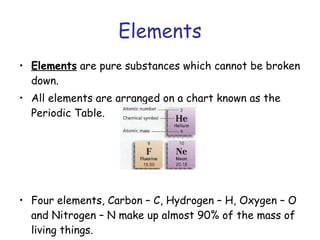
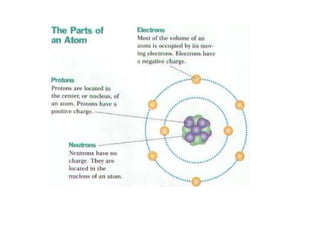
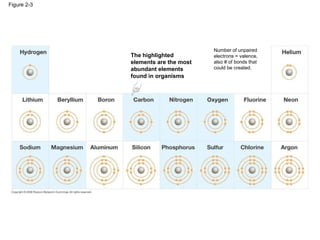
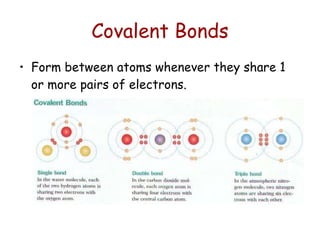
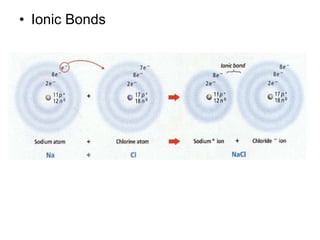
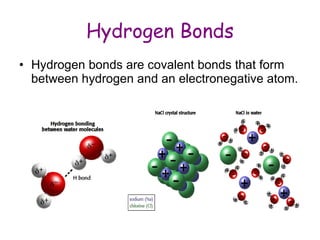
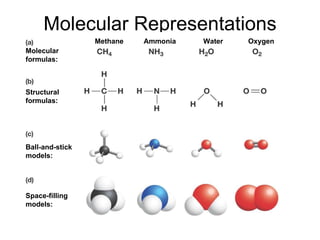
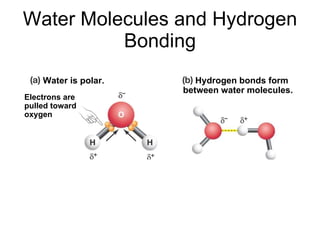
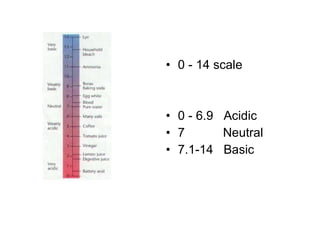
The document summarizes key concepts in chemistry including the composition of matter, elements and atoms, electrons and electron configuration, compounds, chemical bonds, properties of water, solutions, and acids and bases. Matter is composed of elements which are made of atoms. Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Elements combine through chemical bonds to form compounds with unique properties. Water is an important solvent that forms hydrogen bonds and has unique physical properties. Solutions are uniform mixtures where one substance dissolves in another. The pH scale is used to measure acids and bases according to their hydrogen and hydroxide ion concentrations.