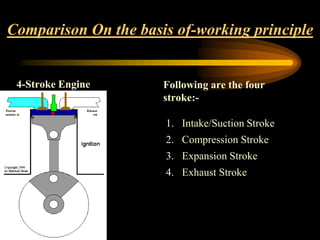
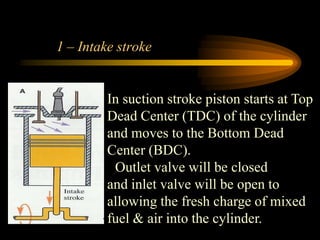
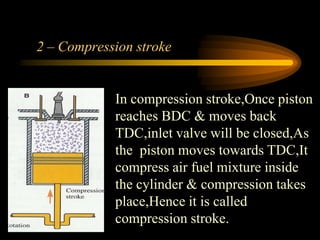
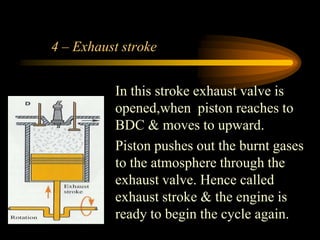
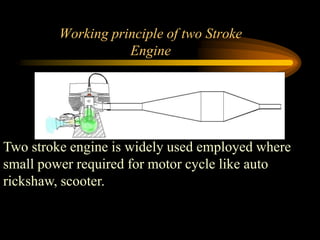
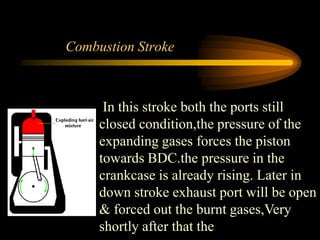
The document compares 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines across several factors. 4-stroke engines have an intake, compression, power, and exhaust stroke per cycle. They are heavier with valves but have higher efficiency. 2-stroke engines have a power stroke every revolution due to ports, making them lighter but less efficient due to incomplete exhaust scavenging causing pollution. Cooling and lubrication are more critical for 2-stroke engines due to their higher revolutions per minute. Overall, 4-stroke engines are more widely used except for small vehicles due to their better performance and lower fuel consumption.