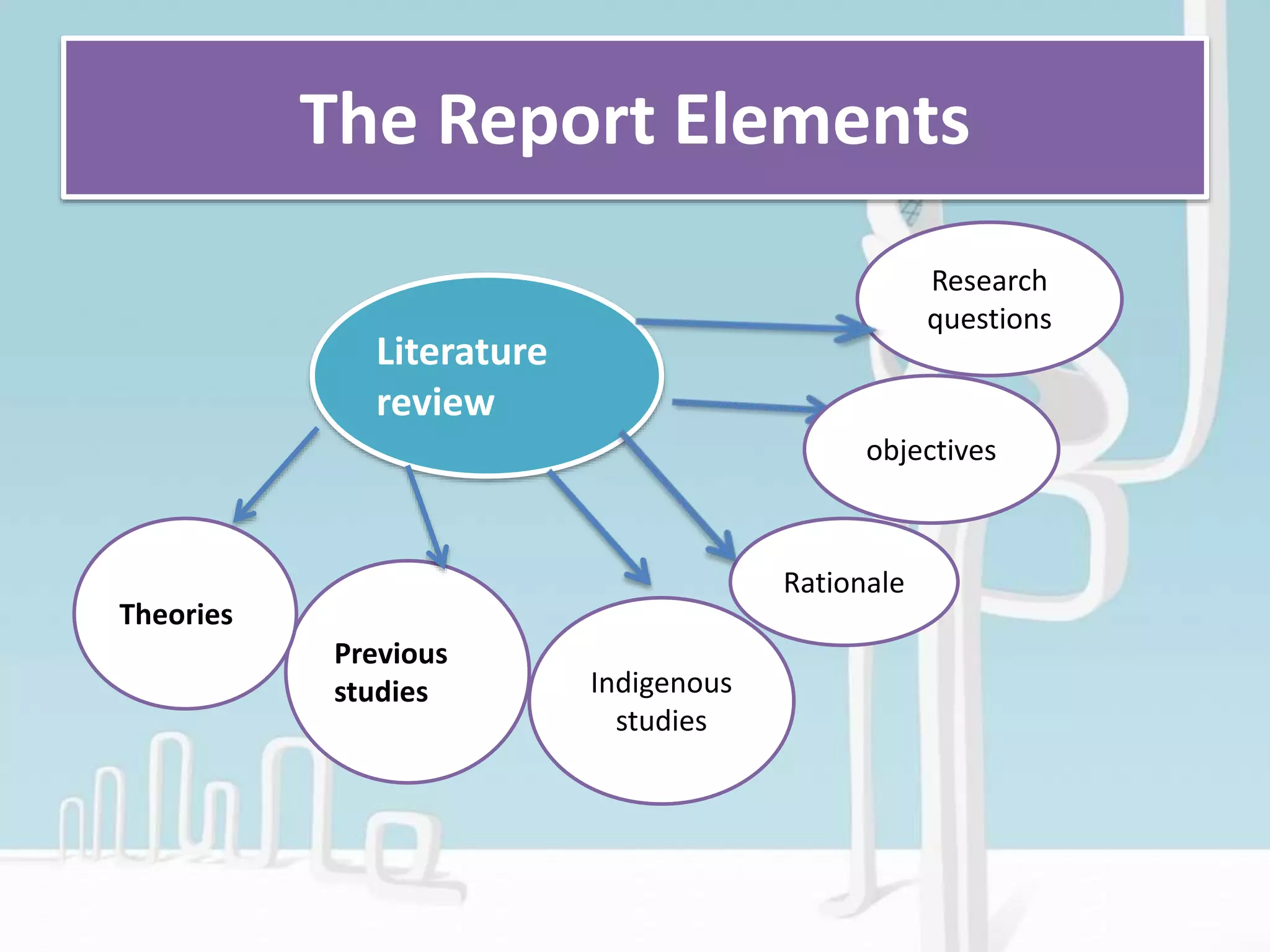
This document provides an overview of scientific report writing. It defines a scientific report as a document that describes the process, progress, and results of technical or scientific research. The document outlines the typical elements and structure of a scientific report, including the title, abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. It also discusses the purposes of scientific reports, which are to share information with other scientists, review other scientists' research, and demonstrate research progress.