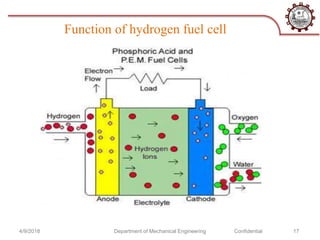
This document discusses hydrogen as an alternative fuel. It outlines several methods for producing hydrogen including natural gas reforming, electrolysis, gasification, and fermentation. It also describes how hydrogen fuel cells work and their advantages as being more efficient than internal combustion engines. However, challenges with hydrogen storage and the costs of extraction are discussed as disadvantages. The document concludes that while hydrogen is a promising alternative fuel, further research is still needed to make its implementation more sustainable and reliable.















![References
[1] "Hydrogen Basics." Alternative Fuels Data Center.
Alternative Fuels Data Center Website, 24 Oct. 2013.
Web. 28 May 2015.
[2] Program, Fuel Cell Technologies. Hydrogen and Fuel
Cell Technologies Program: Fuel Cells Fact Sheet (n.d.).
Website: www.eere.energy.gov/informationcenter. U.S.
Department of Energy, Nov. 2010. Web. 28 May 2015. 28
May 2015.
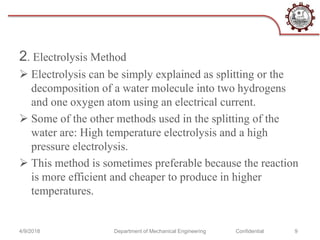
[3] Jim, 0 'Brien, "High Temperature Electrolysis for
Efficient Hydrogen Production from Nuclear Energy".
Electrolytic Hydrogen Production Workshop. Feb 27,
2014.
4/9/2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Confidential 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrogenasanalternativefuel-180409093947/85/Hydrogen-as-an-alternative-fuel-22-320.jpg)
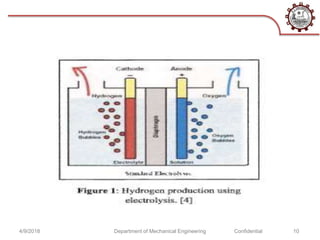
![ Website:http://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2014/08/fl
8/fcto _ 2014 _electrolytic_ h2 _wk shp_obrienl.pdf [4]
"Understanding Electrolysis". Website:
http://www.viewzone.com/verichipx.html, Web. 28 May
2015. ·
[5] Yongzhen Yao, et.al, '1Iigh hydrogen yield from a
two-step process of dark-and photo-fermentation of
sucrose". Vol. 32, pp. 200-206, 2007. 28 May 2015.
Website:
http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=l8477081.
4/9/2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Confidential 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrogenasanalternativefuel-180409093947/85/Hydrogen-as-an-alternative-fuel-23-320.jpg)
![ [6] Nancy Garland, et al. "Materials Issues in Polymer
Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells" Vol. 3. Issue. 4, pp. 85.
2008. 28 May 2015. Website: http
://www.sigmaaldrich.com/technical-
documents/articles/materialmatters/materials-issues-
in.html
4/9/2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Confidential 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrogenasanalternativefuel-180409093947/85/Hydrogen-as-an-alternative-fuel-24-320.jpg)
