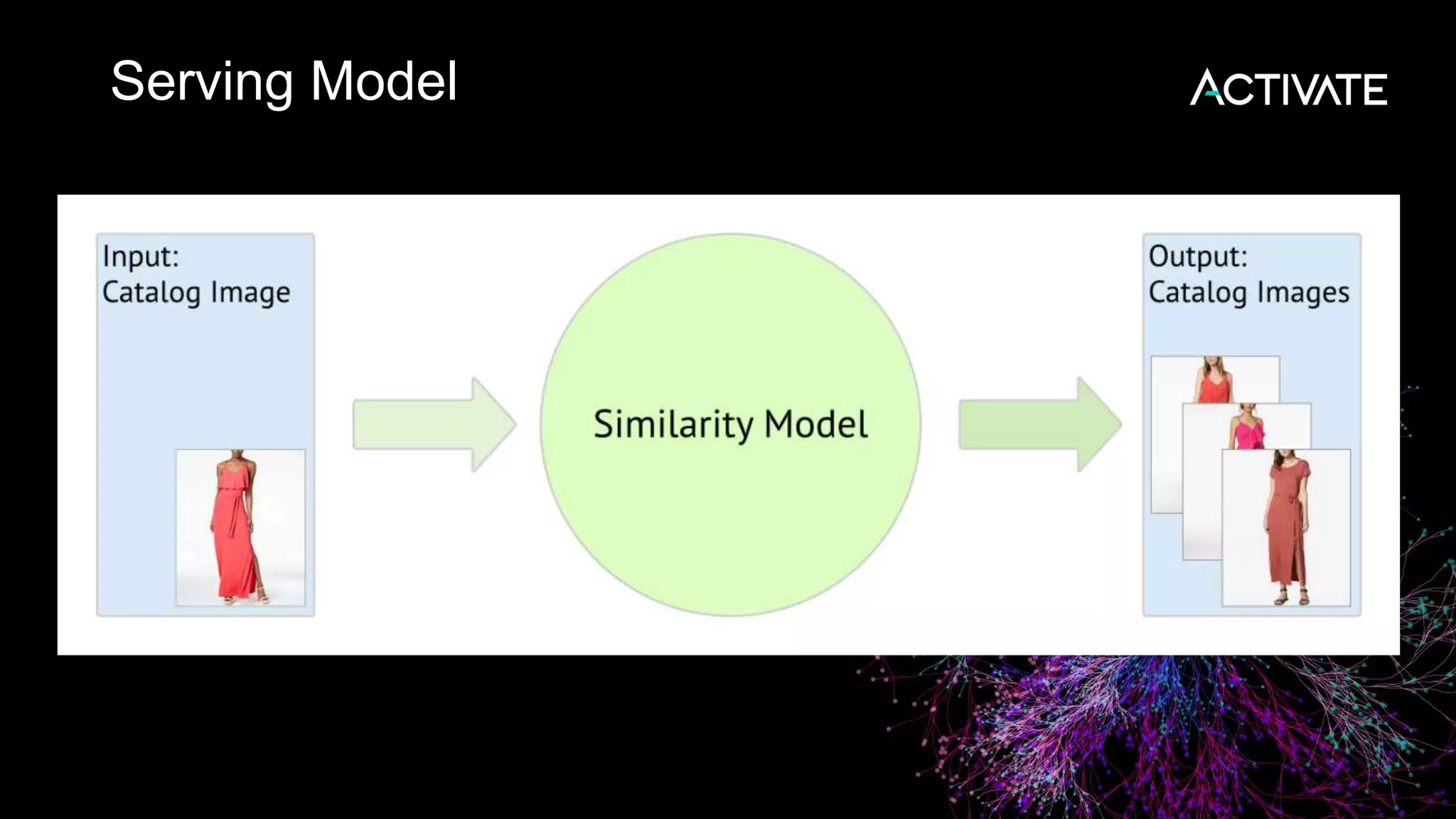
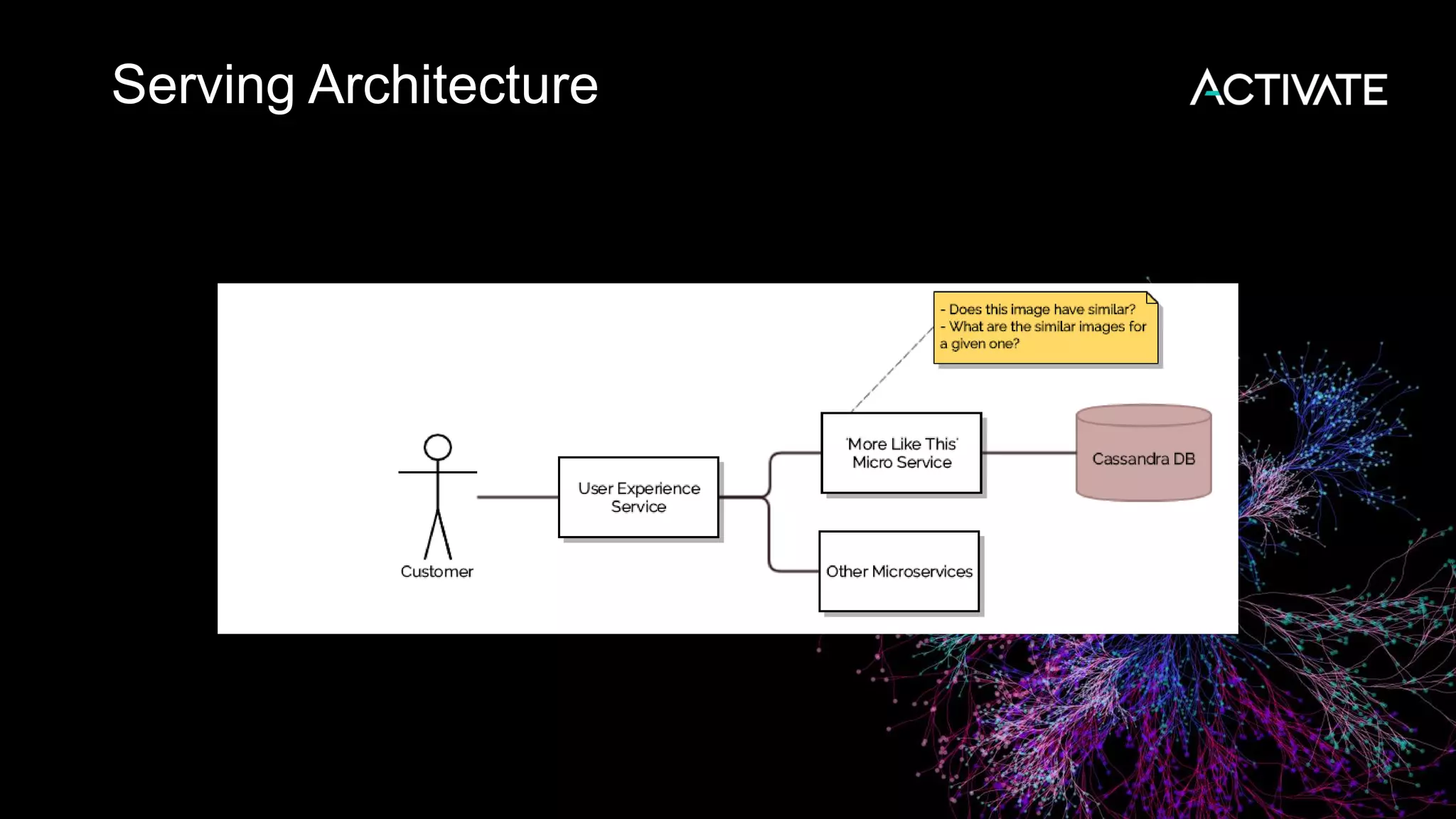
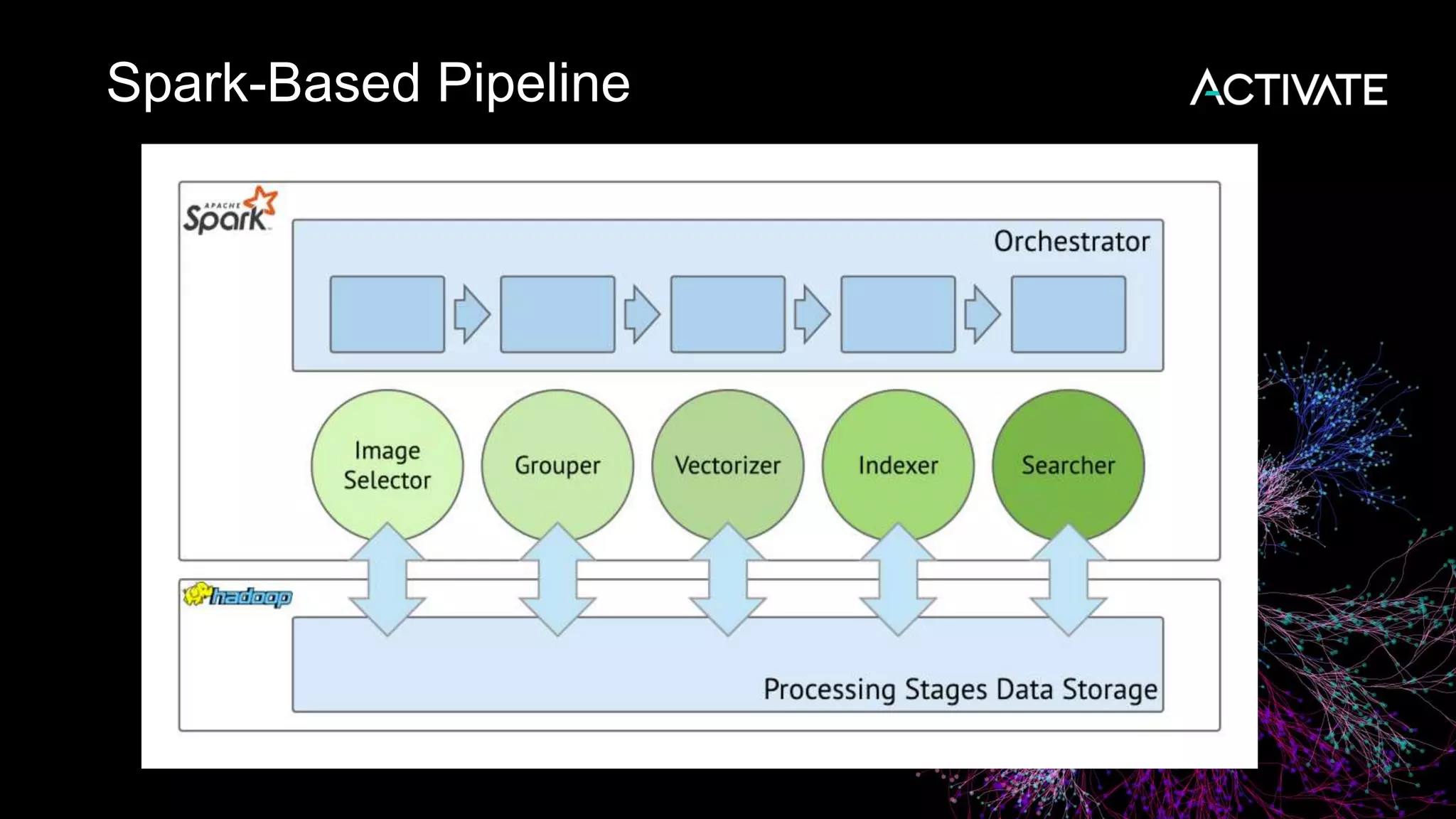
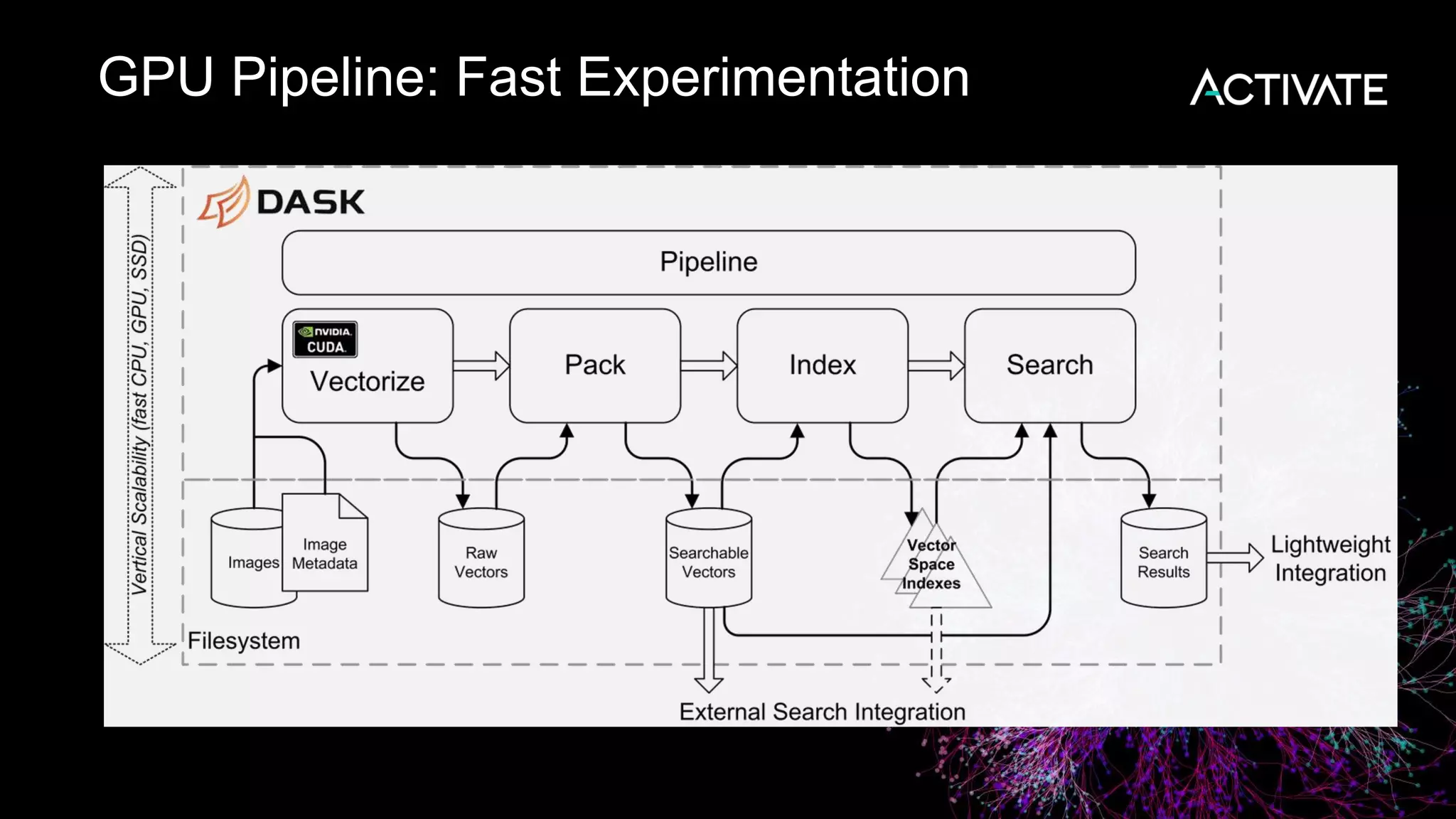
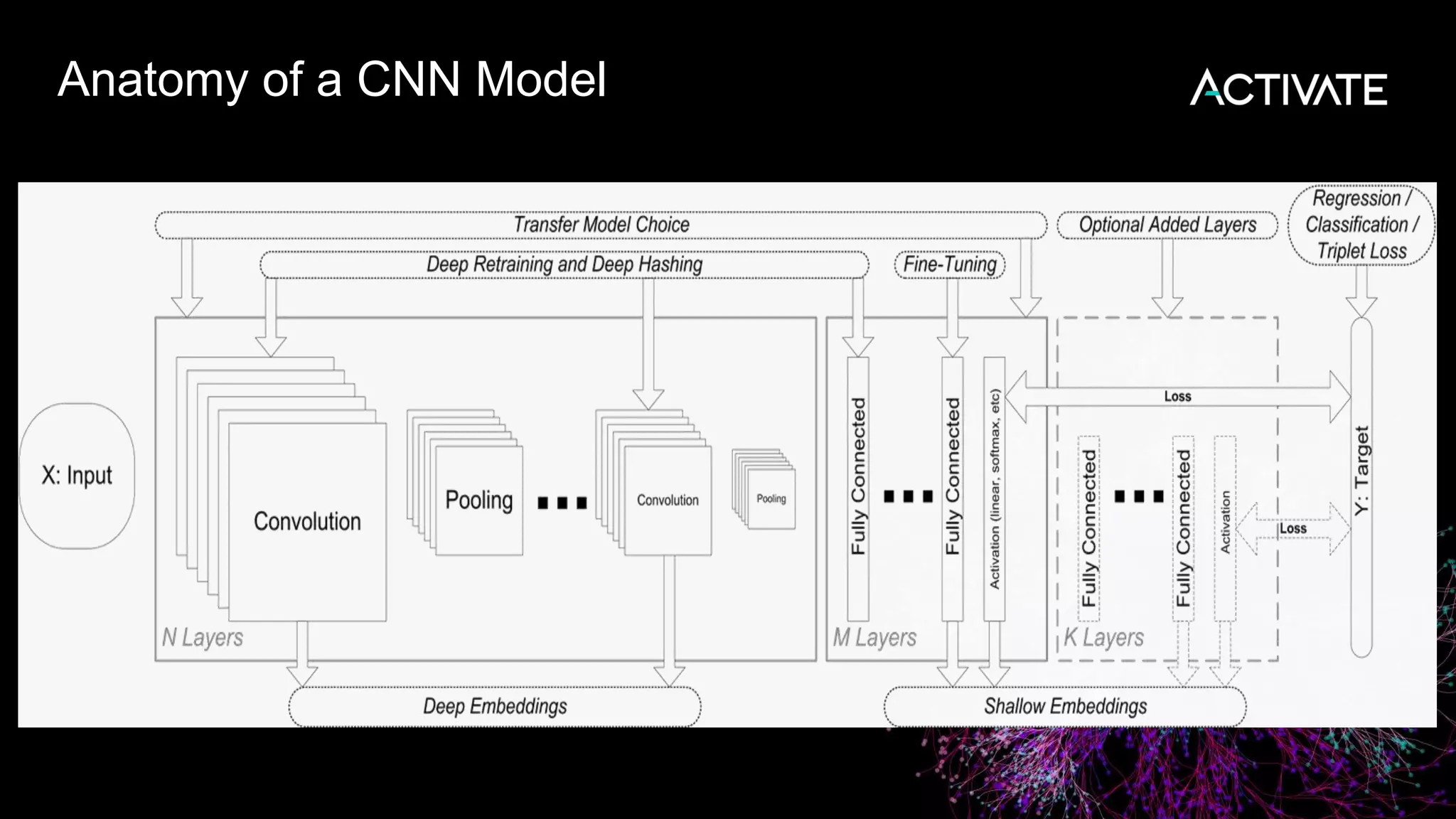
2) The feature implementation uses transfer learning with pretrained models like MobileNet that are fine-tuned using a triplet loss approach and indexed in Lucene to support fast nearest neighbor search.
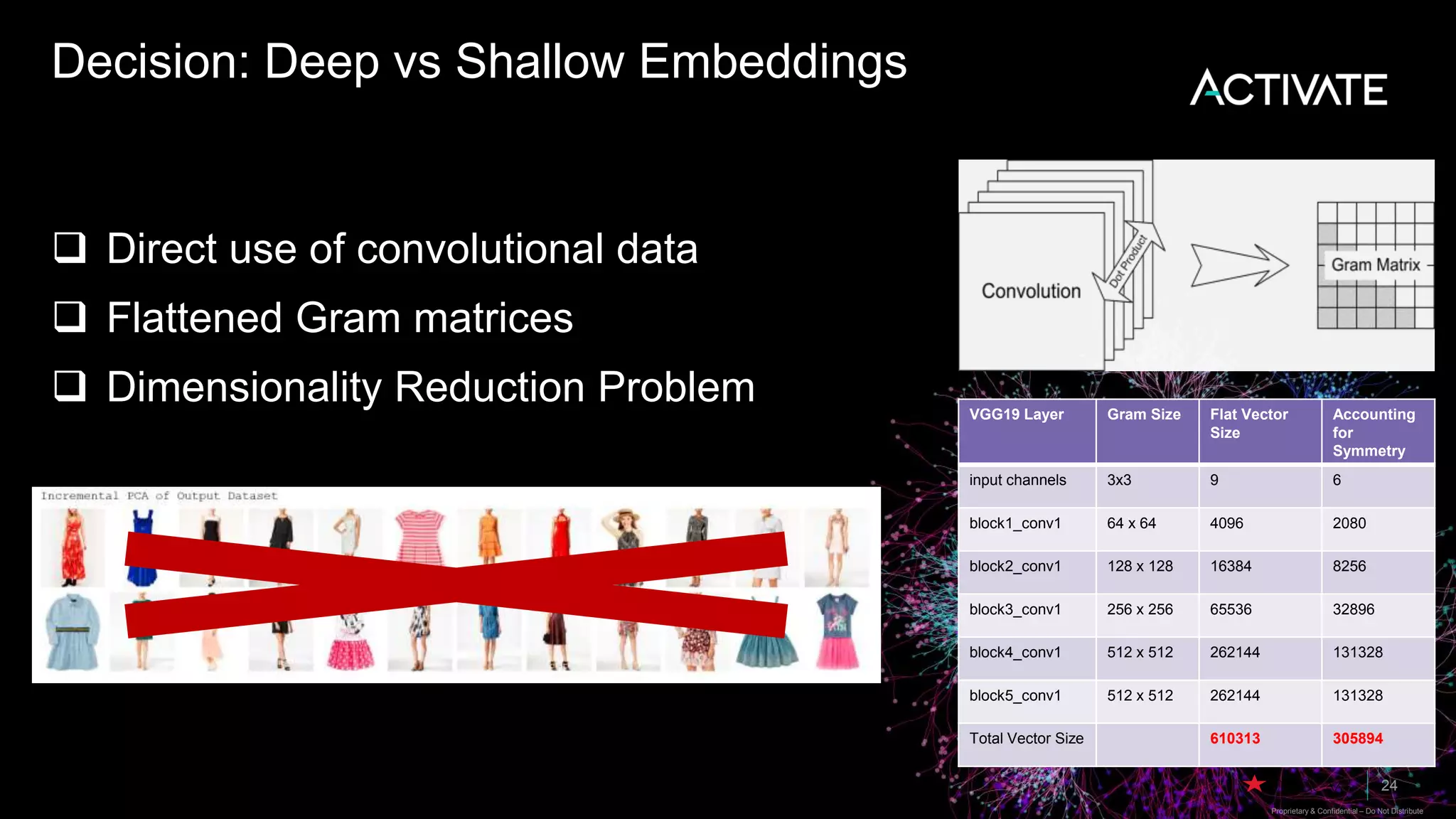
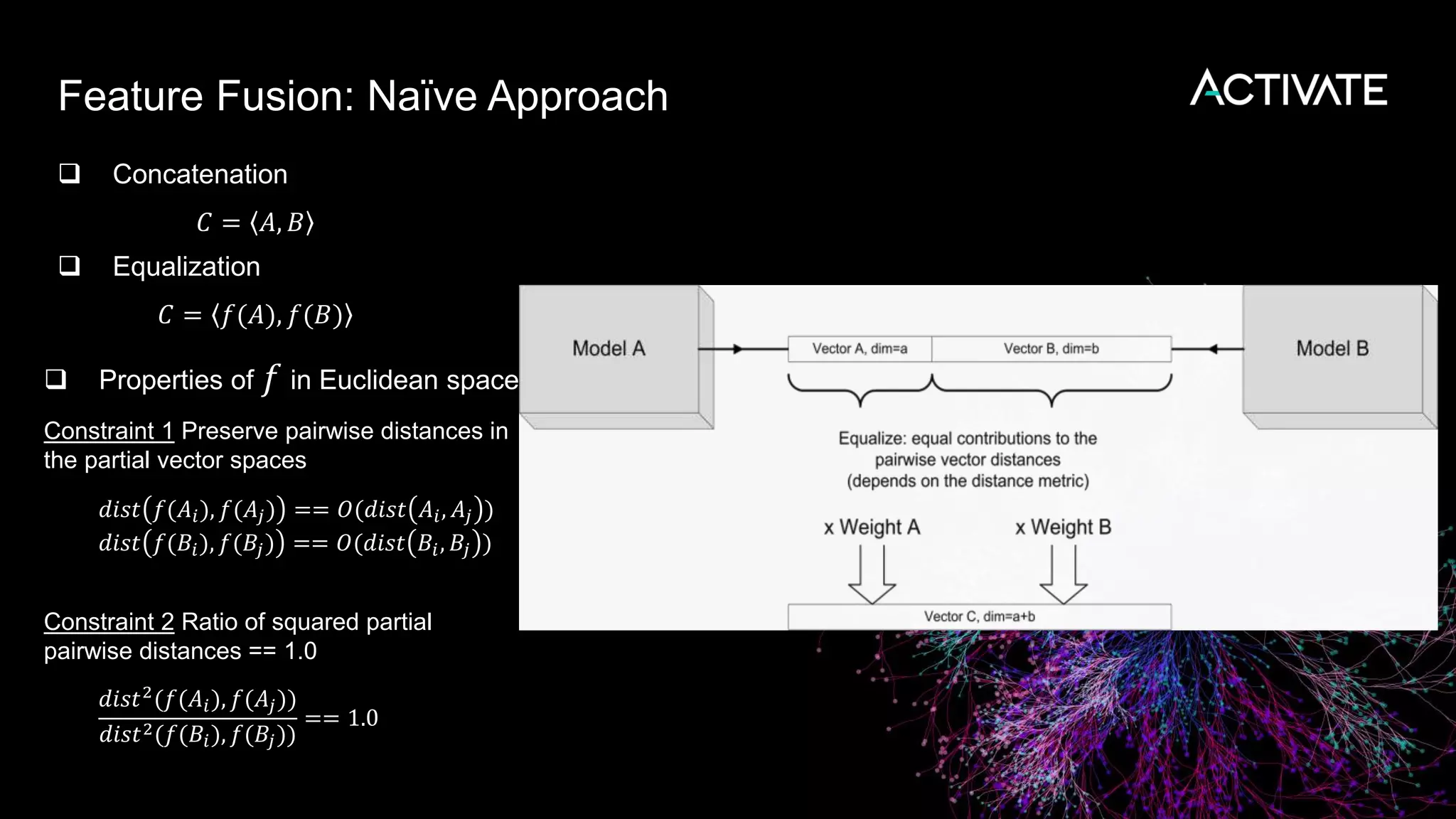
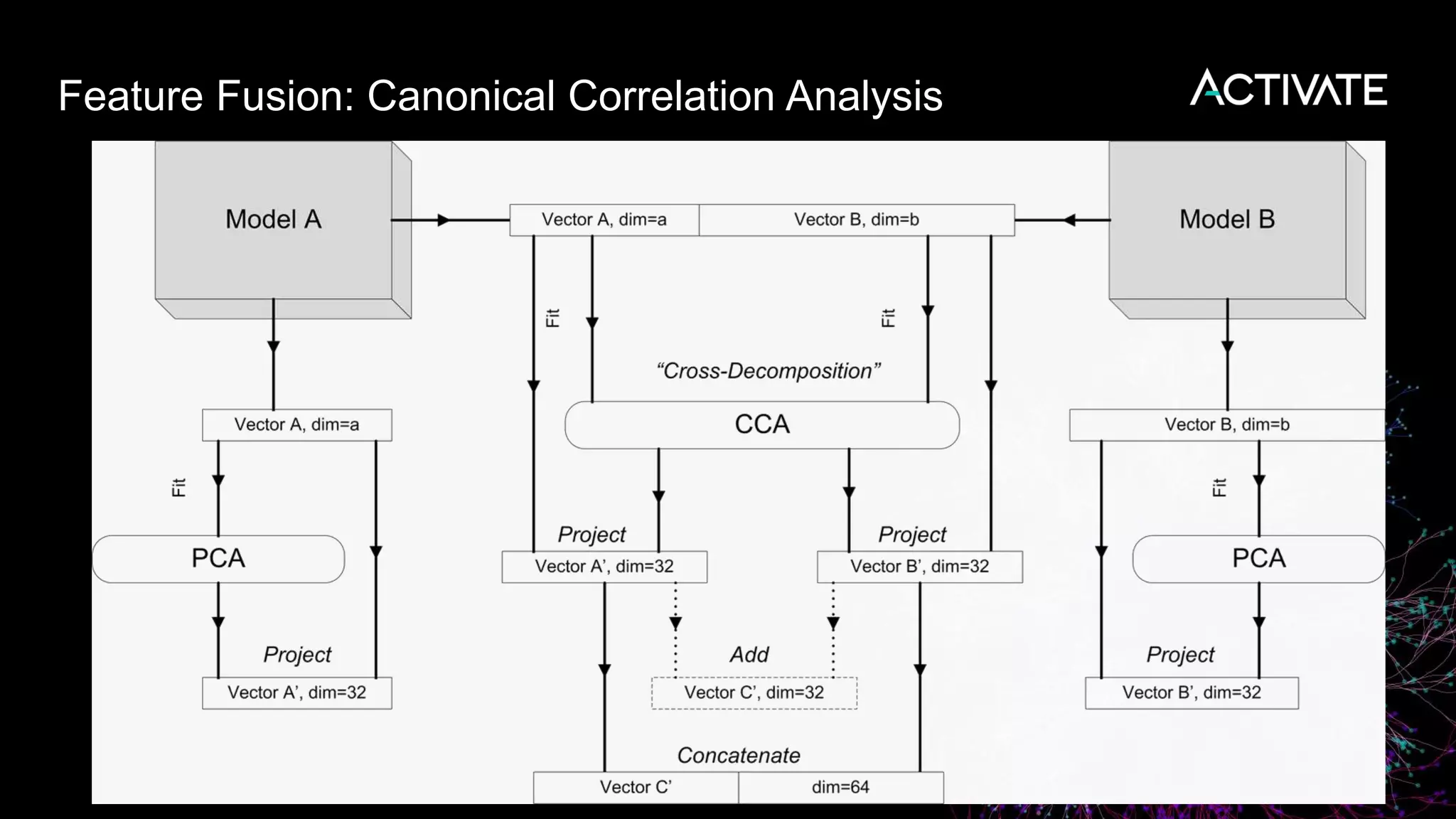
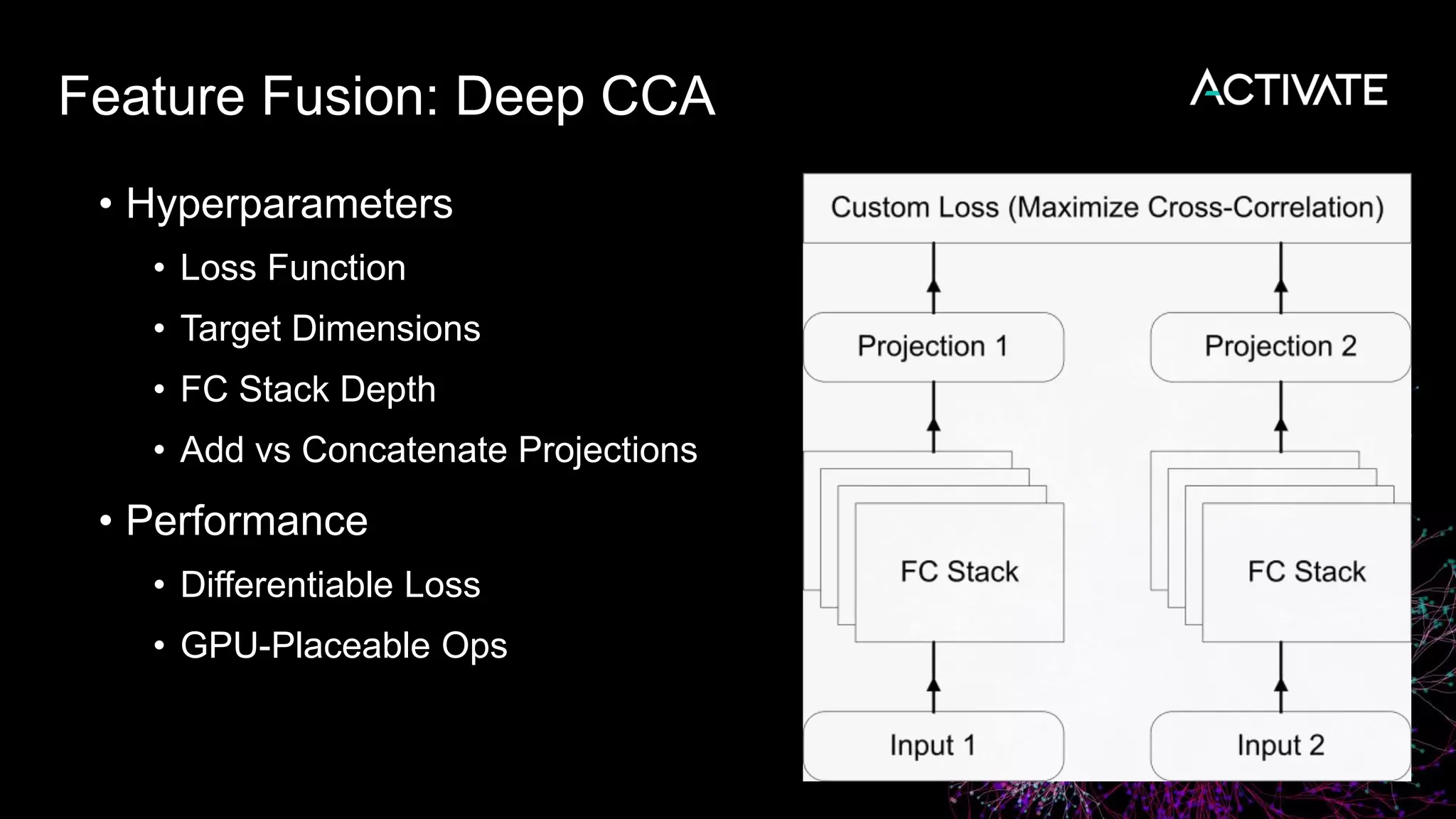
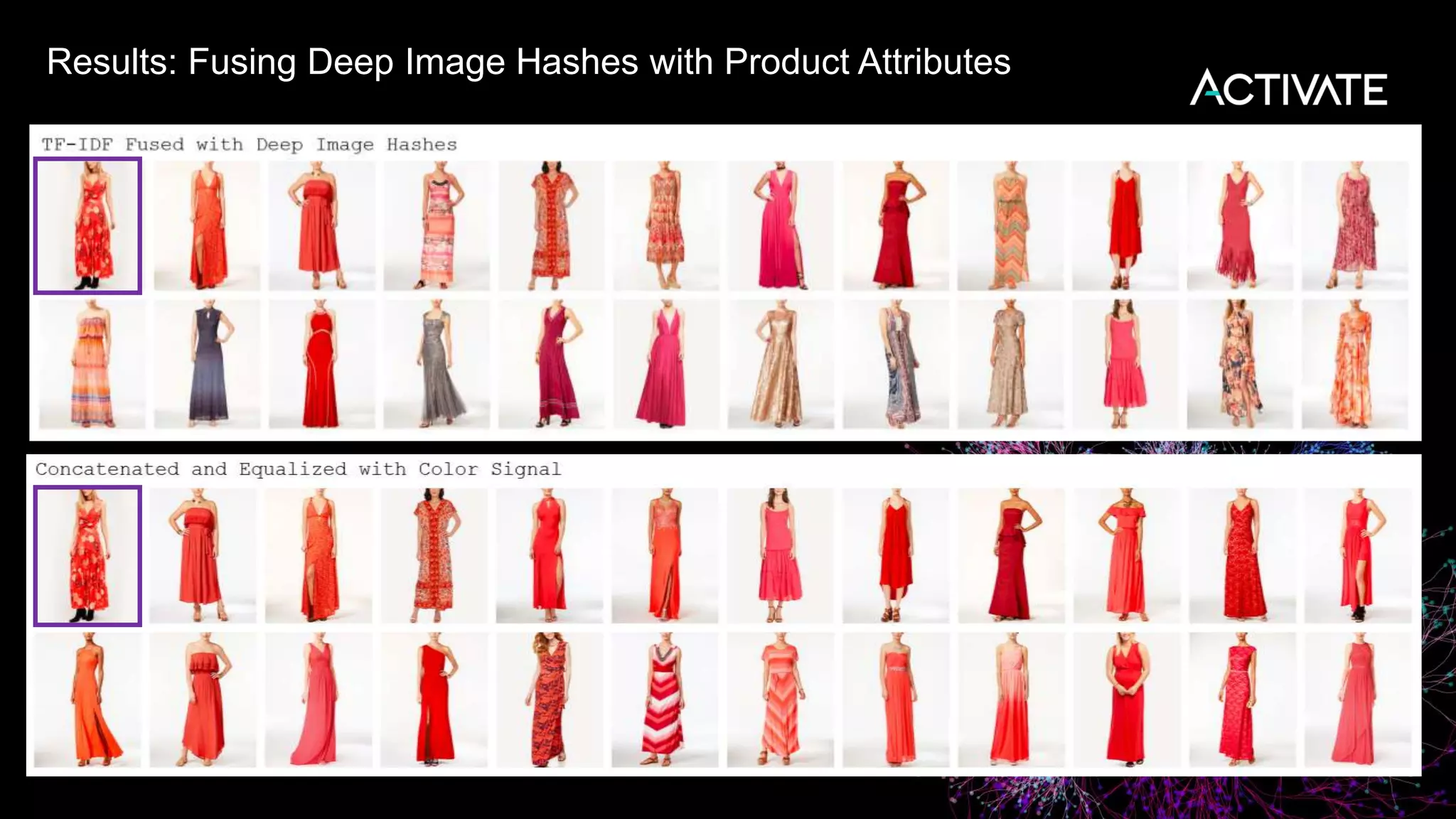
3) Engineering decisions around model architecture, embeddings, feature fusion, distance metrics, and indexing were required to deploy the solution at scale for Macy's large product catalog.





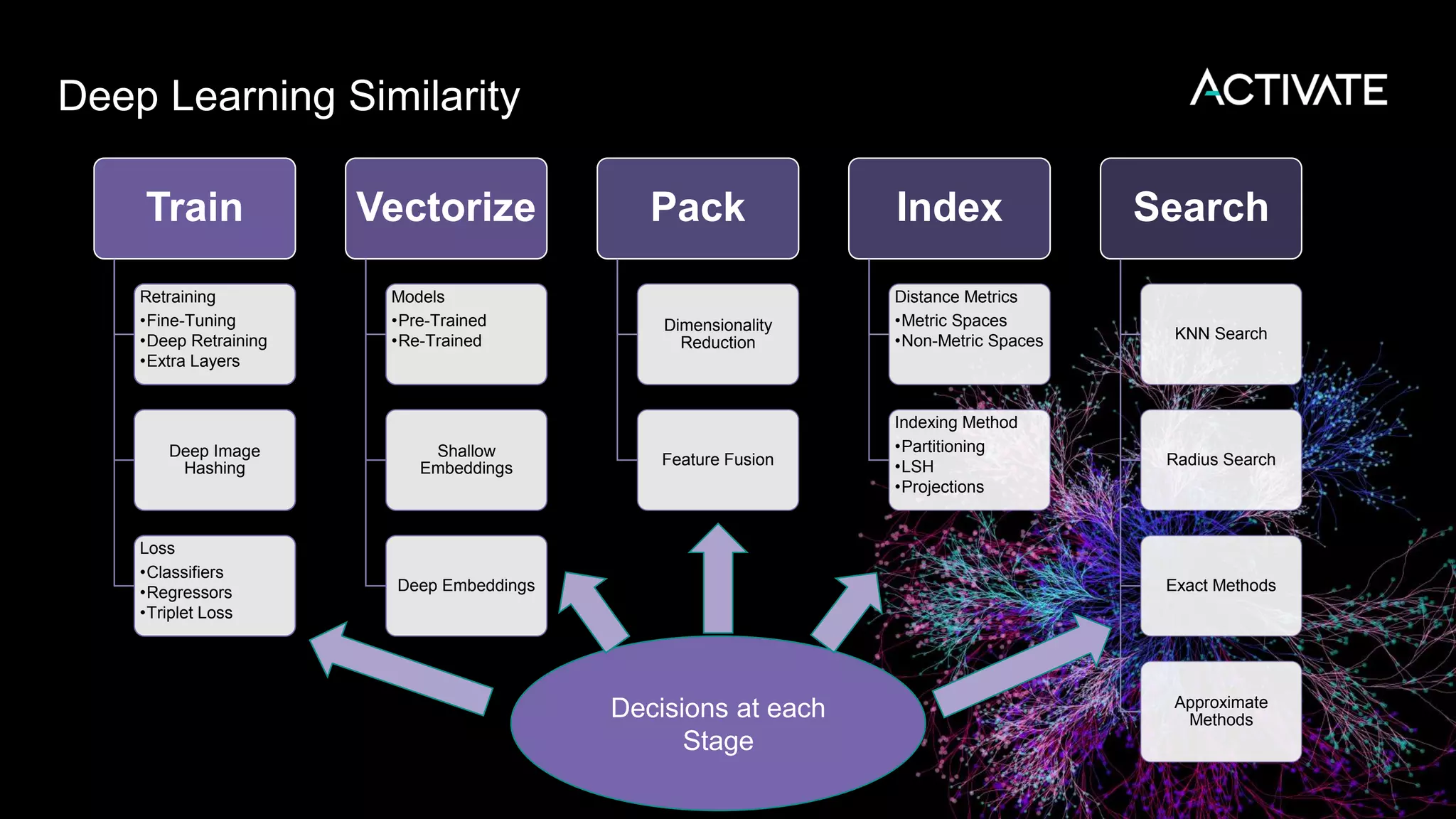













![Results: Cosine vs Euclidean
Cosine distance is a special case of Euclidean distance
𝑐𝑜𝑠_𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡(𝑥, 𝑦) = 1 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑥, 𝑦 = 1 −
𝑖 𝑥𝑖 𝑦𝑖
𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=
𝐿2
2 𝑥
𝑥 2
,
𝑦
𝑦 2
2
Fast to compute for sparse vectors and ranges [0,1] for all-positive vectors popular in NLP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningatmacys-181030174916/75/Image-Based-E-Commerce-Product-Discovery-A-Deep-Learning-Case-Study-Denis-Kamotsky-Peter-Gazaryan-Macy-s-Inc-36-2048.jpg)