This document covers the basics of installing Linux systems, including the boot process, distribution selection, installation options, and basic administration tasks. It discusses BIOS initialization, the boot loader, kernel initialization, and the init process. Installation methods like USB, DVD, and network installation are presented. Basic system administration like services, processes, mounting disks, and shutdown are also outlined.


![Linux#2 - Installation 4
BIOS Initialization
Power On Self Test recognizes hardware, CPU,
memory, bootable configuration from CMOS
Bootable devices:
CD ROM or Floppy
Drive [IDE, SCSI, SATA, RAID, SSD, SD, microSD, …]
Network
USB devices
8/22/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxintro-02-150317202210-conversion-gate01/85/Linux-introduction-Class-02-4-320.jpg)
![Linux#2 - Installation 5
The Boot Loader
Last step in BIOS
Loads first partition of bootable device
It can present a menu of OS choices
Can also let you choose “Other OS”
Linux boot loaders:
LILO (Linux Loader) – older, static
GRUB (GRand Unified Bootloader) dynamic
Syslinux [for CDs and USBs]
8/22/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxintro-02-150317202210-conversion-gate01/85/Linux-introduction-Class-02-5-320.jpg)

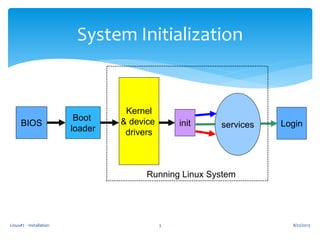
![Linux#2 - Installation 7
init (Initialization)
Init loads scripts from /etc/rc.d
rc.sysinit is the master script at boot time
Loads networking, drivers, encryption, and provides
[OK] or [FAIL] feedback
Based on parameter or /etc/inittab default,
it will execute scripts in rc.x (x=runlevel)
All boot scripts live in init.d,
can be configured via chkconfig
Last script is rc.local
8/22/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxintro-02-150317202210-conversion-gate01/85/Linux-introduction-Class-02-7-320.jpg)

















![Linux#2 - Installation 32
Hands-on Lab-1
Exploring Linux Services
From command line type:
top (press h, q after reading screens)
w [integrated who / uptime]
whoami
ps ax [list all active processes]
pstree
8/22/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxintro-02-150317202210-conversion-gate01/85/Linux-introduction-Class-02-32-320.jpg)