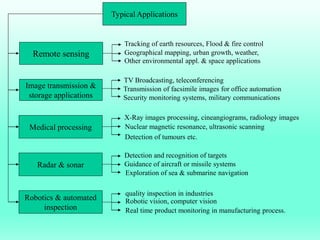
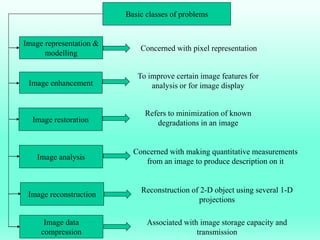
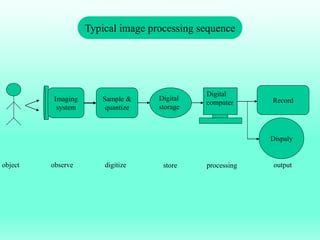
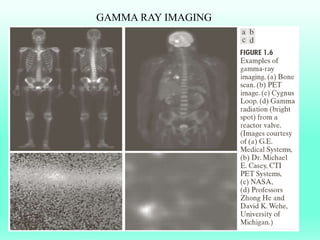
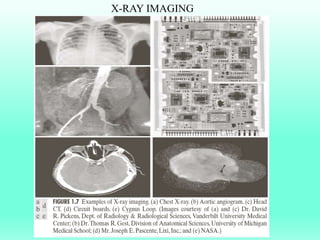
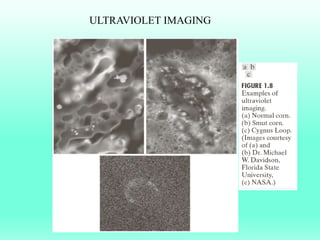
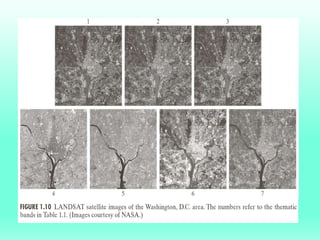
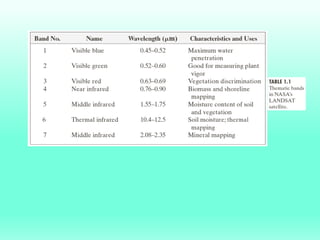
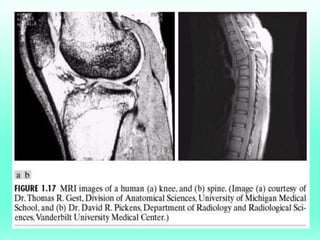
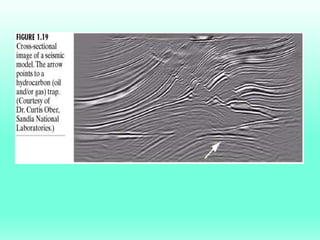
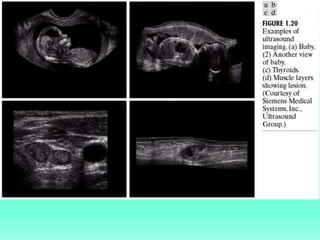
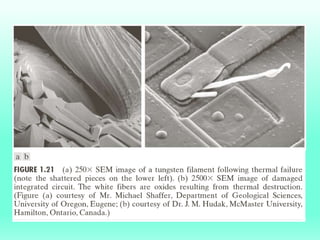
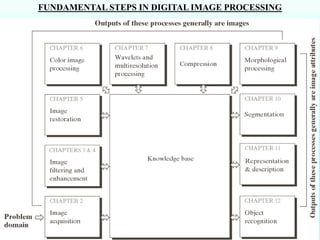
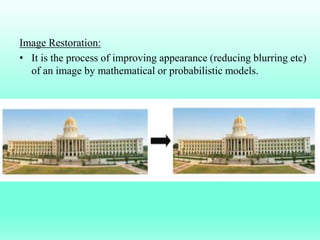
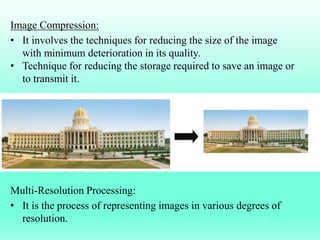
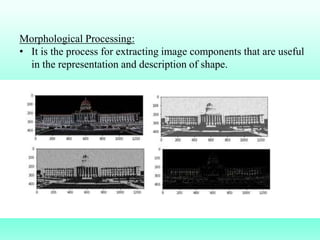
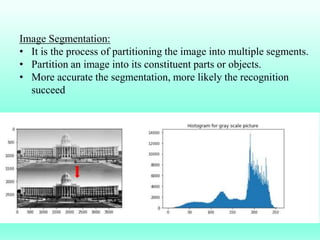
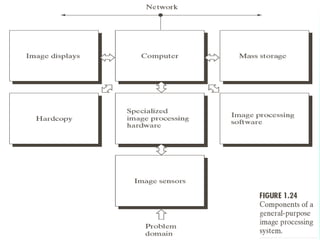
The document discusses the objectives and outcomes of a course on digital image processing. The course aims to introduce students to fundamental image processing techniques including image enhancement, restoration, compression and segmentation. It will also cover color image processing and different methods to represent color images. The syllabus outlines topics like digital image basics, enhancement, restoration, compression, color processing and segmentation that will be covered in the course.