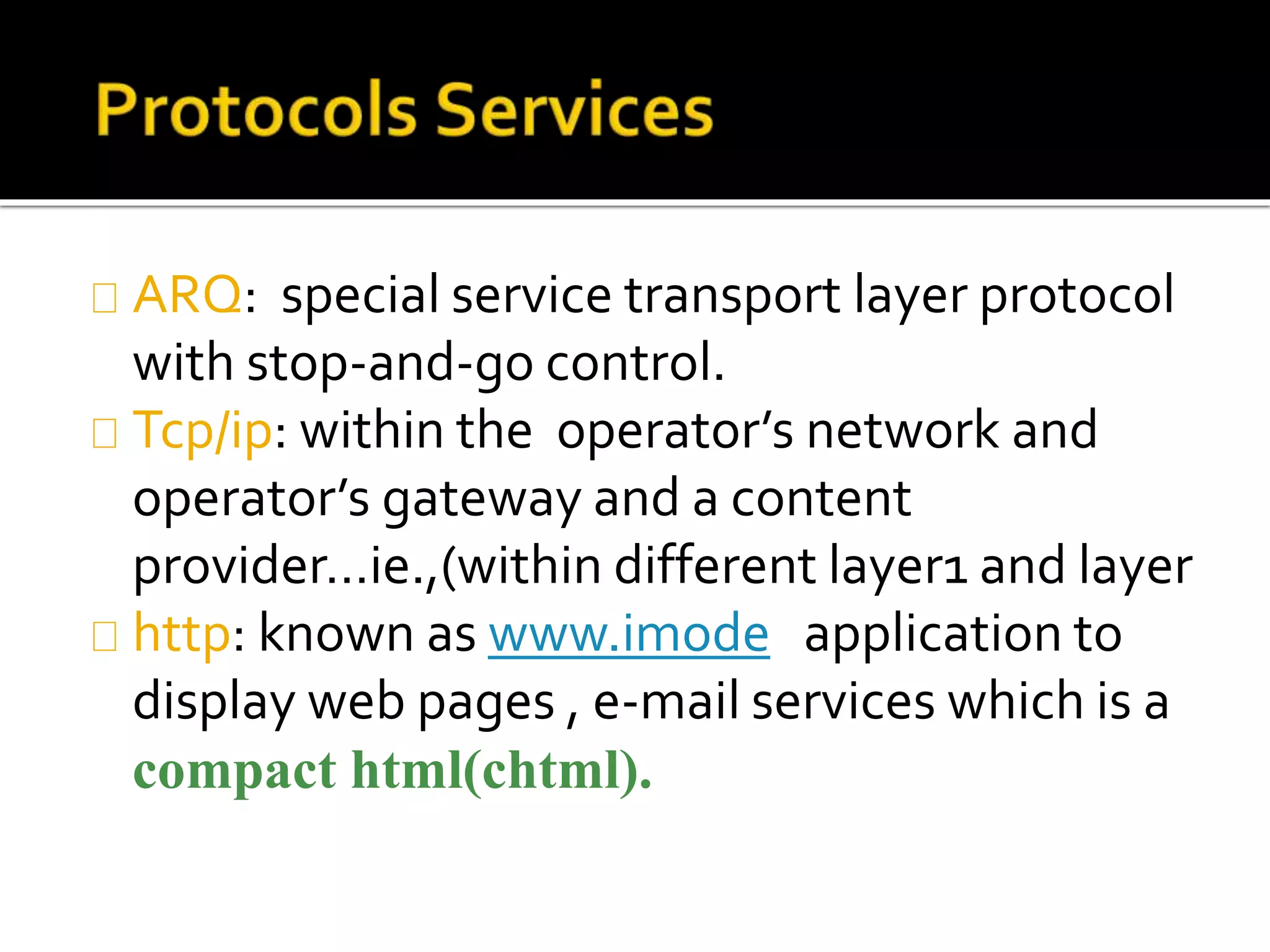
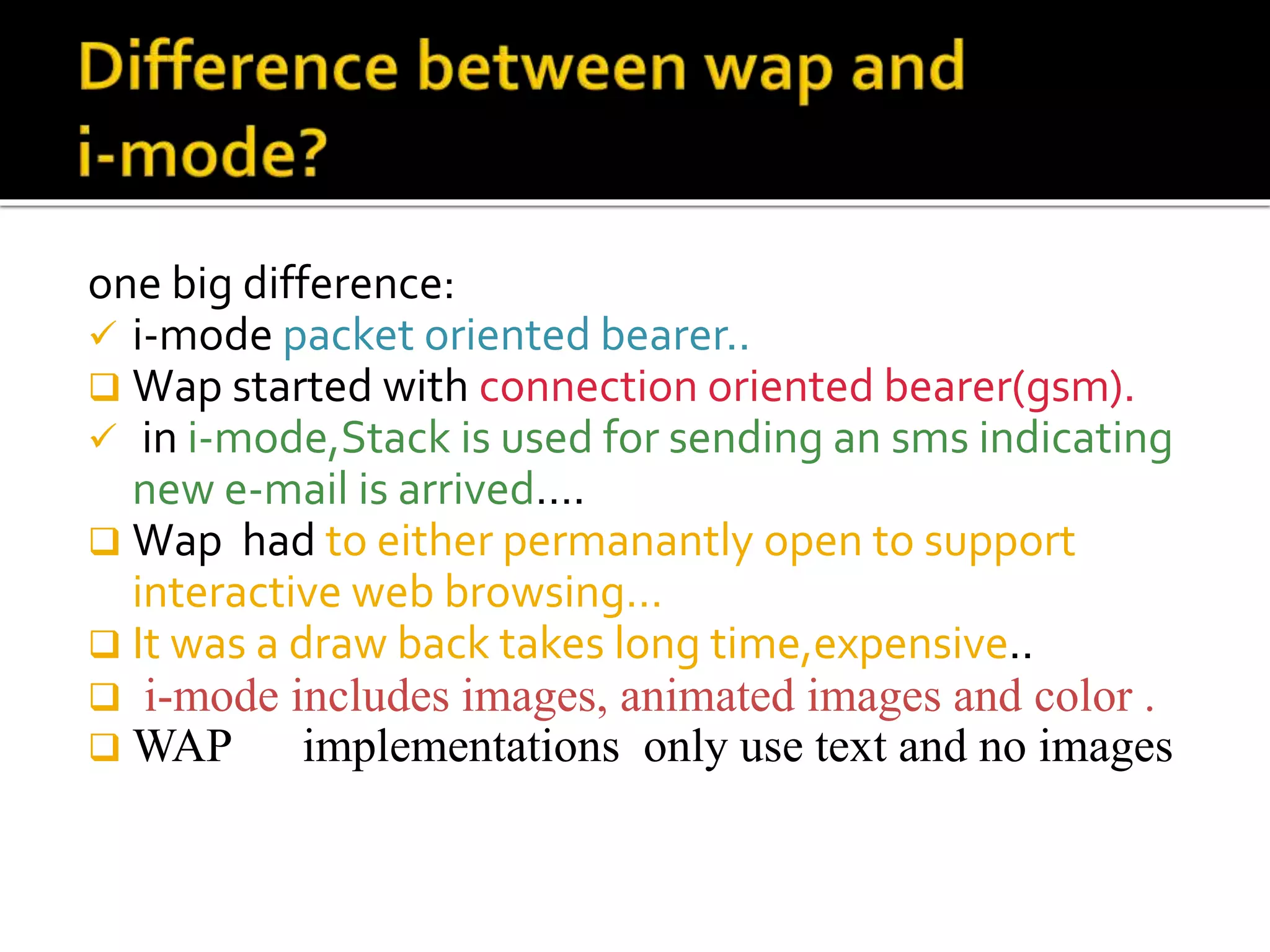
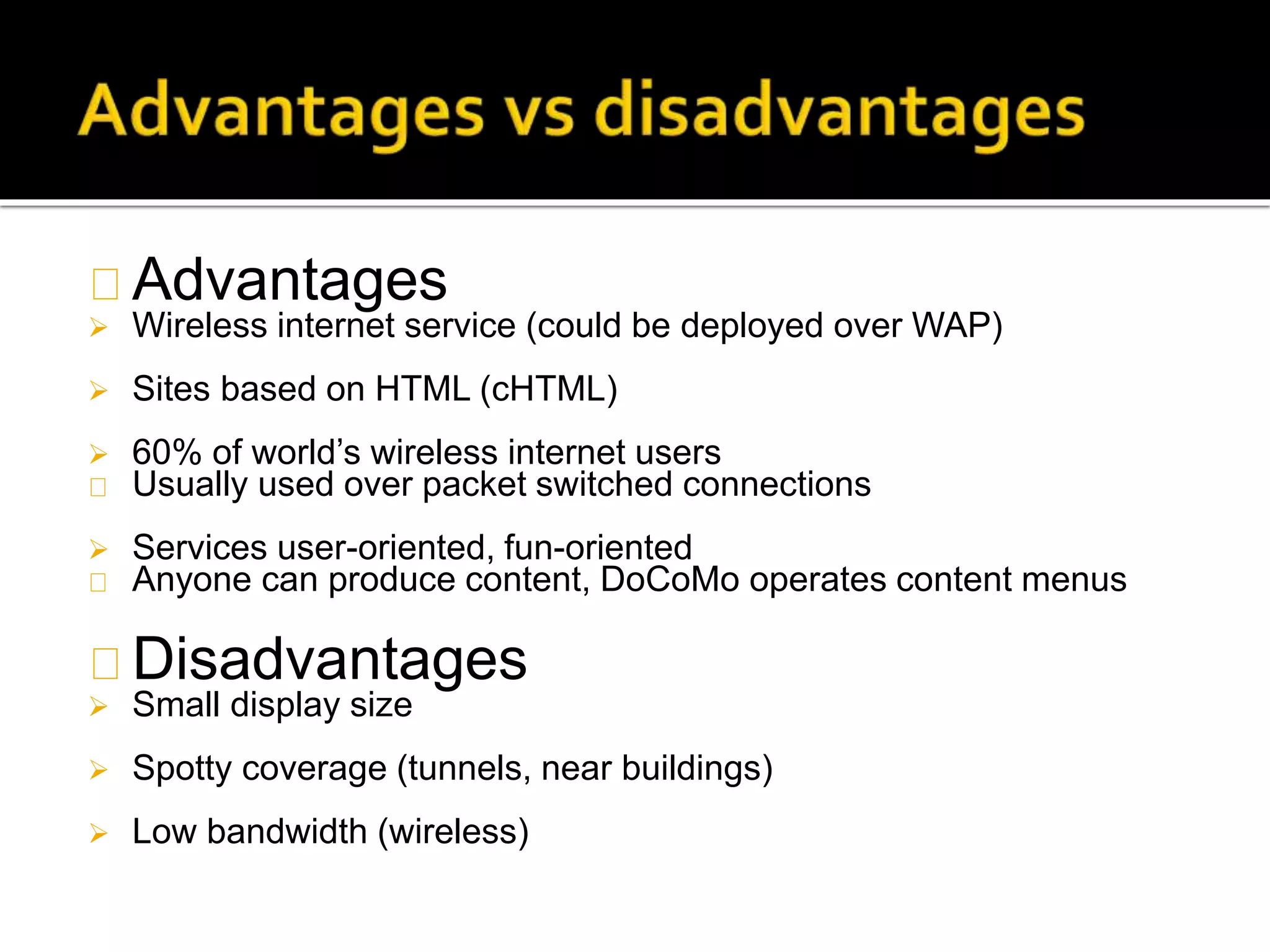
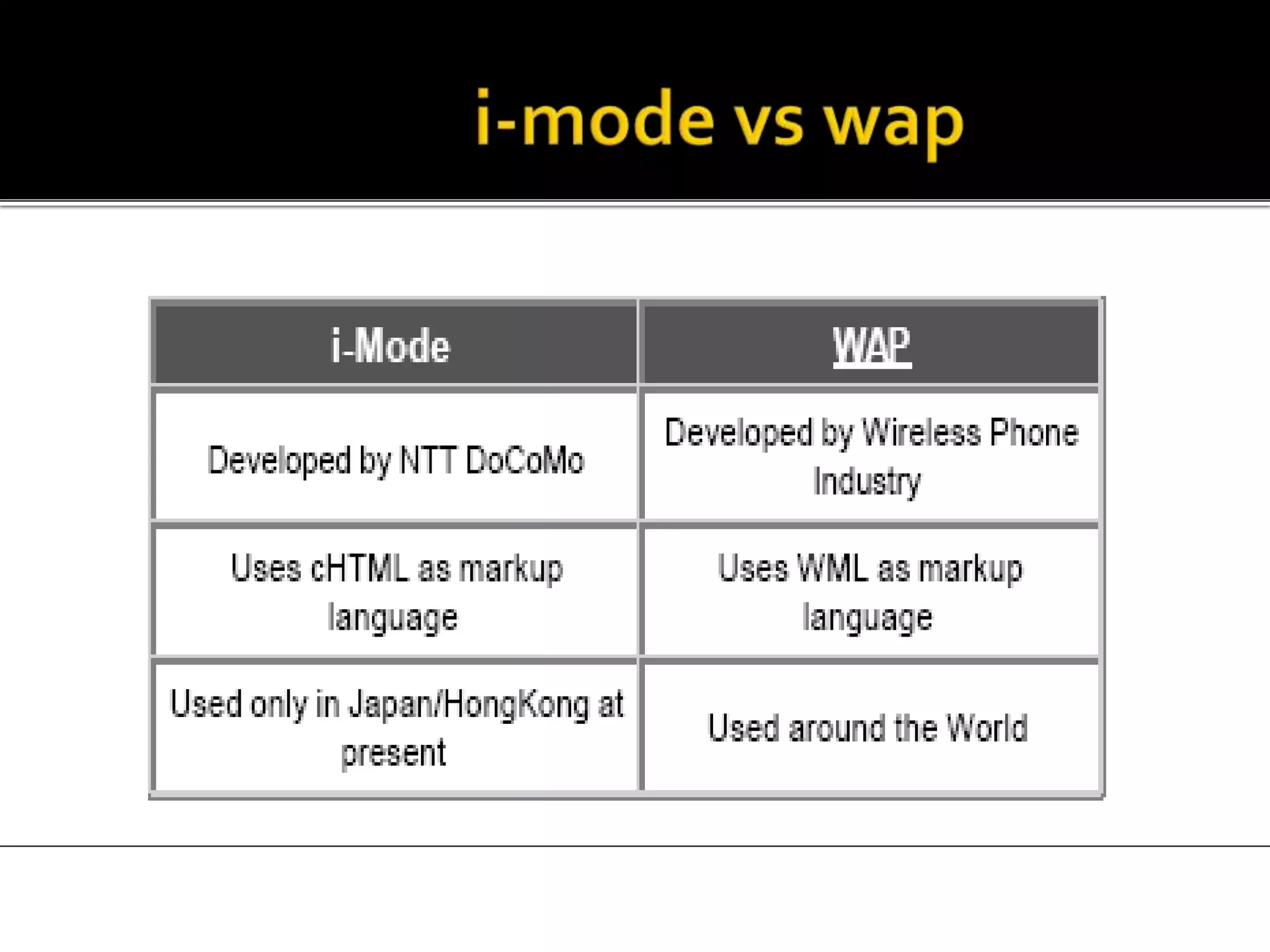
i-mode was launched in Japan in 1999 by NTT DOCOMO as a mobile internet service using HTML formats for content on phones. It was very successful with over 30 million users within 3 years, dominating other mobile networks, due to its easy-to-use features like color screens, images and email. Key aspects included packet-based transmission, Java applets, location-based services and content produced specifically for small screens. While WAP failed due to complex connections, i-mode thrived by optimizing the mobile internet experience.