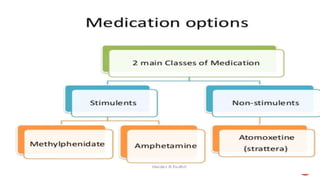
This document discusses attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It defines ADHD as a persistent pattern of inattention and hyperactivity that is more frequent in children than their peers. There are three main types of ADHD: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive, and combined. The causes include changes in brain structure, genetics, biochemical factors like deficits in dopamine and norepinephrine, prenatal exposure to drugs or chemicals, and gender with boys being more commonly affected than girls. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment including medications and behavioral therapy, and nursing interventions are outlined.