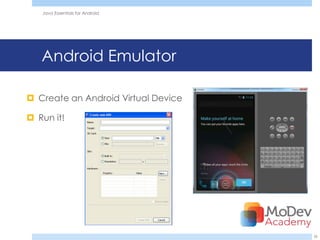
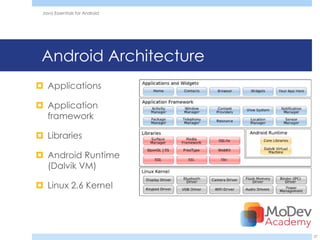
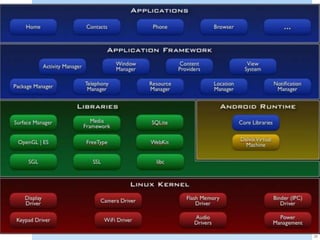
This document provides an overview and agenda for a training session on Java Essentials for Android. The training will be delivered by Adrian Mikeliunas and will cover topics like Java similarities and differences in Android, Android programming with Java in Eclipse, and resources for Android development. It also includes details about the MoDevAcademy which offers professional mobile developer training courses.