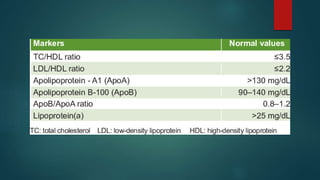
Hyperlipidemia is characterized by elevated levels of lipids in the blood, which can be primary (genetic) or secondary (due to other conditions). Common causes include poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity, while risk factors can lead to serious cardiovascular issues. Treatment options include medications such as statins and lifestyle changes aimed at improving heart health.