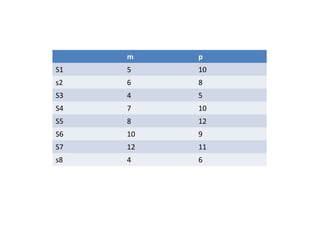
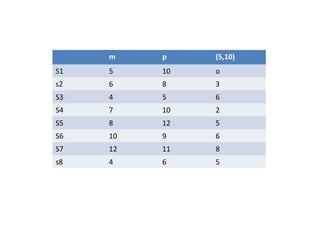
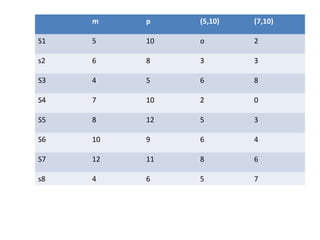
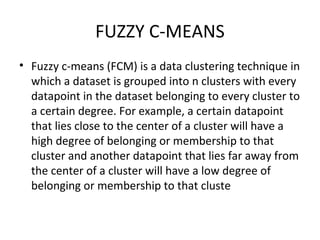
This document discusses clustering techniques for wireless sensor networks. It describes hierarchical routing protocols that involve clustering sensor nodes into cluster heads and non-cluster heads. It then explains fuzzy c-means clustering, which allows data points to belong to multiple clusters to different degrees, unlike hard clustering methods. Finally, it proposes using fuzzy c-means clustering as an energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks due to its ability to handle uncertain or incomplete data.