Embed presentation



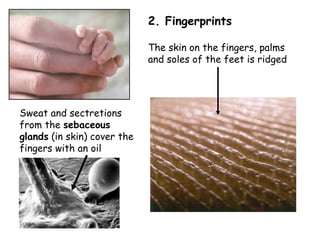
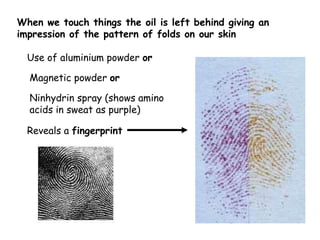
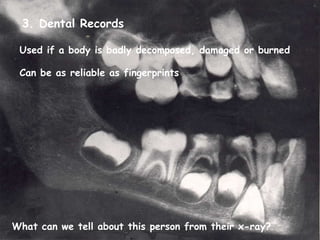




A forensic pathologist can use several clues to identify a dead body, including identification papers carried by the deceased, fingerprints, dental records, and genetic fingerprinting. Fingerprints and genetic fingerprints are especially reliable for identification as they contain unique patterns for each individual. A genetic fingerprint analyzes repeated sections of non-coding DNA known as satellites that vary in number of repeats from person to person.










