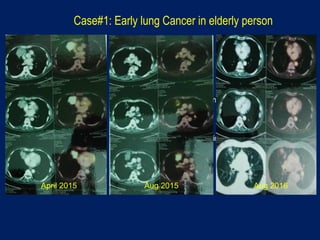
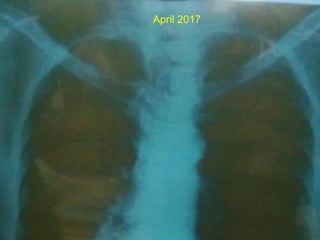
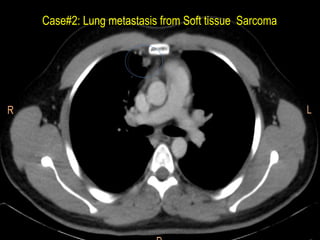
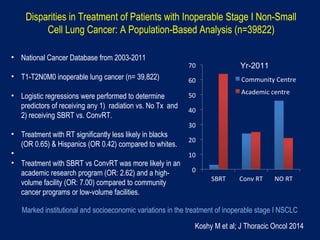
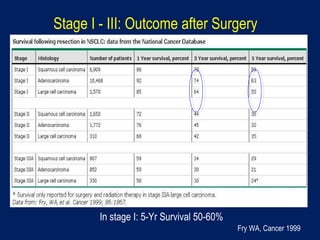
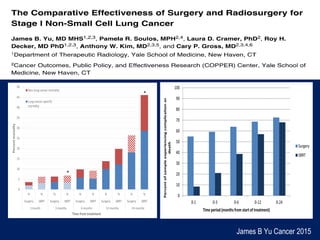
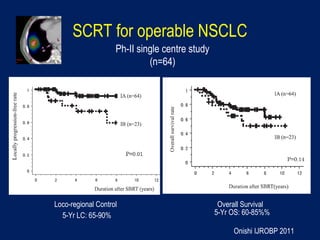
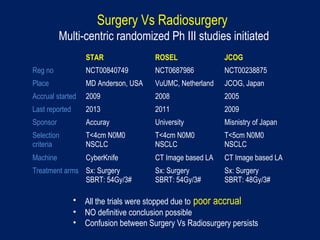
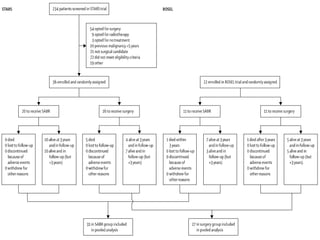
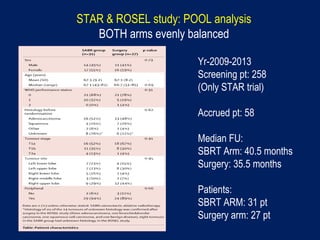
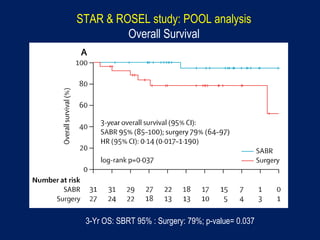
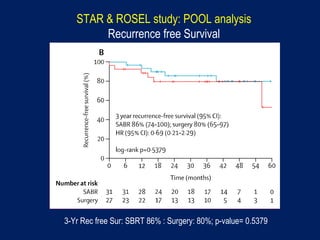
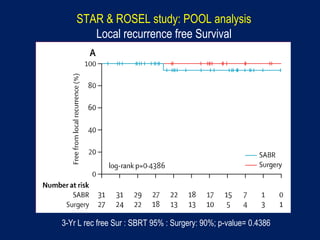
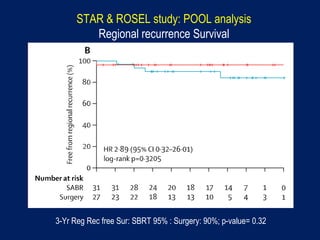
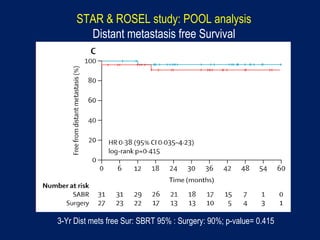
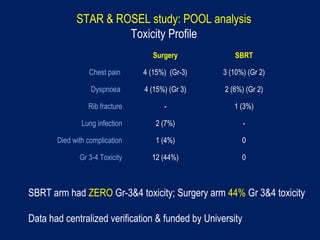
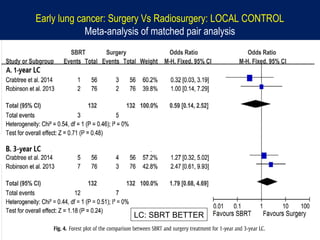
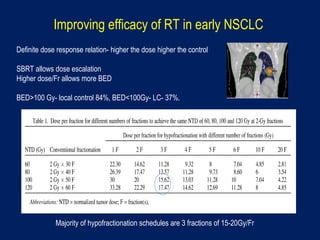
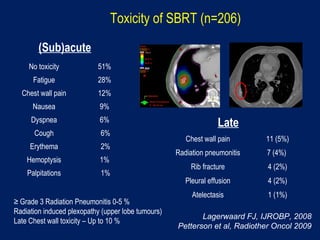
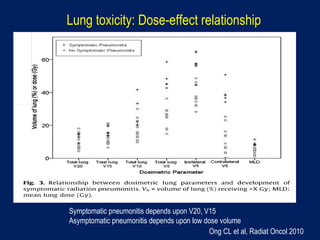
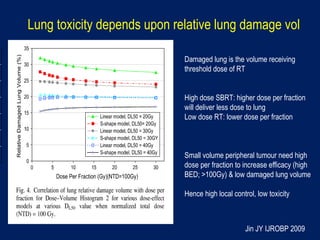
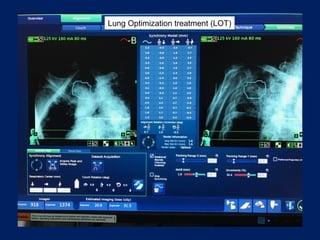
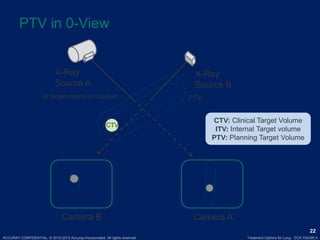
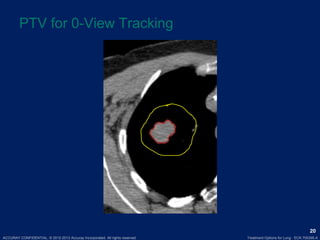
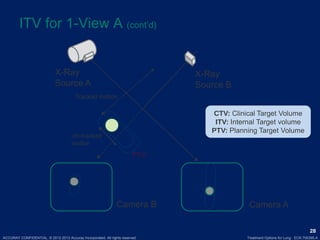
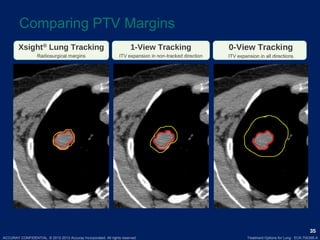
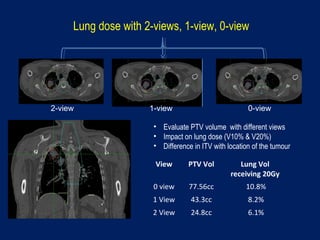
This document discusses treatment approaches for early lung cancer, highlighting the effectiveness of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) compared to surgical options. It presents data indicating disparities in treatment access among different racial groups and emphasizes the potential for SBRT in patients who are medically compromised or prefer non-invasive options. Various studies are referenced, revealing challenges in recruitment for trials comparing SBRT and surgery, alongside outcomes suggesting that SBRT may offer comparable or superior efficacy with lower toxicity.