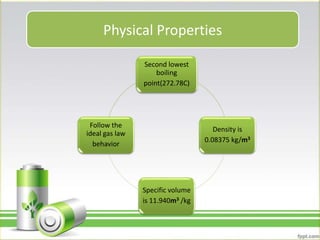
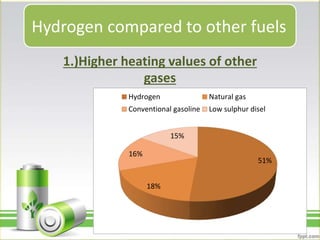
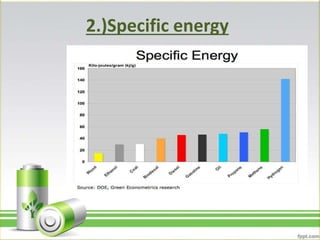
Hydrogen has several uses as an energy source. It can be used in hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, powering vehicles. It is also used as rocket fuel due to being lightweight and burning intensely. Additionally, hydrogen and deuterium are used in lamps to produce UV radiation. Hydrogen has a higher specific energy than fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, but infrastructure needs to be developed further for widespread use.