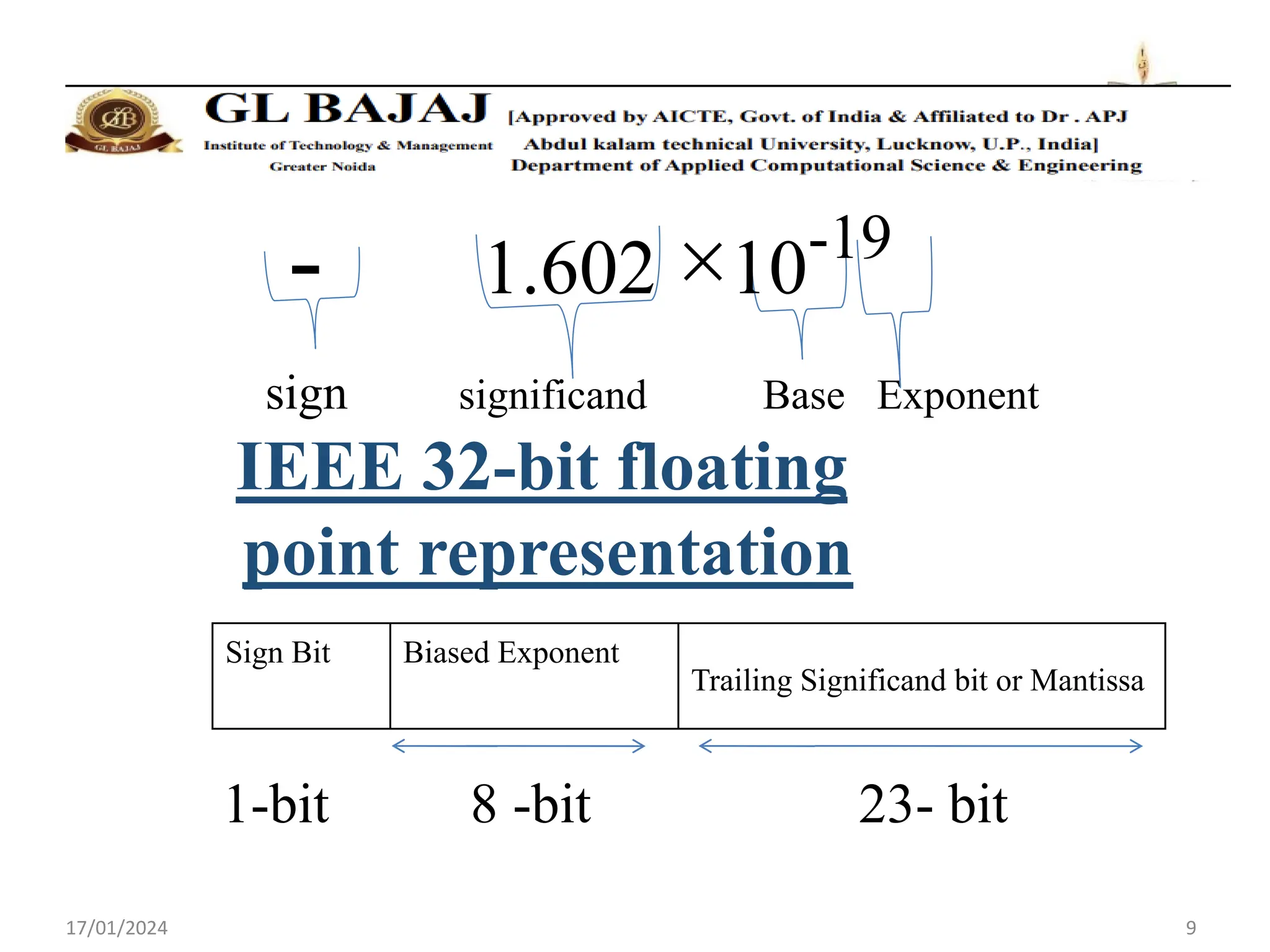
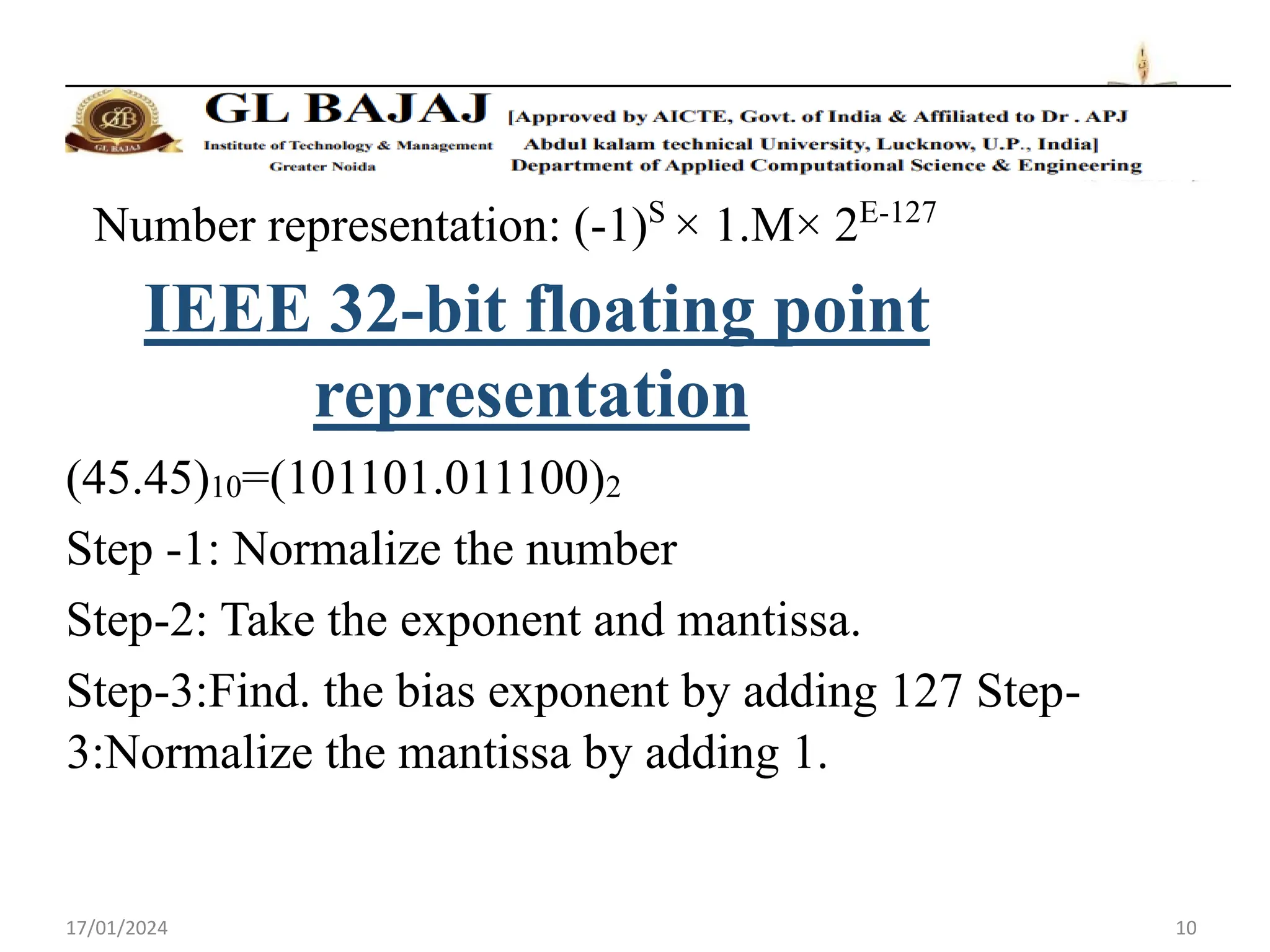
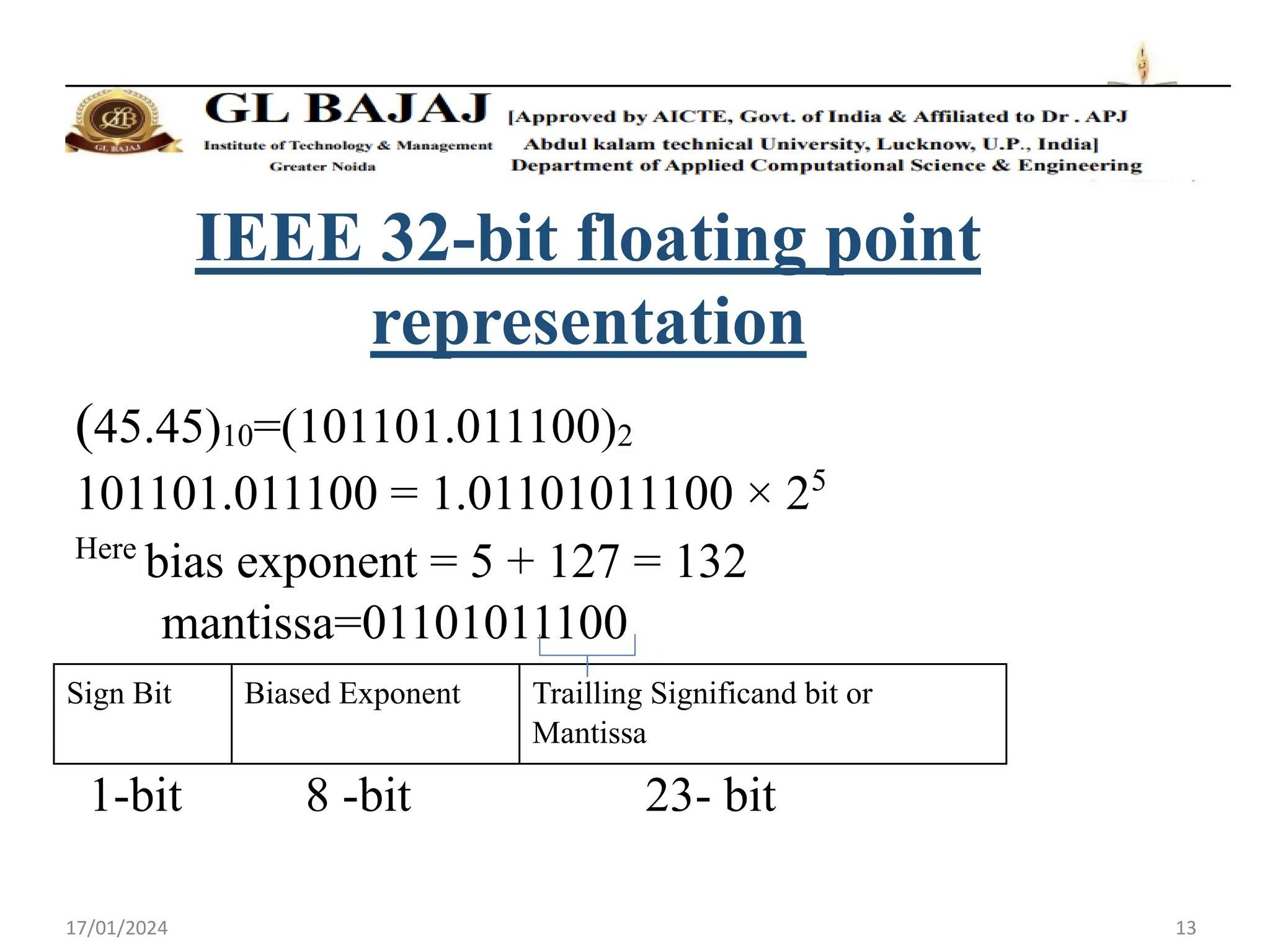
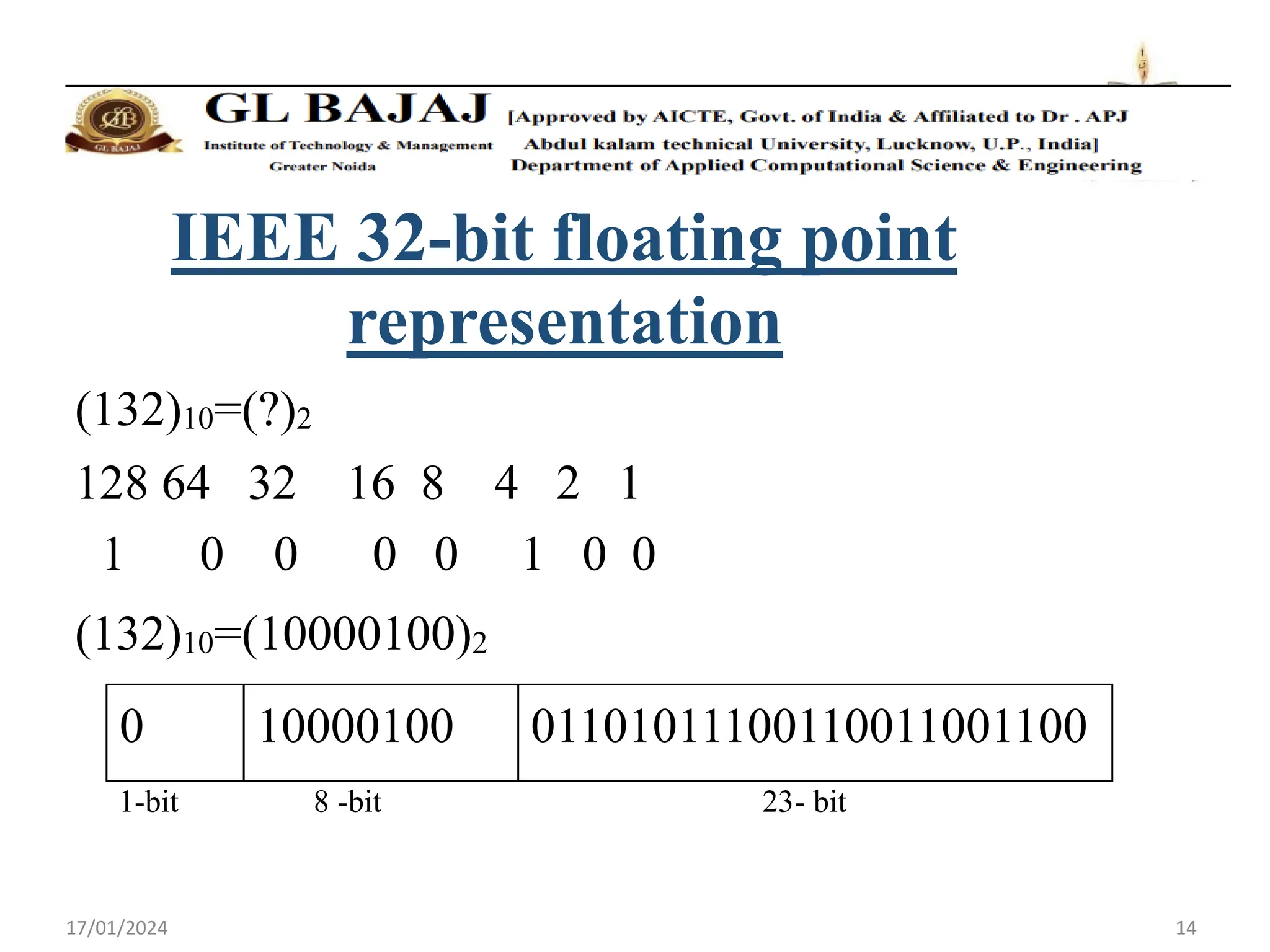
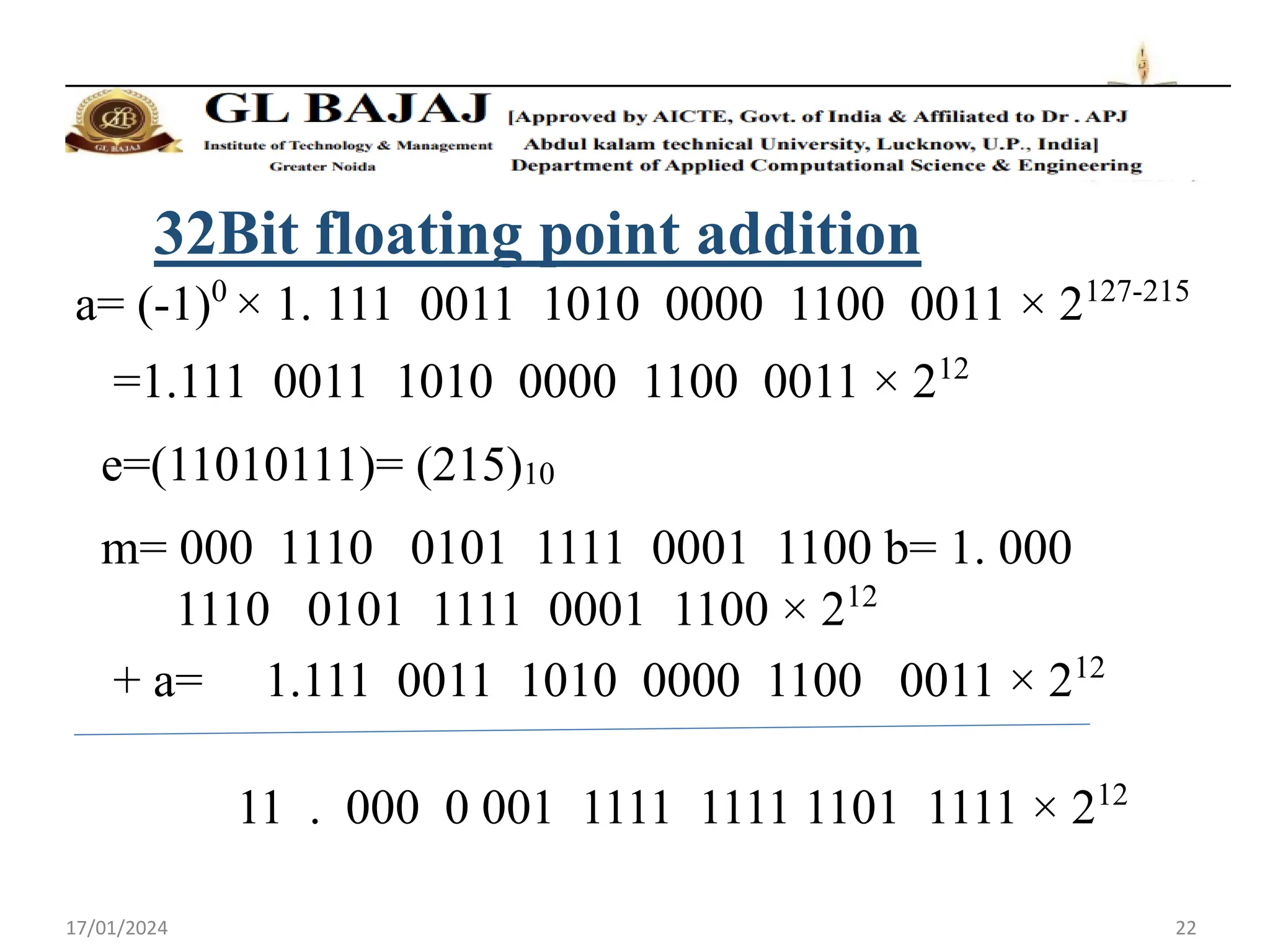
The document discusses floating point number representation according to the IEEE 754 standard. It describes:
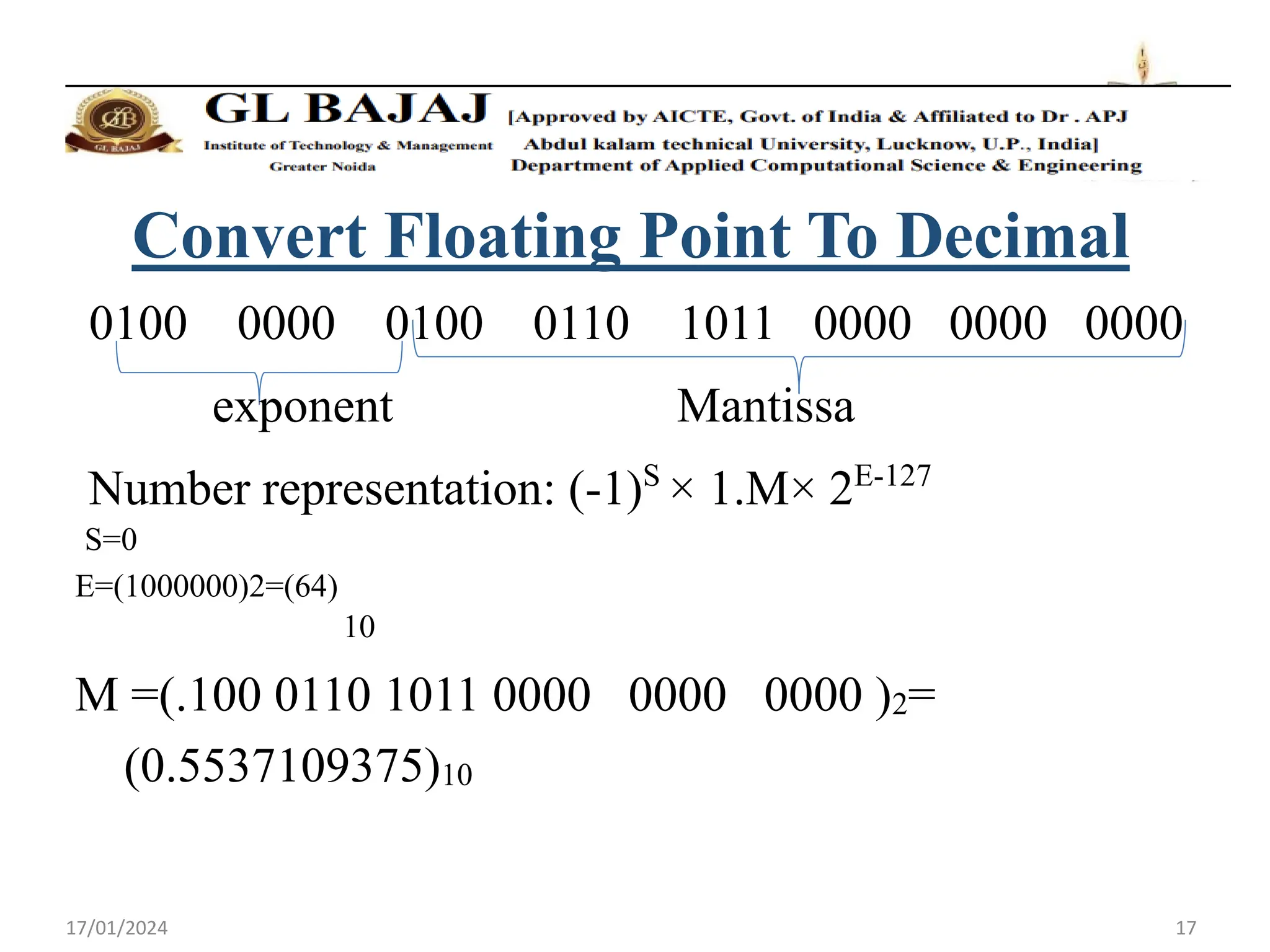
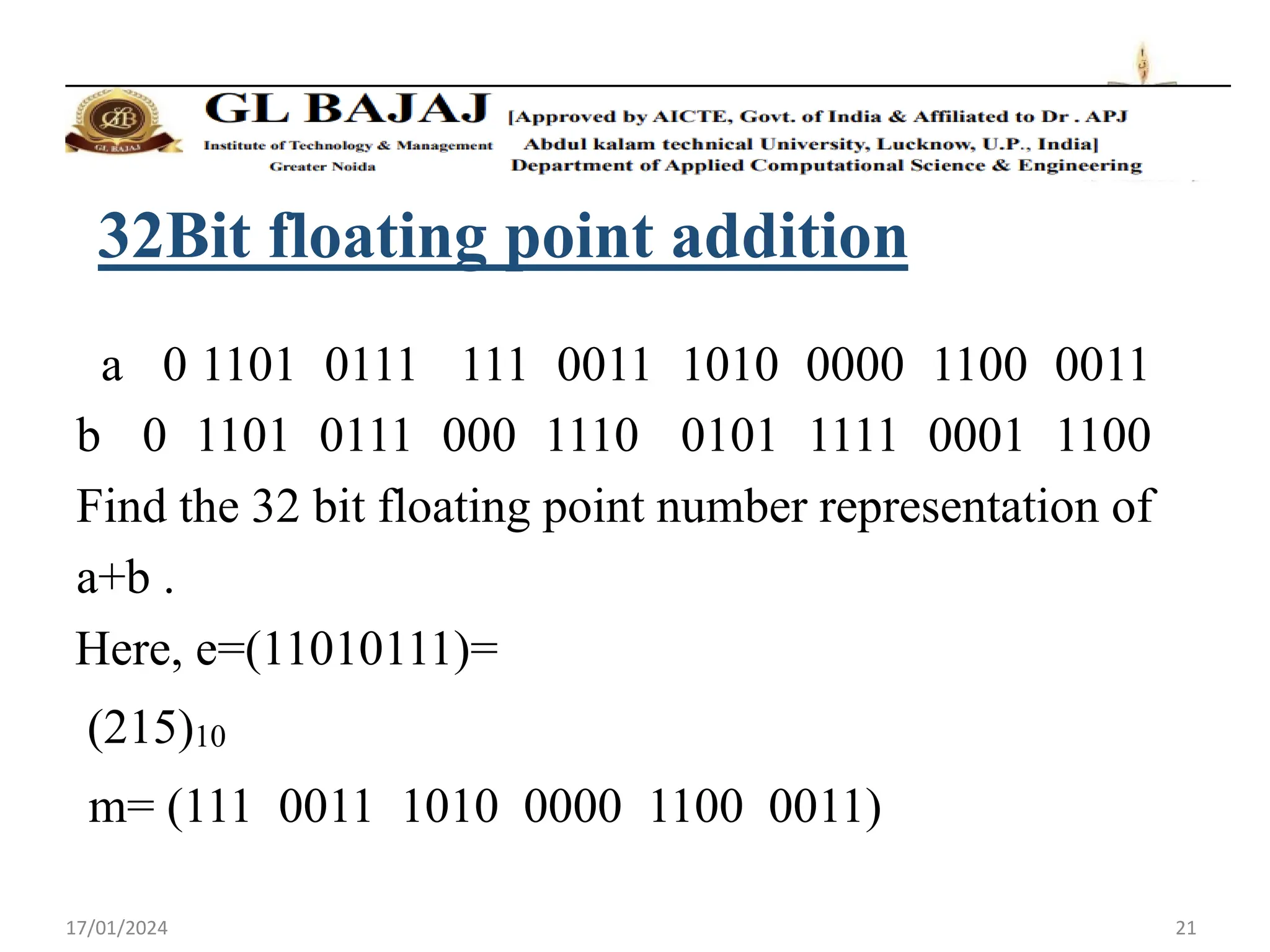
- Single precision representation uses 32 bits with 1 sign bit, 8 exponent bits, and 23 mantissa bits.
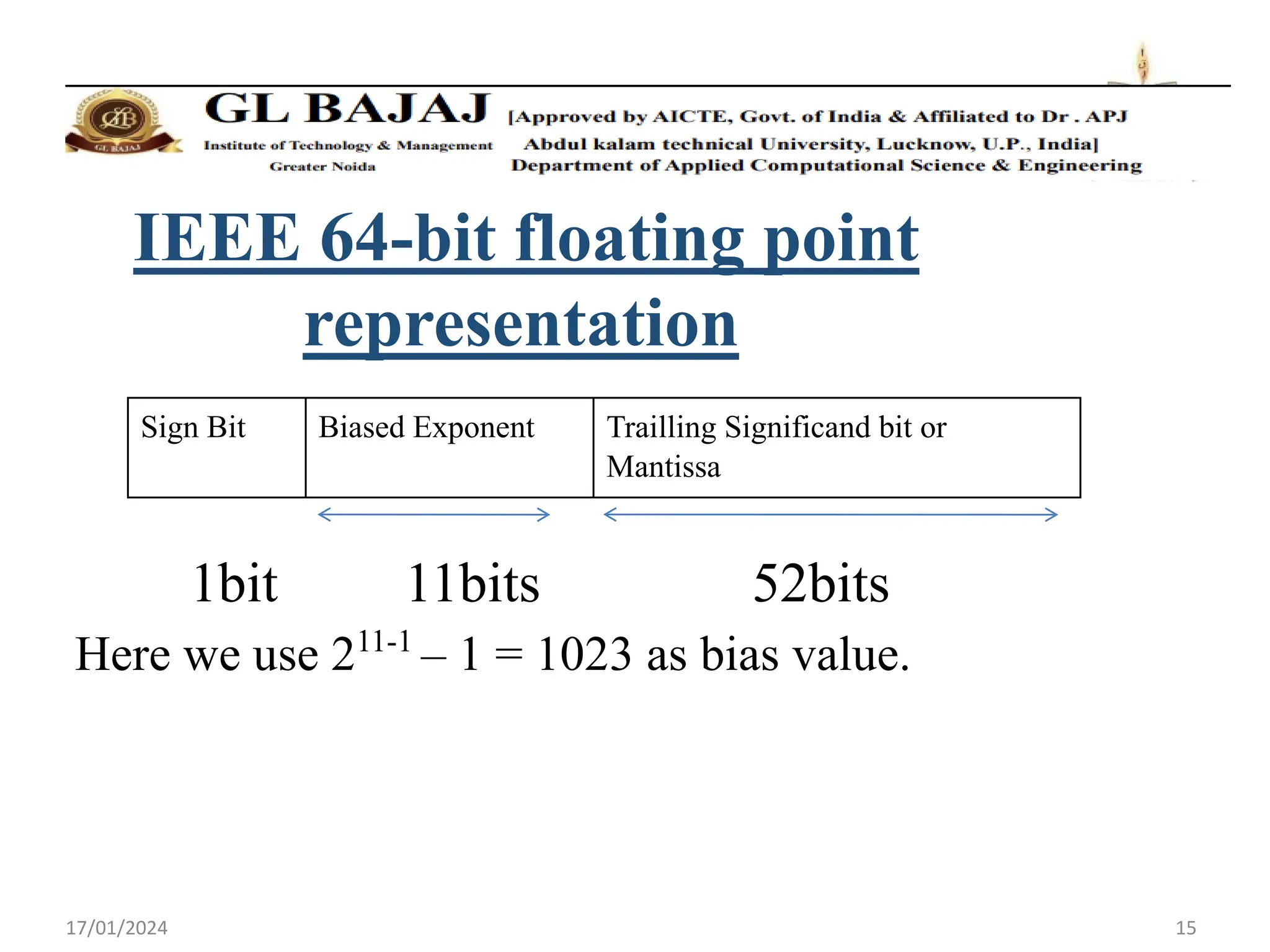
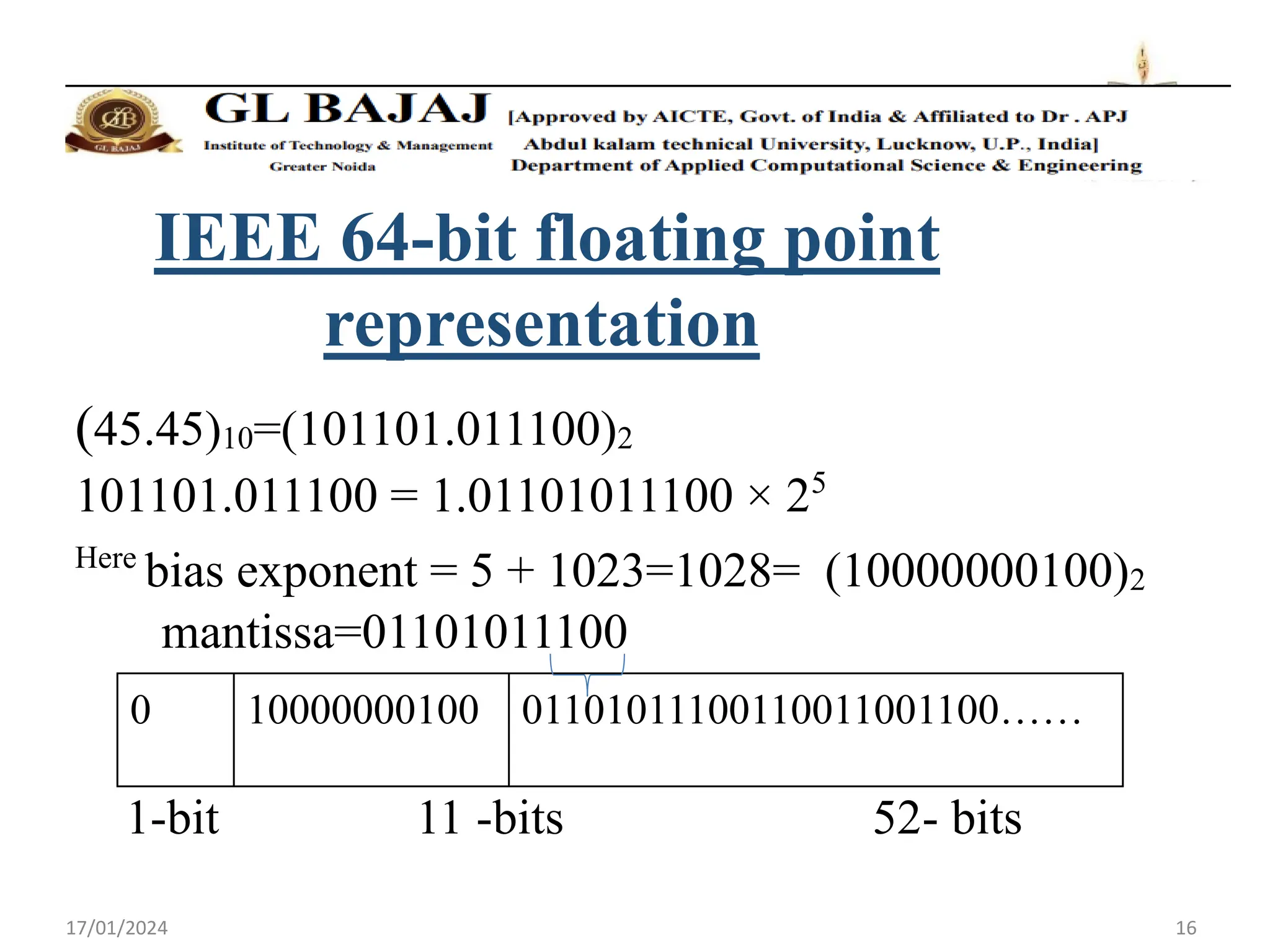
- Double precision representation uses 64 bits with 1 sign bit, 11 exponent bits, and 52 mantissa bits.
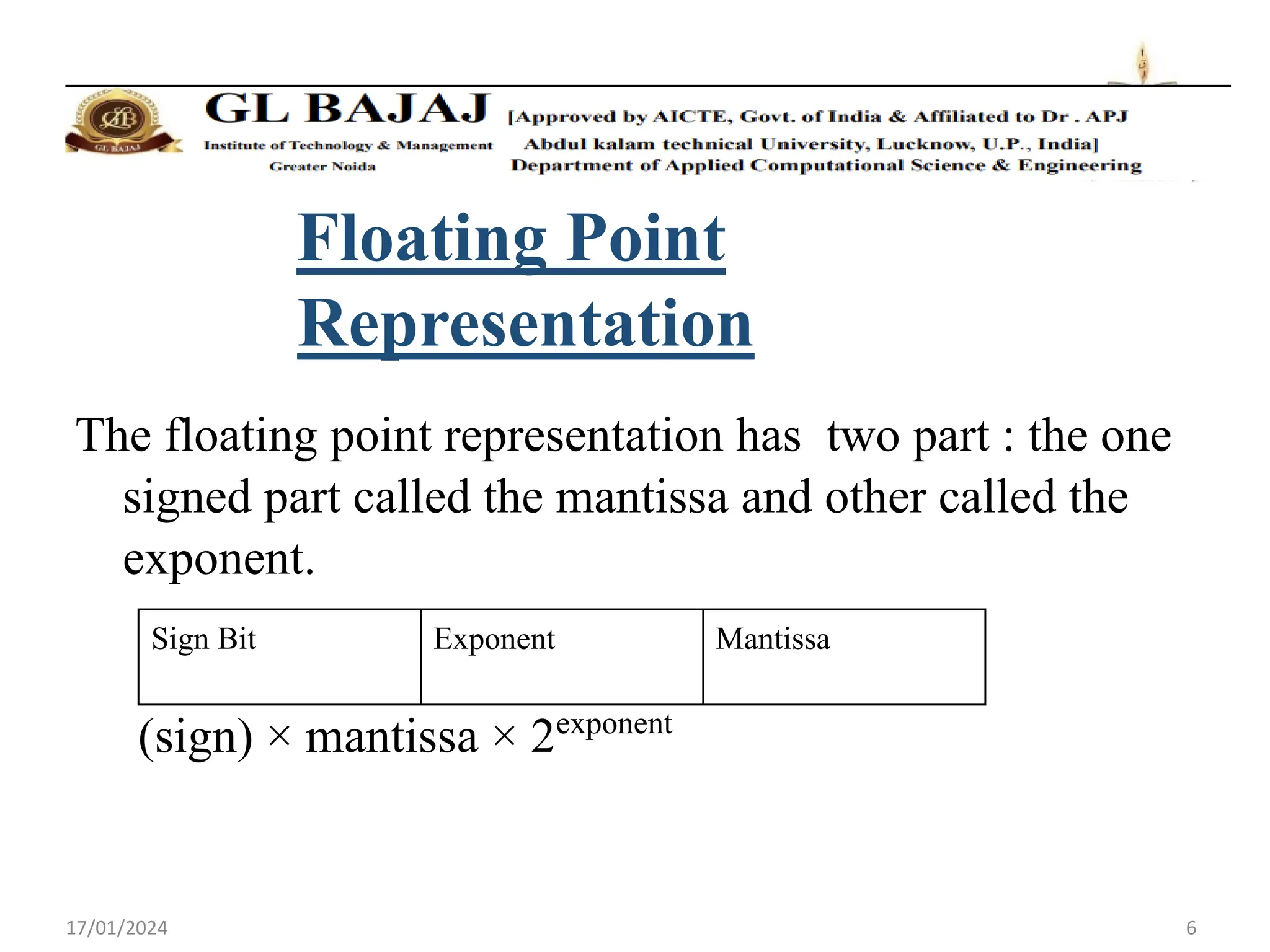
- Floating point numbers are represented as (-1)S × 1.M × 2E, where S is the sign bit, M is the mantissa, and E is the exponent.
- Addition of floating point numbers involves normalizing the numbers to the same exponent before adding the mantissas.