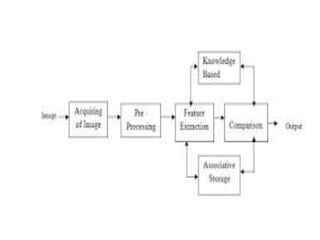
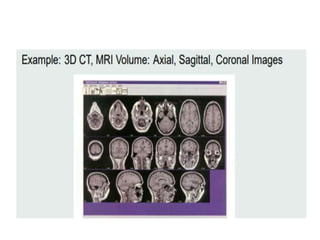
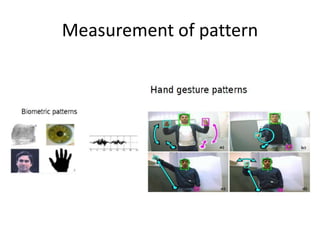
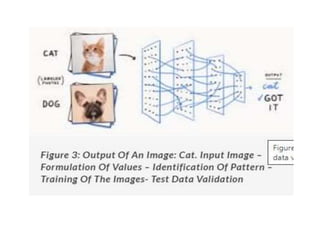
Image processing involves converting images to digital form and performing operations to enhance or extract information. It treats images as 2D signals and applies algorithms. The main purposes are visualization, sharpening/restoration, retrieval, pattern measurement, and recognition. Visualization creates images to observe invisible objects. Sharpening/restoration compensates for defects like blur and noise. Retrieval finds images matching user requests. Pattern measurement quantifies objects in images. Recognition identifies objects/features in images or video. Advantages include improved quality, ability to process degraded images, customization, and mathematical operations. Disadvantages are storage/processing requirements, environmental degradation impacts, and difficult segmentation. Applications include criminology, medicine, military, transportation, and