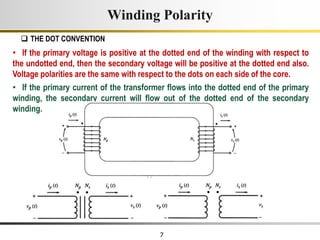
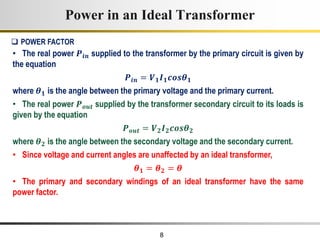
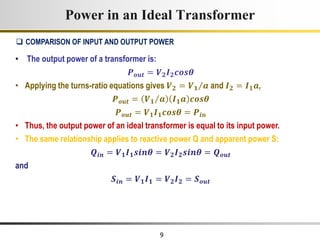
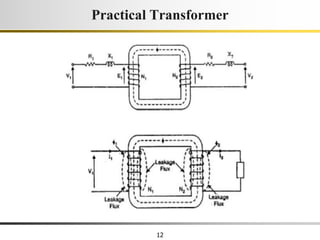
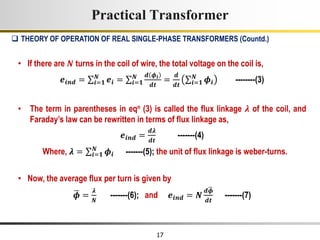
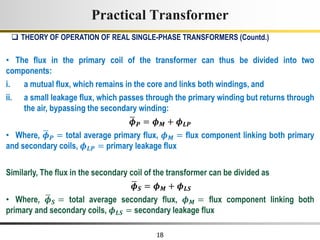
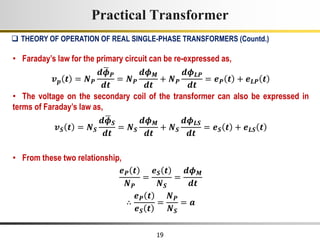
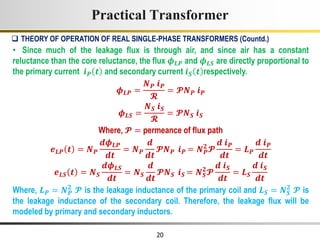
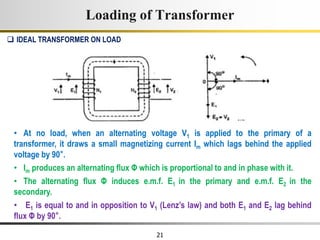
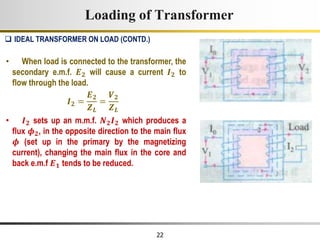
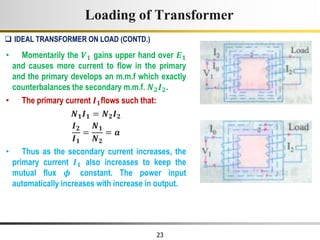
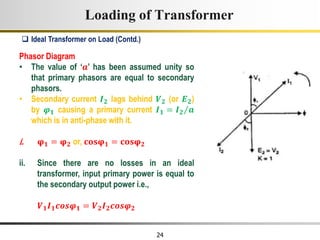
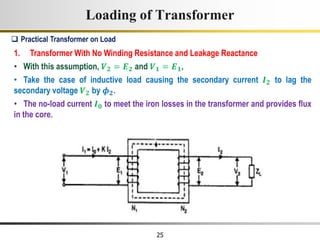
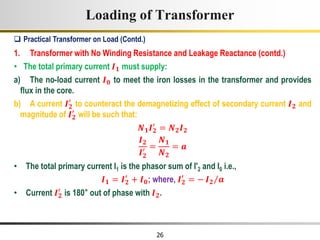
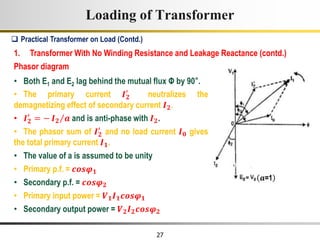
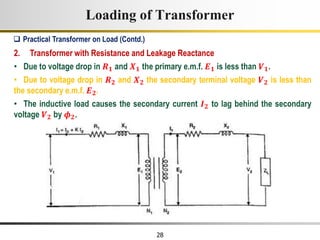
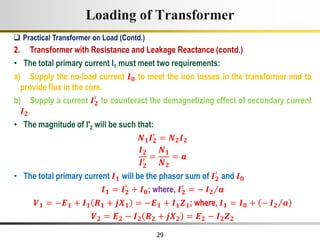
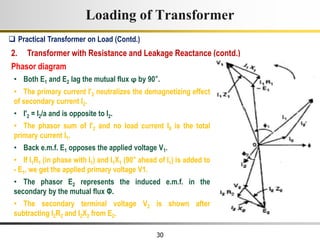
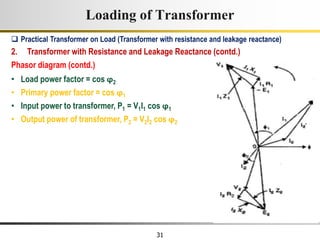
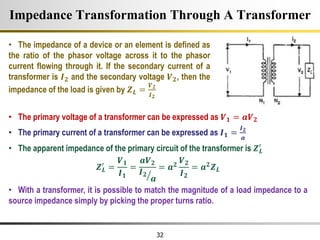
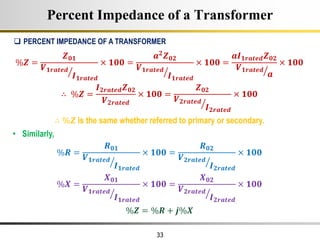
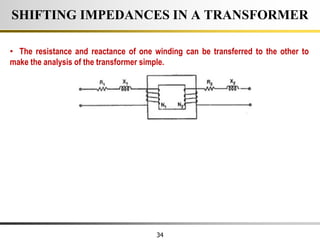
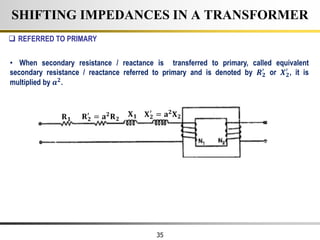
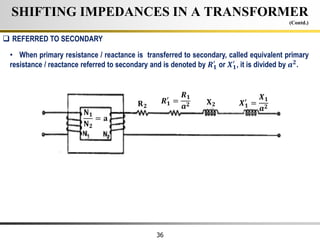
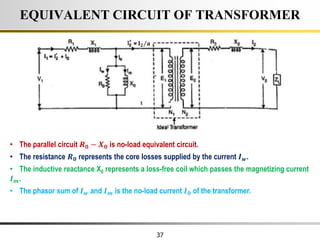
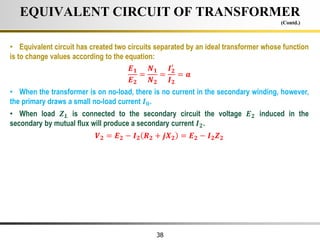
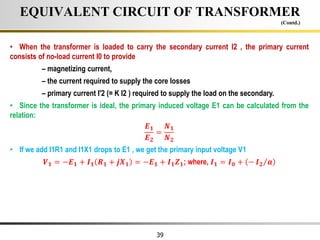
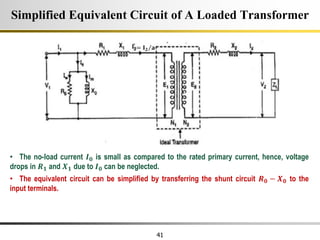
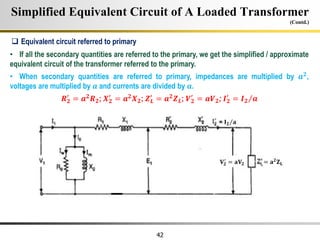
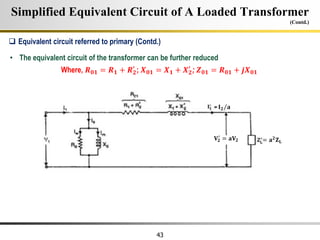
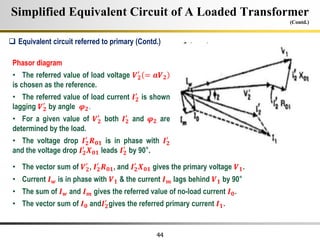
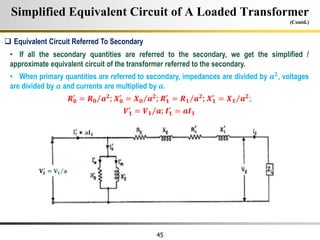
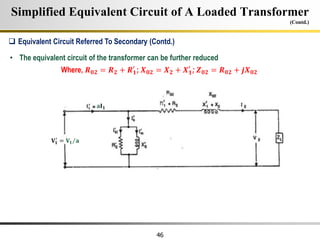
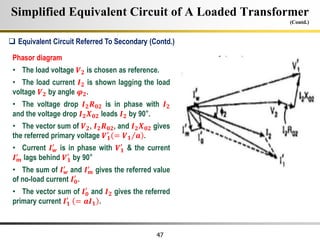
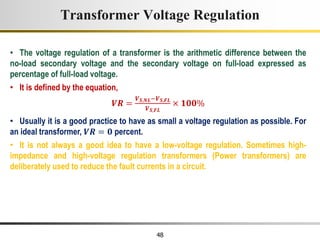
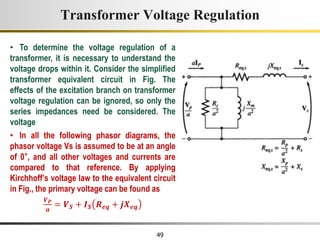
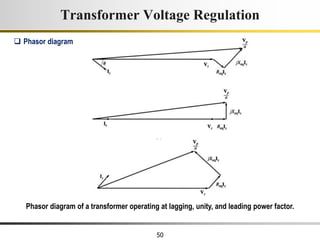
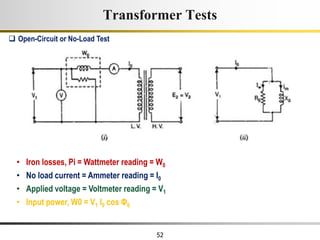
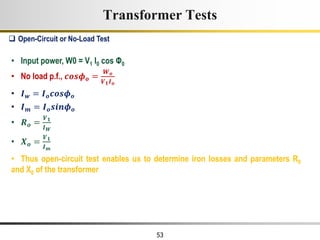
The document describes the key characteristics and equations of an ideal transformer and how they differ from a practical transformer.
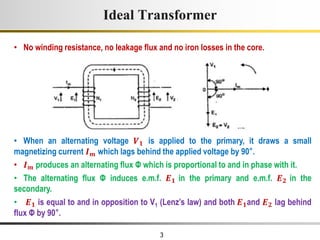
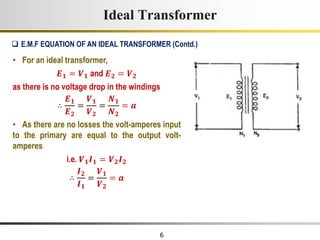
1) An ideal transformer has no winding resistance, no leakage flux, and no core losses. It transfers power efficiently between its primary and secondary windings according to turns ratio.
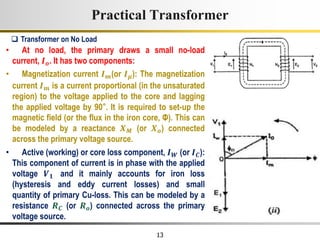
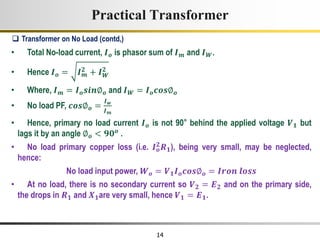
2) A practical transformer has winding resistance, leakage flux, and core losses that reduce its efficiency compared to an ideal model. It draws a small magnetizing current to produce flux and a power loss component to account for iron losses.
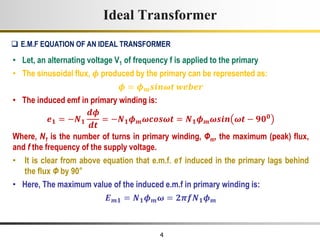
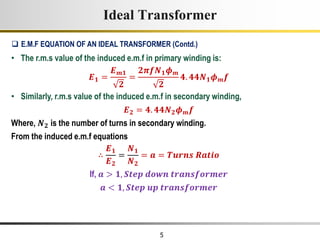
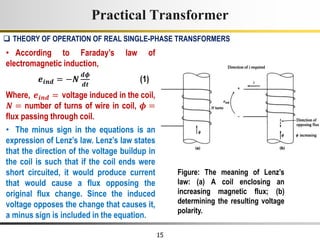
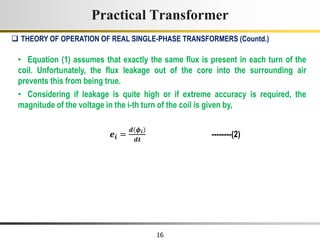
3) Faraday's law of induction and Lenz's law explain how an alternating voltage is induced in transformer windings via a changing magnetic flux. In practice, some flux leaks and does not