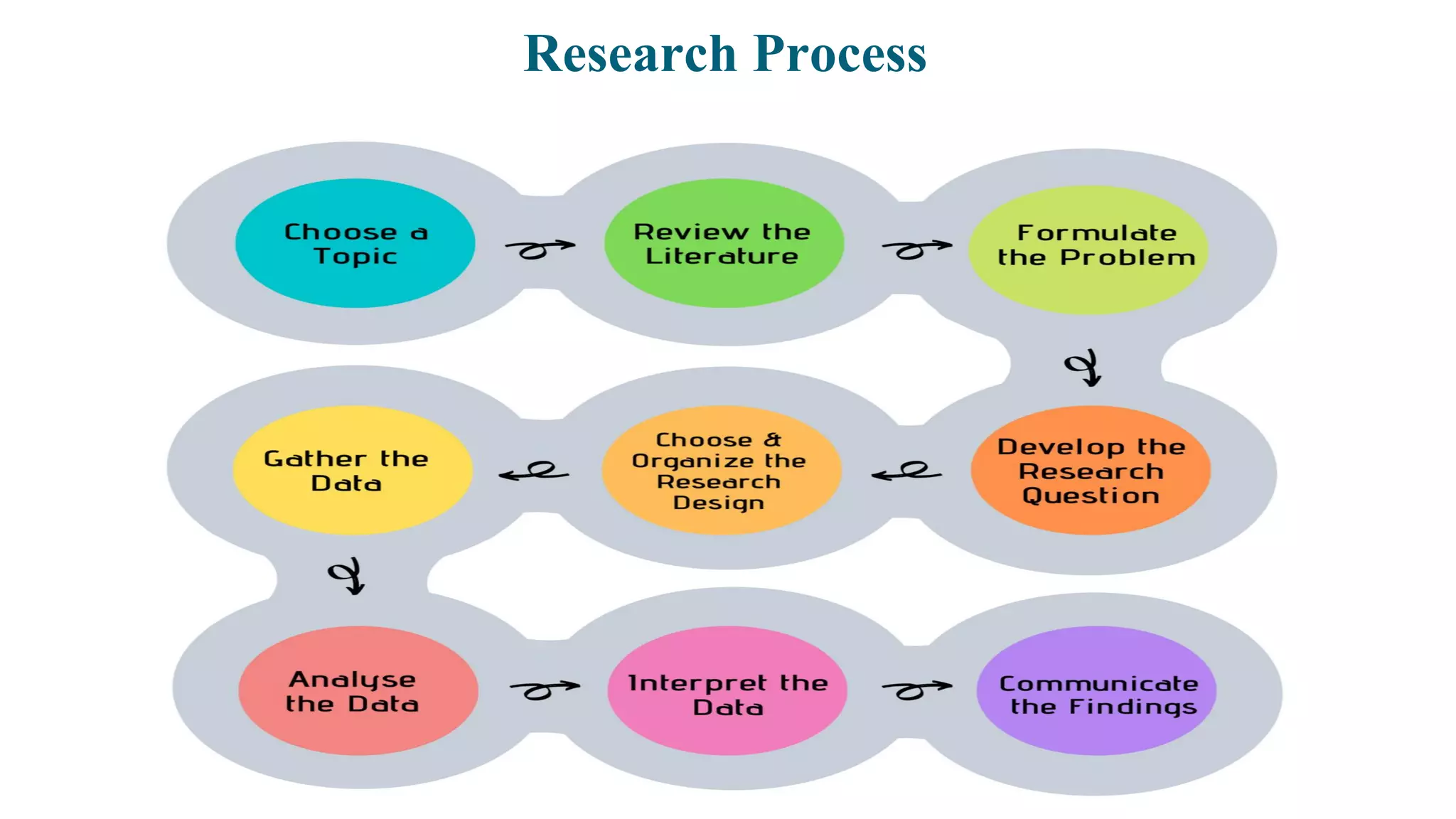
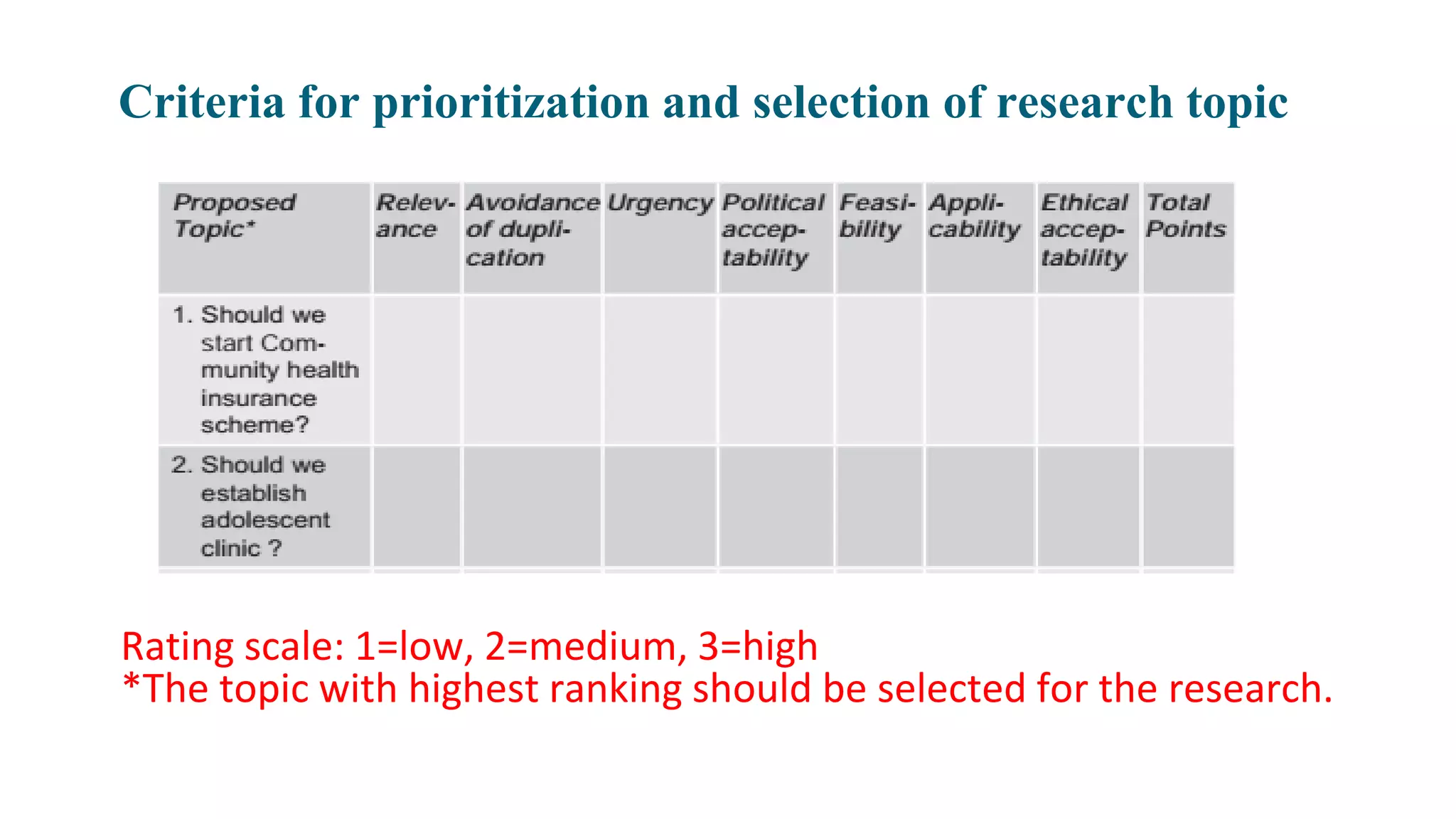
This document discusses key aspects of identifying and prioritizing research problems, including selecting a research topic and writing a problem statement. It provides criteria for selecting a research topic, such as relevance, avoidance of duplication, and feasibility. A good problem statement identifies a gap in understanding or weakness in existing data, explains the significance of this lack, and describes how the research will contribute new knowledge and why it matters. The problem statement should be concise, around one page, and define the problem without findings or data, proposing a way to systematically research a solution.