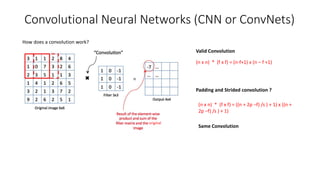
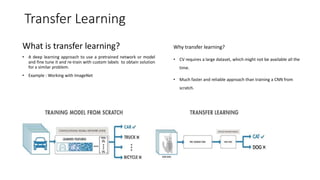
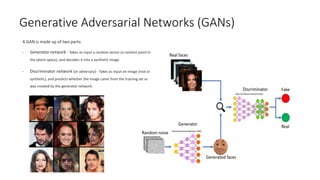
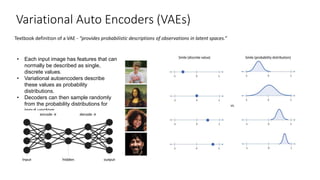
The document introduces various computer vision topics including convolutional neural networks, popular CNN architectures, data augmentation, transfer learning, object detection, neural style transfer, generative adversarial networks, and variational autoencoders. It provides overviews of each topic and discusses concepts such as how convolutions work, common CNN architectures like ResNet and VGG, why data augmentation is important, how transfer learning can utilize pre-trained models, how object detection algorithms like YOLO work, the content and style losses used in neural style transfer, how GANs use generators and discriminators, and how VAEs describe images with probability distributions. The document aims to discuss these topics at a practical level and provide insights through examples.