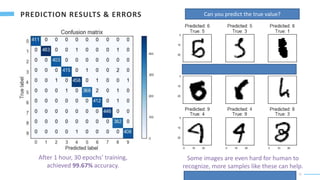
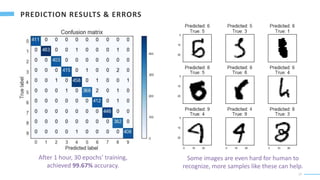
A convolutional neural network is used to recognize handwritten digits from images. The CNN uses convolutional and max pooling layers to extract local features from the images. These local features are then fed into fully connected layers to combine them into global features used to predict the digit (0-9) in each image with a softmax output layer. The model is trained on 60,000 images and achieves 99.67% accuracy on the test set after 30 training epochs. While powerful, it is unclear if humans can fully understand the "mind" and logic of artificial neural networks.

![2
MNIST database
(Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology database)
60,000 training images; 10,000 testing images
Kaggle Challenge
42,000 training images; 28,000 testing images
Predict
Input Image Pixel Value
Handwritten Digit
784 (28*28) Pixels
Pixel color coding [0,255]
Label
[0,9]
Input Result
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MNIST_database
Handwritten Digits
28
28
28
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-2-320.jpg)
![3
Input
28*28
Conv 1
3*3
26*26*16
16 filters
Max pool 1
2*2
Conv 2
3*3
24*24*16
16 filters
12*12*16
Conv 3
3*3
10*10*32
32 filters
Max pool 2
2*2
Conv 4
3*3
32 filters
4*4*32
Flatten
512
Full
Connected
512 1024
Full
Connected
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Max
Prediction
Probability
Dense 1
Relu
Dense 2
Relu
Dense 3
Full
Connected
Predicted
Label
[0,9]
Softmax
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network LeNet - 5 AlexNet VGG 16
8*8*32
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yann_LeCun
Trainable
Parameters:
814,778](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-3-320.jpg)

![8
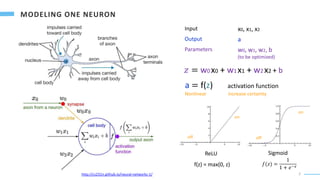
Fully Connected Layers
All the input from the previous layer are
combined at each node.
x0
x1
x2
x3
𝑎0
[1]
= 𝑓(𝑤0,0
1
∙ 𝑥0 + 𝑤1,0
1
∙ 𝑥1 + 𝑤2,0
1
∙ 𝑥2 + 𝑤3,0
1
∙ 𝑥3 + 𝑏0
1
)
All the local features extracted in previous
layers are fully connected with different
weights to construct global features.
Complicated relationship between input can
be revealed by deep networks.
https://github.com/drewnoff/spark-notebook-ml-labs/tree/master/labs/DLFramework
𝑎0
[1]
𝑎1
[1]
𝑎2
[1]
𝑎3
[1]
𝑎4
[1]
𝑎5
[1]
𝑎0
[2]
𝑎1
[2]
𝑎2
[2]
𝑎3
[2]
𝑎4
[2]
𝑎5
[2]
𝑎0
[3]
𝑎1
[3]
𝑎2
[3]
𝑎3
[3]
𝑎4
[3]
𝑎5
[3]
𝑎1
[1]
= 𝑓(𝑤0,1
1
∙ 𝑥0 + 𝑤1,1
1
∙ 𝑥1 + 𝑤2,1
1
∙ 𝑥2 + 𝑤3,1
1
∙ 𝑥3 + 𝑏1
1
)
…...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-8-320.jpg)
![9
…………
𝑎0
[𝐿−1]
𝑎1
[𝐿−1]
𝑎2
[𝐿−2]
𝑎1023
[𝐿−1]
……………..….…………
𝑧0 = 𝑤0,0
𝐿
∙ 𝑎0
𝐿−1
+ 𝑤1,0
𝐿
∙ 𝑎1
𝐿−1
+ 𝑤2,0
𝐿
∙ 𝑎2
𝐿−1
+ ⋯ + 𝑤1023,0
𝐿
∙ 𝑎1023
[𝐿−1]
+ 𝑏0
𝐿
0
1
2
9
Linear combination of inputs from previous layer:
𝑦0 =
𝑒𝑧0
𝑒𝑧0+𝑒𝑧1+𝑒𝑧2+⋯+𝑒𝑧9
L-1 layer
L layer
Softmax, normalize the result:
𝑦0
𝑦1
𝑦2
𝑦9
𝑦0 + 𝑦1 + 𝑦2 + … + 𝑦9 = 1
Probability that 𝑦 = 0
𝑦 =[ 𝑦0, 𝑦1, 𝑦2, … 𝑦9 ]
Prediction:
True value: y = [ y0 , y1 , y2 , … y9]
E.g. y = 0
𝑦 =[ 𝟎. 𝟗, 0.02, 0.01, 0.02, … 0.04]
y = [ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Loss function: 𝐿 𝑦, 𝑦 = −
𝑖=0
9
𝑦𝑖 log(𝑦𝑖) 𝐿 𝑦, 𝑦 = −1 ∗ log 0.9 = 0.046
L ≥ 0, 𝑎𝑡 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ 𝑦 = y,
Cost function:
𝐿 𝑦, 𝑦 = −1 ∗ log 1 = 0
𝐽(𝑤, 𝑏) = 1
𝑚 𝑚 𝐿 𝑦,𝑦 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑚 𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒𝑠
𝐺𝑜𝑎𝑙: 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛.
A Friendly Introduction to Cross-Entropy Loss
𝑤0,0
𝐿
𝑤1023,0
𝐿](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-9-320.jpg)
![10
…………
𝑎0
[𝐿−1]
𝑎1
[𝐿−1]
𝑎2
[𝐿−2]
𝑎1023
[𝐿−1]
……………..….…………
L-1 layer
L layer
𝑦0
𝑦1
𝑦2
𝑦9
𝑊[𝐿]
𝑏[𝐿]
𝑎0
[𝐿−2]
𝑎1
[𝐿−2]
𝑎2
[𝐿−2]
𝑎1023
[𝐿−2]
……………..….…………
L-2 layer
𝑊[𝐿−1]
𝑏[𝐿−1]
0
1
2
9
𝐺𝑜𝑎𝑙: 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑏𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑒𝑒𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑦 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑡𝑟𝑢𝑒 𝑦.
1. With the initial parameters W and b, predict the label 𝑦 with
forward propagation, calculate the cost.
2. 𝑂𝑝𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐿 𝑙𝑎𝑦𝑒𝑟, 𝑊[𝐿]
& 𝑏[𝐿]
,
assuming inputs from L-1 layer, 𝐴[𝐿−1]
do not change.
3. 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝐿– 1 𝑙𝑎𝑦𝑒𝑟 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 , 𝐴[𝐿−1]
,
which is needed to minimize the cost funtion,
assuming parameters 𝑊[𝐿]
& 𝑏[𝐿]
do not change.
4. 𝑂𝑝𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑧𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝐿– 1 𝑙𝑎𝑦𝑒𝑟, 𝑊[𝐿−1] & 𝑏[𝐿−1] ,
𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑒𝑠𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑠 of 𝐴[𝐿−1]
.
5. Proceed like this all the way to the first layer,
optimize the parameters W and b of all layers.
6. Running forward propagation and backpropagation once is called
one epoch, run multiple epochs until cost is near minimum value.
𝐴[𝐿−2] 𝐴[𝐿−1] Forward Propagation
Backpropagation https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backpropagation https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geoffrey_Hinton](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-10-320.jpg)
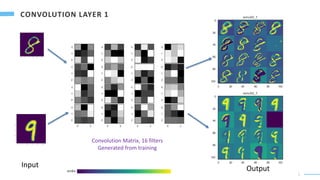
![1
6
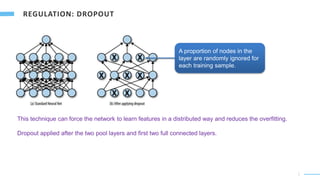
The machine will combined the 1024 final values to judge the label [0,9].
light
signals
Logical
signals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-16-320.jpg)
![1
8
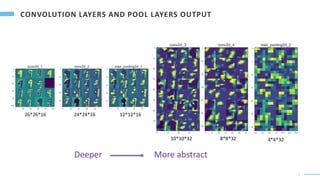
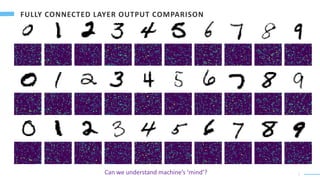
• Convolutional Neural Network is very powerful for analyzing visual image.
• The convolutional layers can capture the local features.
• The pooling layers can concentrate the local changes, as well as reduce the noise and data size.
• The full connected layers can combine all the local features to generate global features .
• The global features are combined to make the final judgement, here the probability of label [0,9].
• Can human understand Artificial Neural Networks?
• Is there any similarity between brain and CNN to process the visual information?
• What is the meaning of local and global features generated by machines?
• Can human understand machines’ logic?
Python code of the project at kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/dingli/digits-recognition-with-cnn-keras](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitrecognizerbyconvolutionalneuralnetwork-220212125552/85/Digit-recognizer-by-convolutional-neural-network-18-320.jpg)