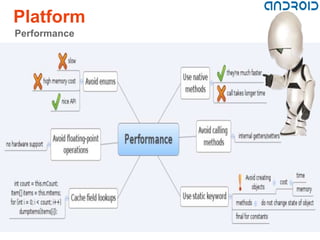
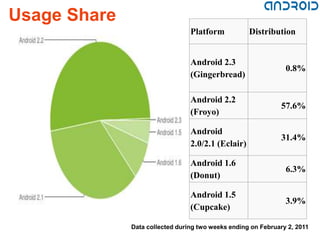
The document provides an overview of Android, a mobile operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance, based on the Linux kernel. It discusses the features, architecture, security, and development requirements of the Android platform, along with a brief history of its versions and future possibilities. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and limitations of using Android for mobile application development.