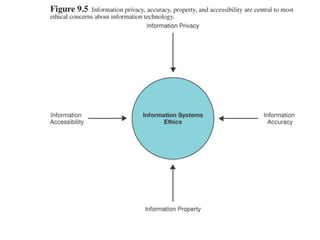
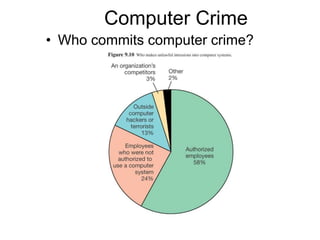
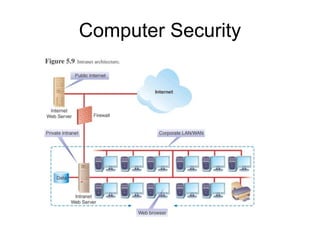
This document discusses information systems ethics, computer crime, and security. It covers topics such as privacy, accuracy and ownership of information, types of computer crimes like hacking and software piracy, computer viruses, and security measures to protect computers and data including encryption, firewalls, and antivirus software. Computer ethics aims to establish standards for appropriate use of information systems regarding issues of privacy, information sharing, and accessibility.