Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times
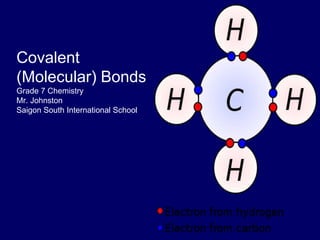




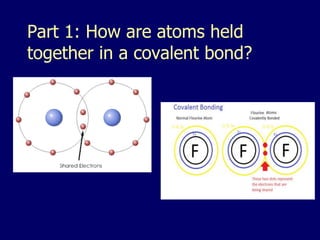
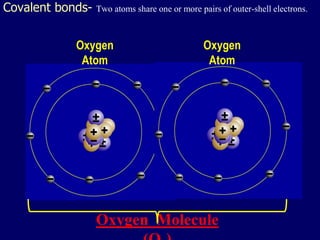
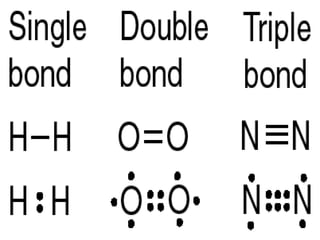






The document discusses covalent bonds, which are formed by the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms. It outlines the properties of molecular compounds, such as their inability to conduct electricity and generally lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds. It also explains the difference between nonpolar and polar covalent bonds based on the equality of electron sharing.














