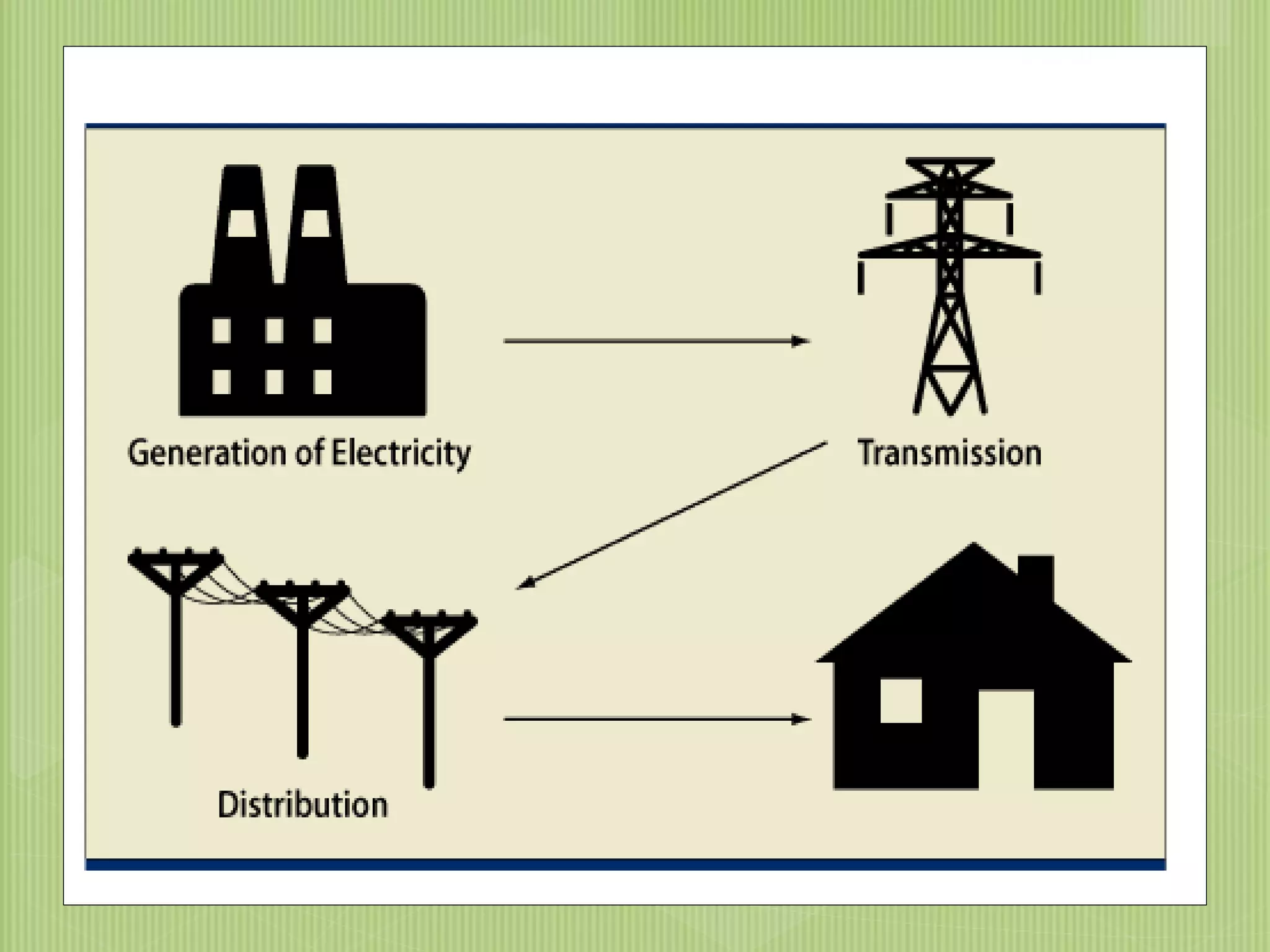
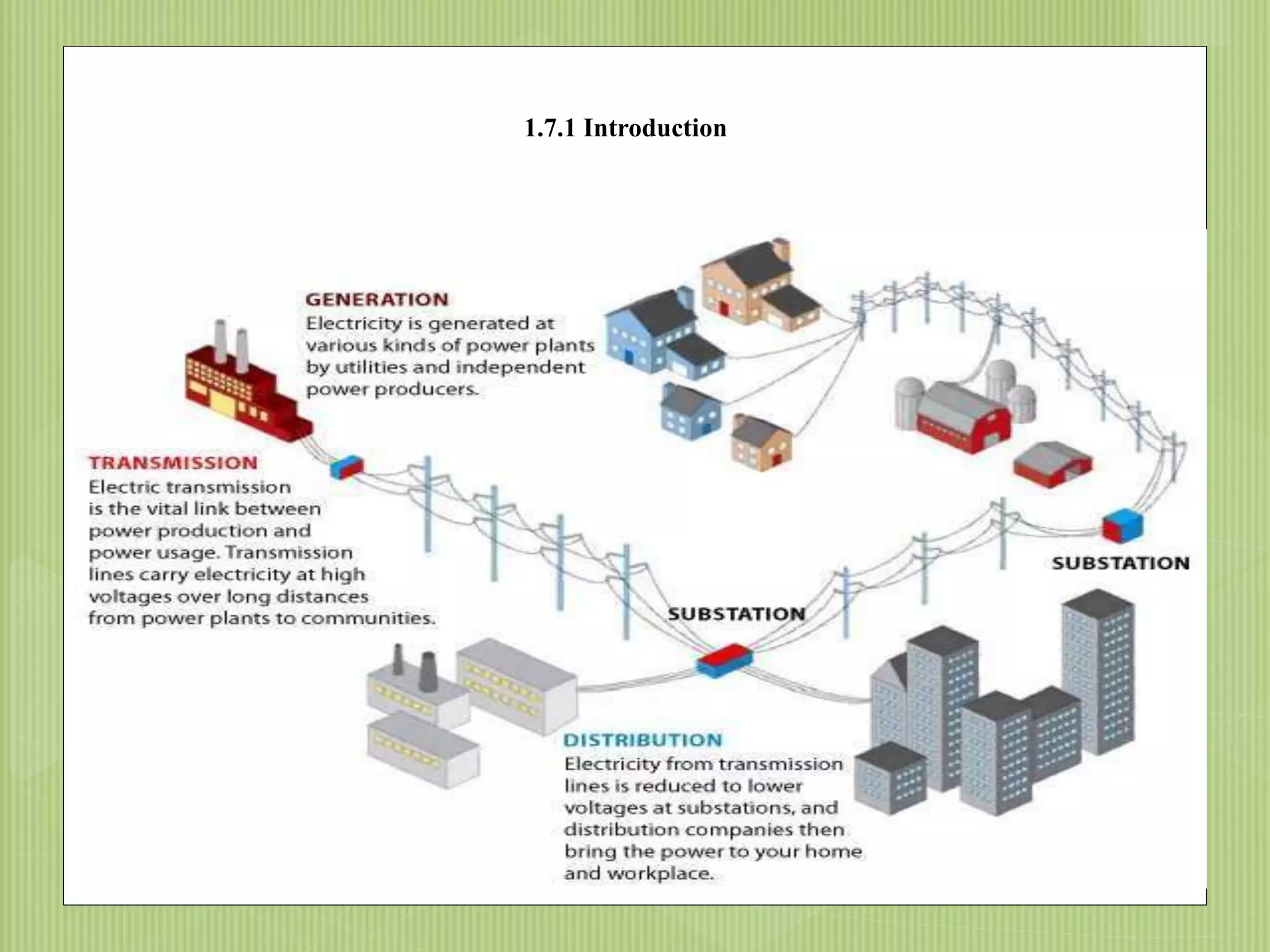
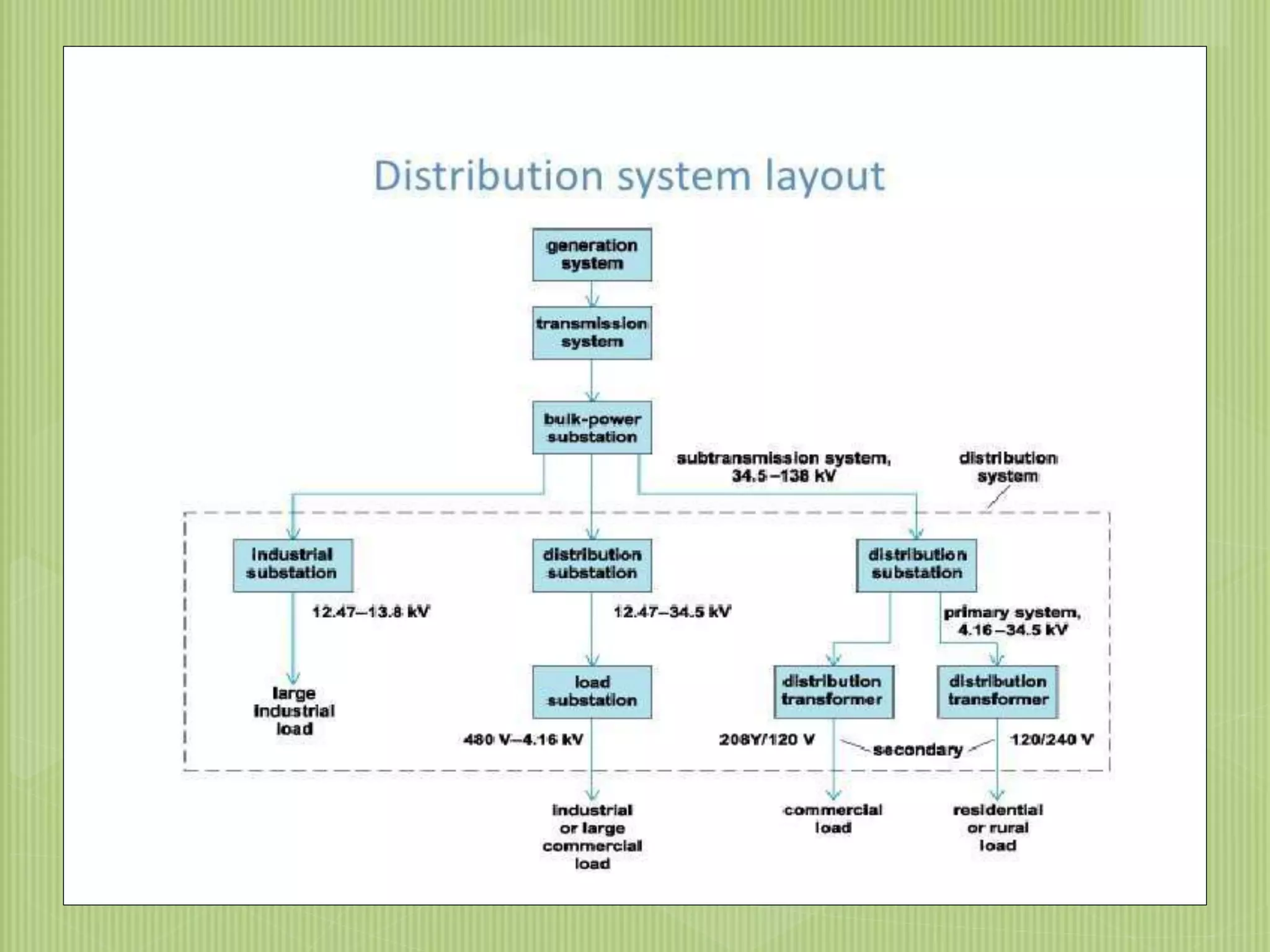
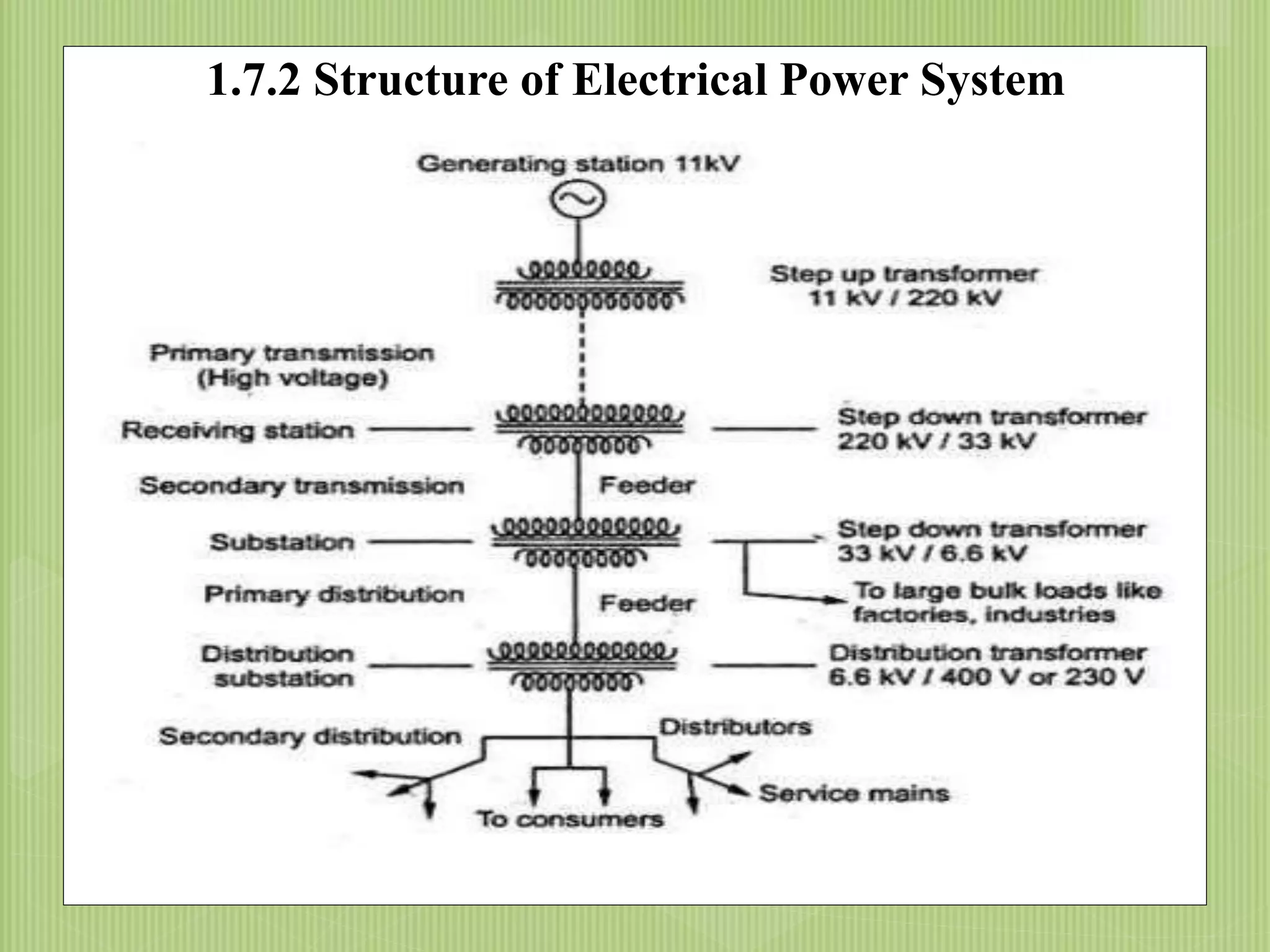
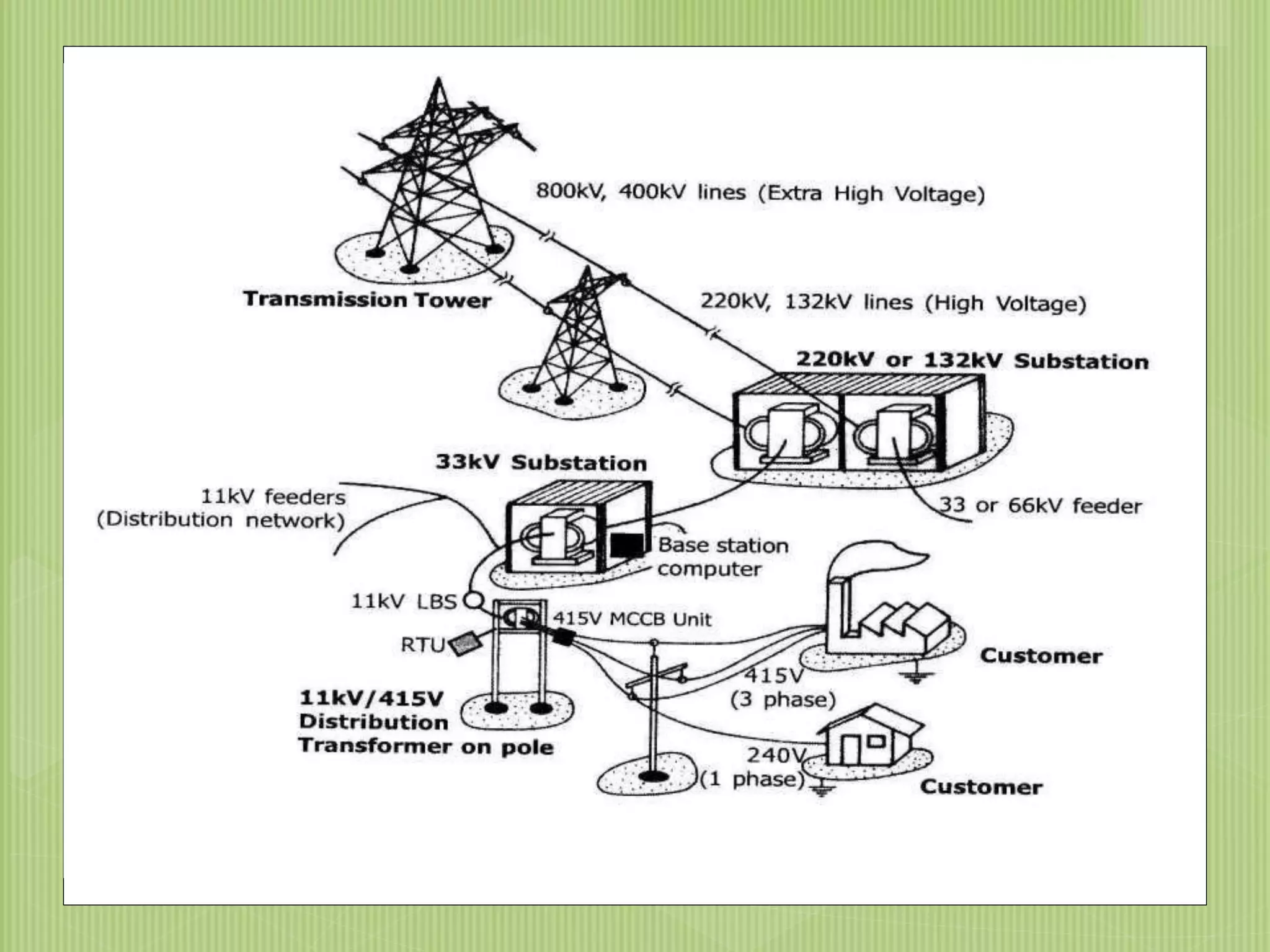
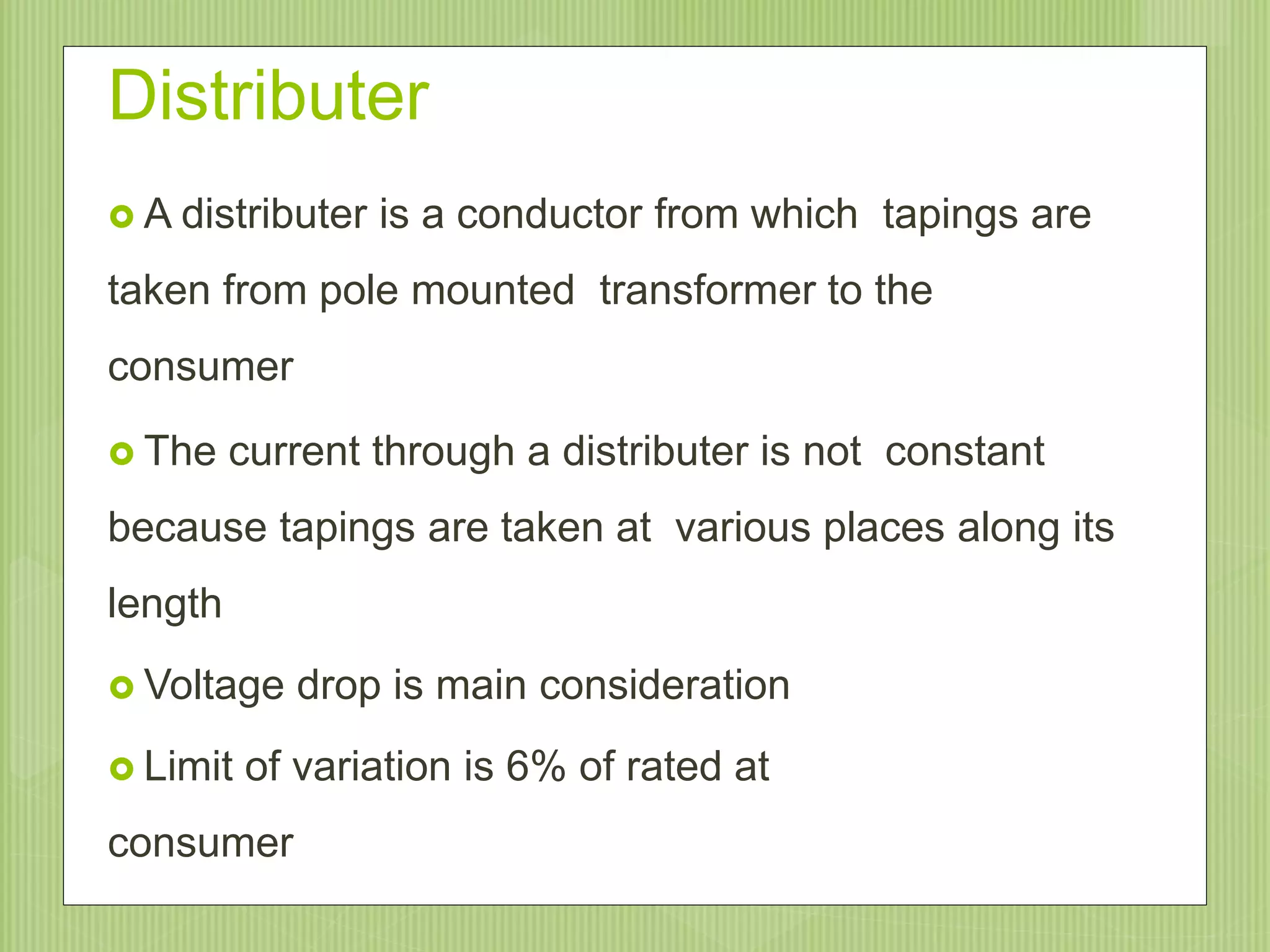
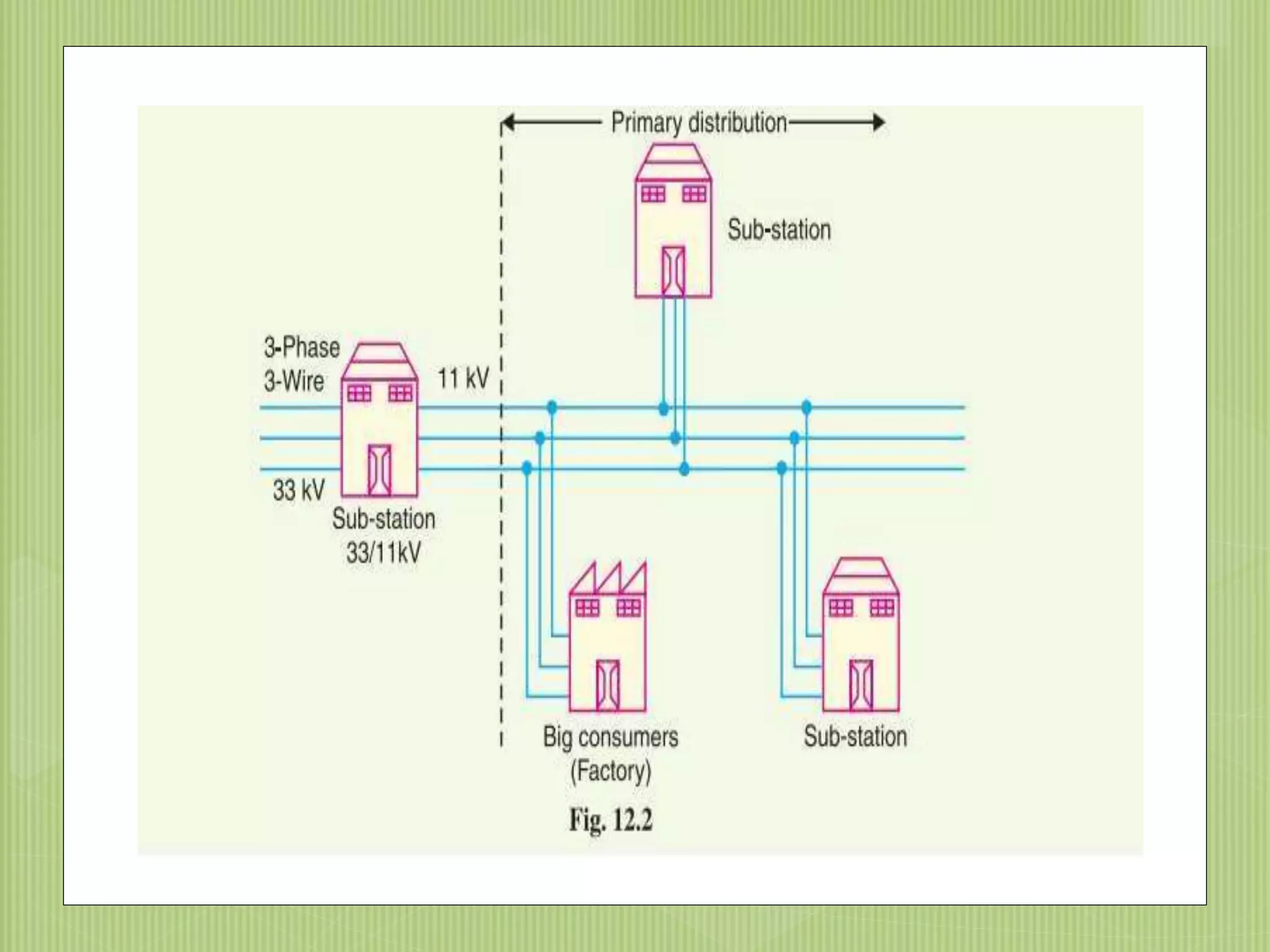
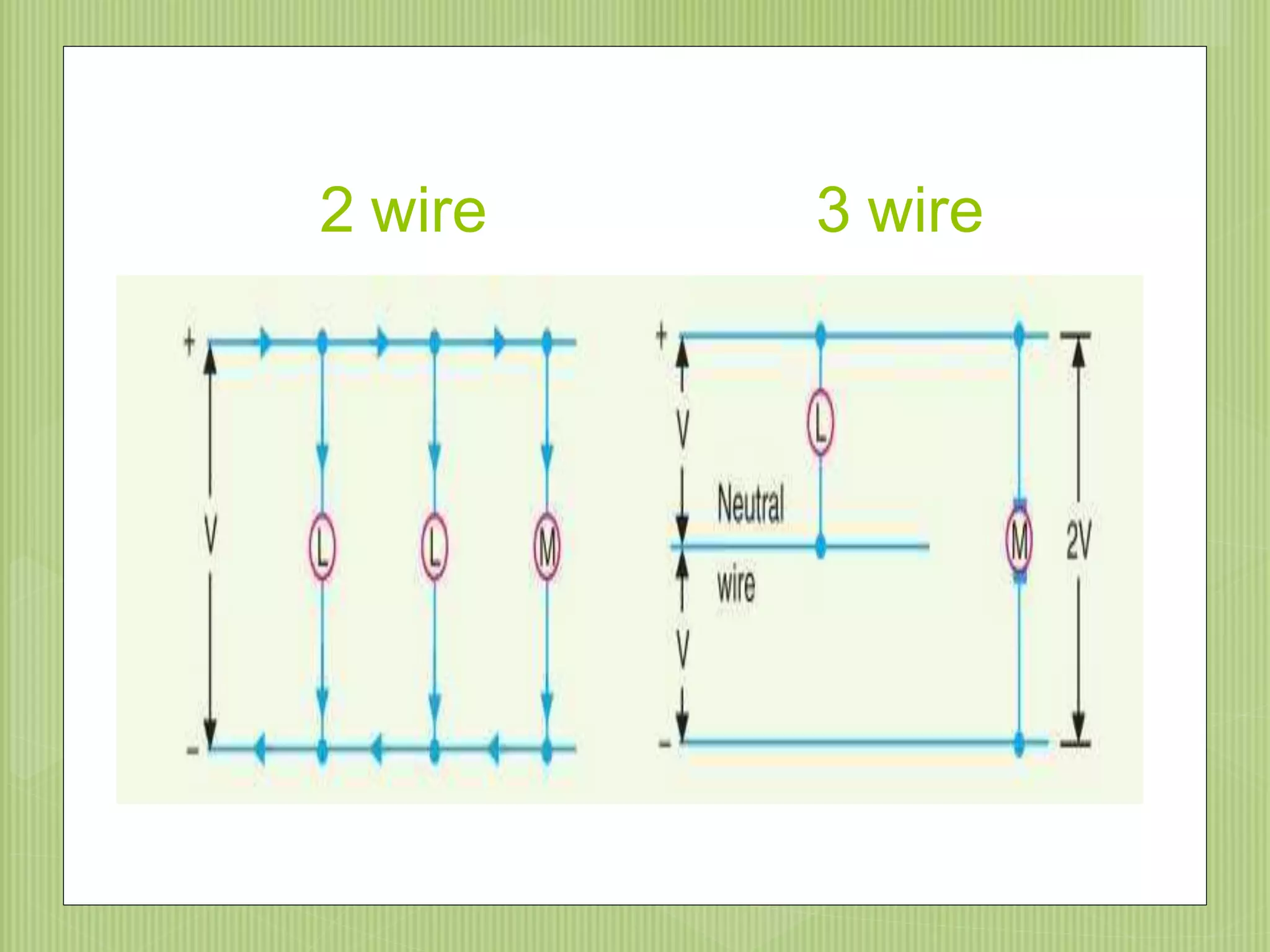
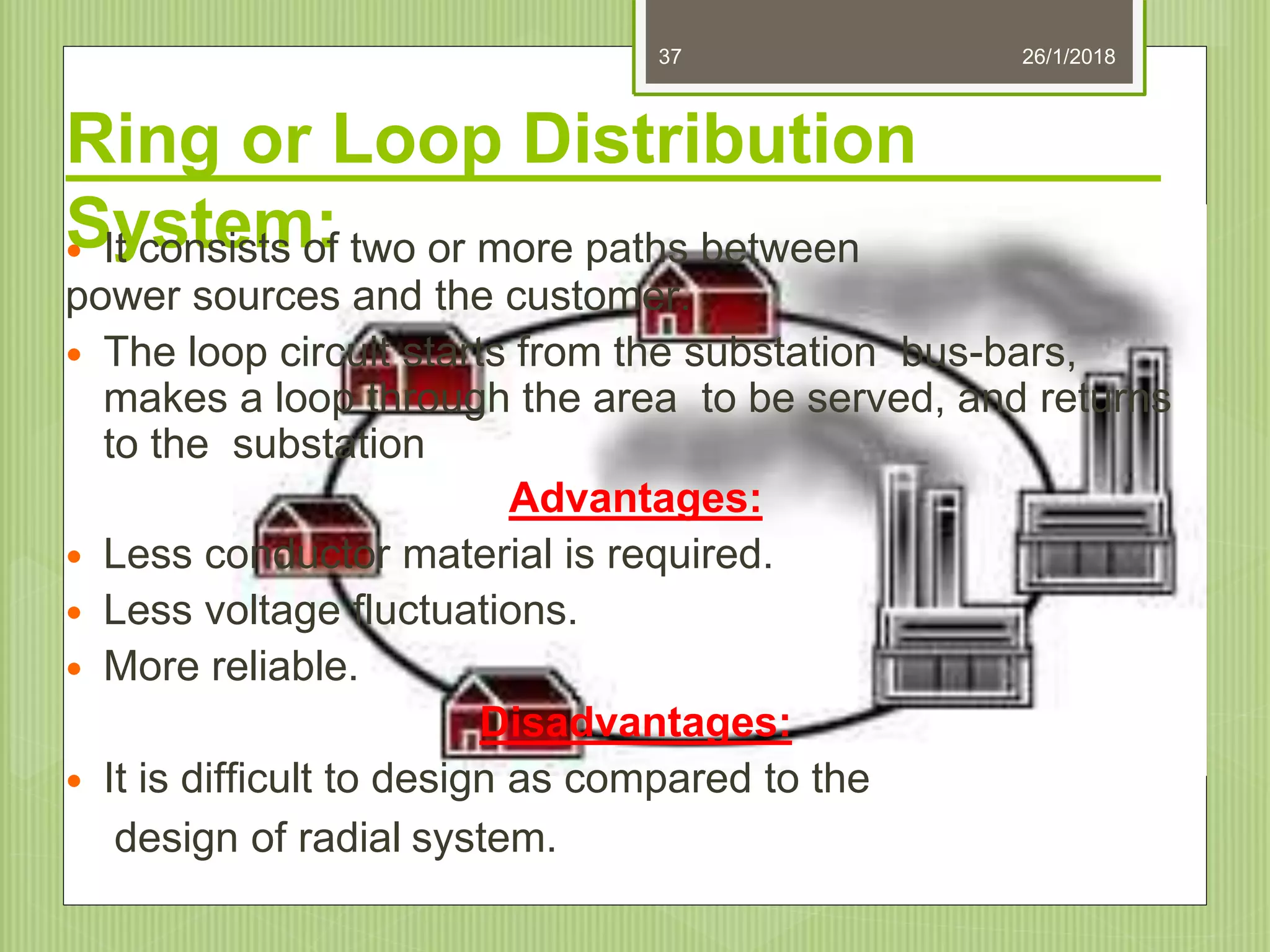
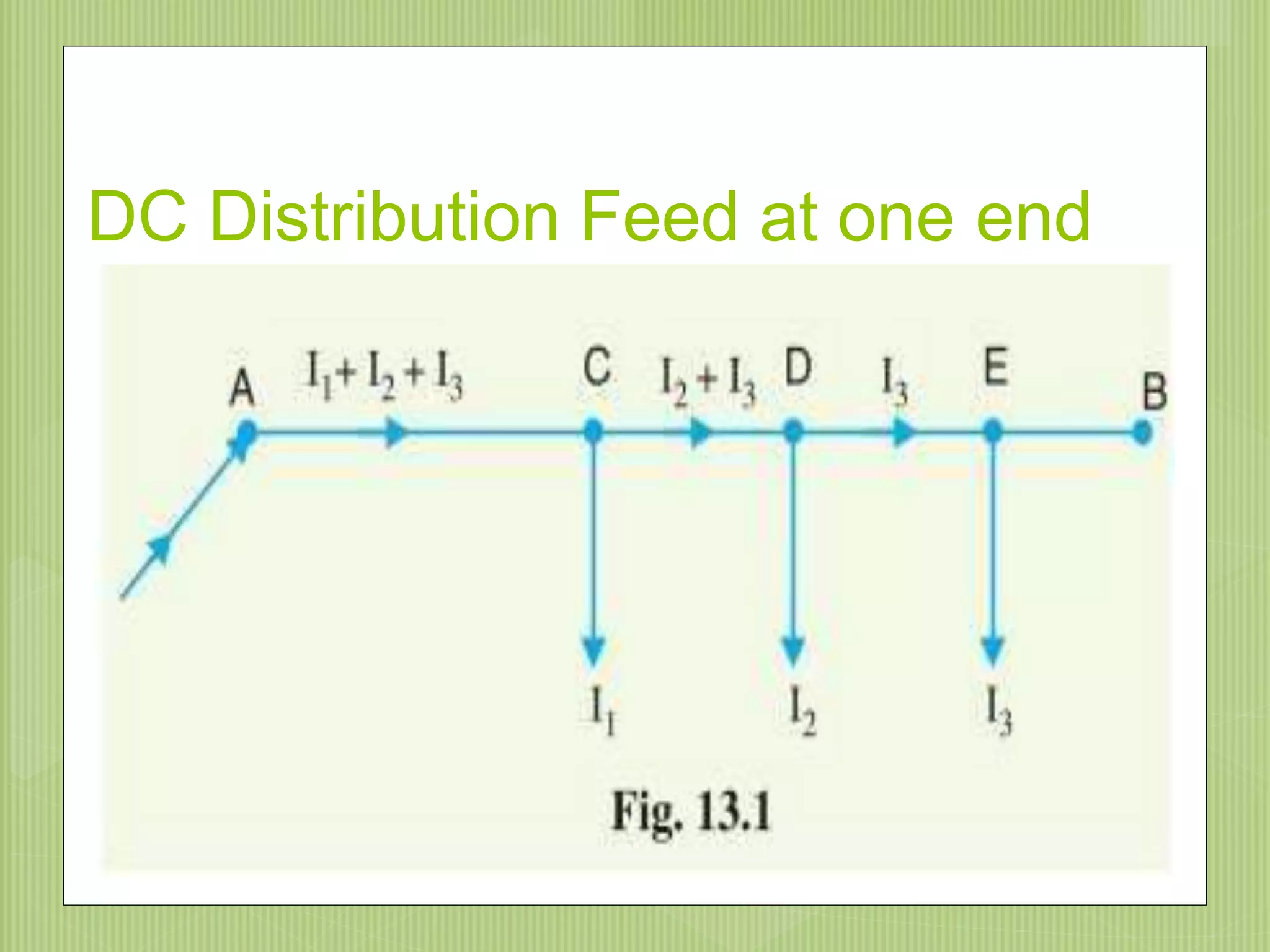
The document discusses electrical power transmission and distribution systems. It describes distribution systems as existing between substations fed by transmission systems and consumer meters. Distribution lines generally consist of feeders, distributors, and service mains. Feeders connect substations to areas where power is distributed, while distributors branch off to consumers with tapings. Service mains connect distributors to consumer meters. Distribution systems can be classified based on factors like voltage level, construction type, and connection scheme.