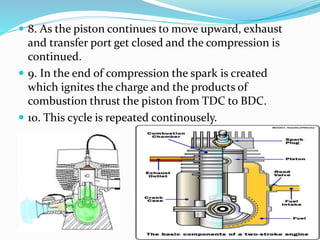
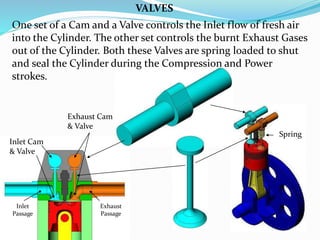
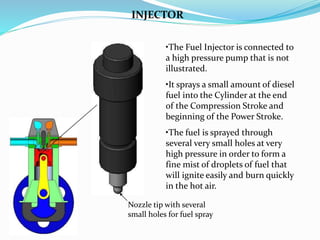
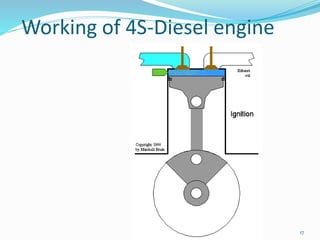
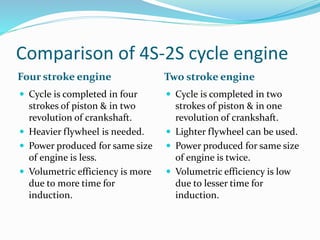
This document provides information about 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. It defines a 2-stroke engine as completing its cycle in one crankshaft revolution, while a 4-stroke engine takes two revolutions. The basic parts of each engine are described, along with their working principles. Advantages of 2-stroke engines include higher power density, while disadvantages include lower fuel efficiency. A comparison notes that 4-stroke engines have higher volumetric efficiency but lower power density than 2-stroke engines.