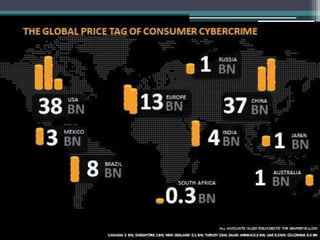
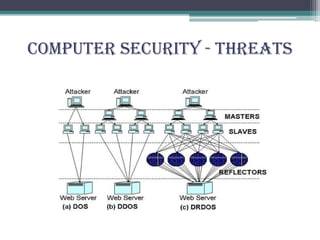
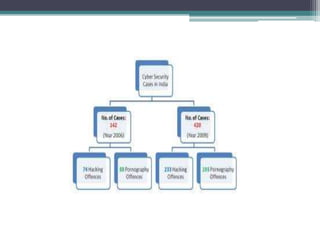
Cyber crimes are illegal activities committed using computers or the internet. This presentation discusses the history, categories, types and impact of cyber crimes as well as cyber security, laws and prevention. It defines cyber crimes, outlines categories such as crimes against persons, property and government, and describes frequently used types like hacking and viruses. The presentation also discusses computer security threats, terminology, and the need for cyber laws to address criminal exploitation online.