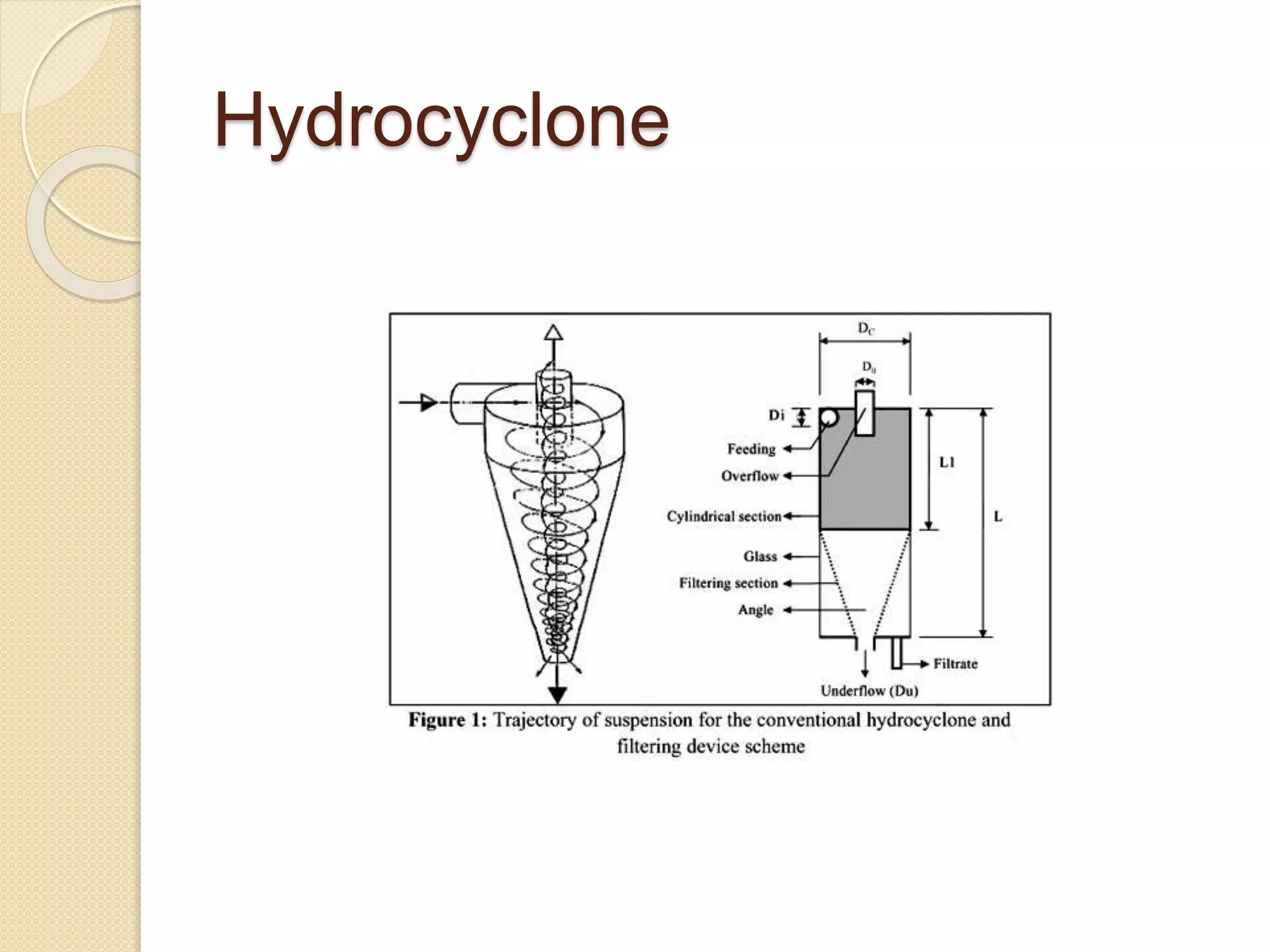
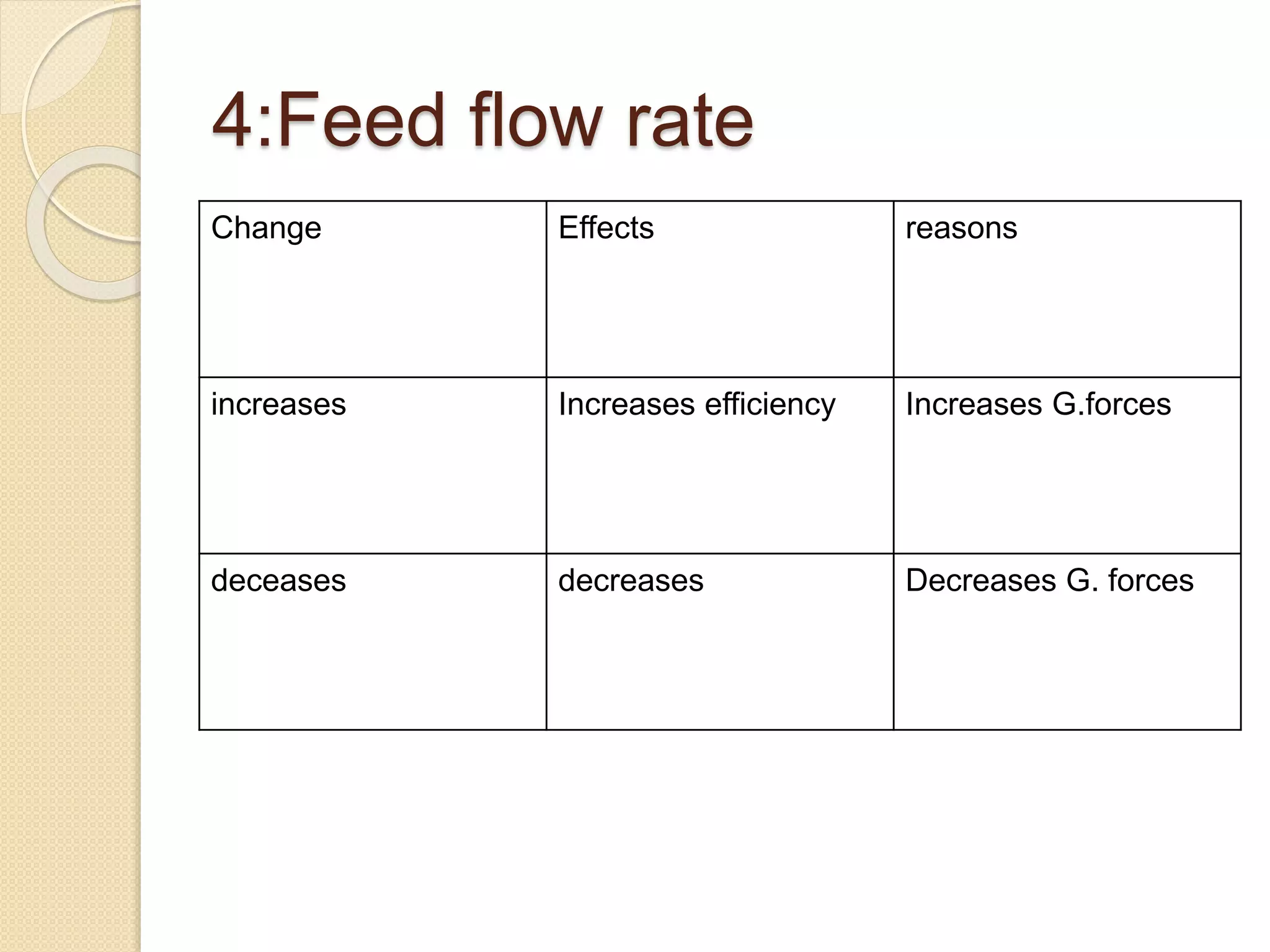
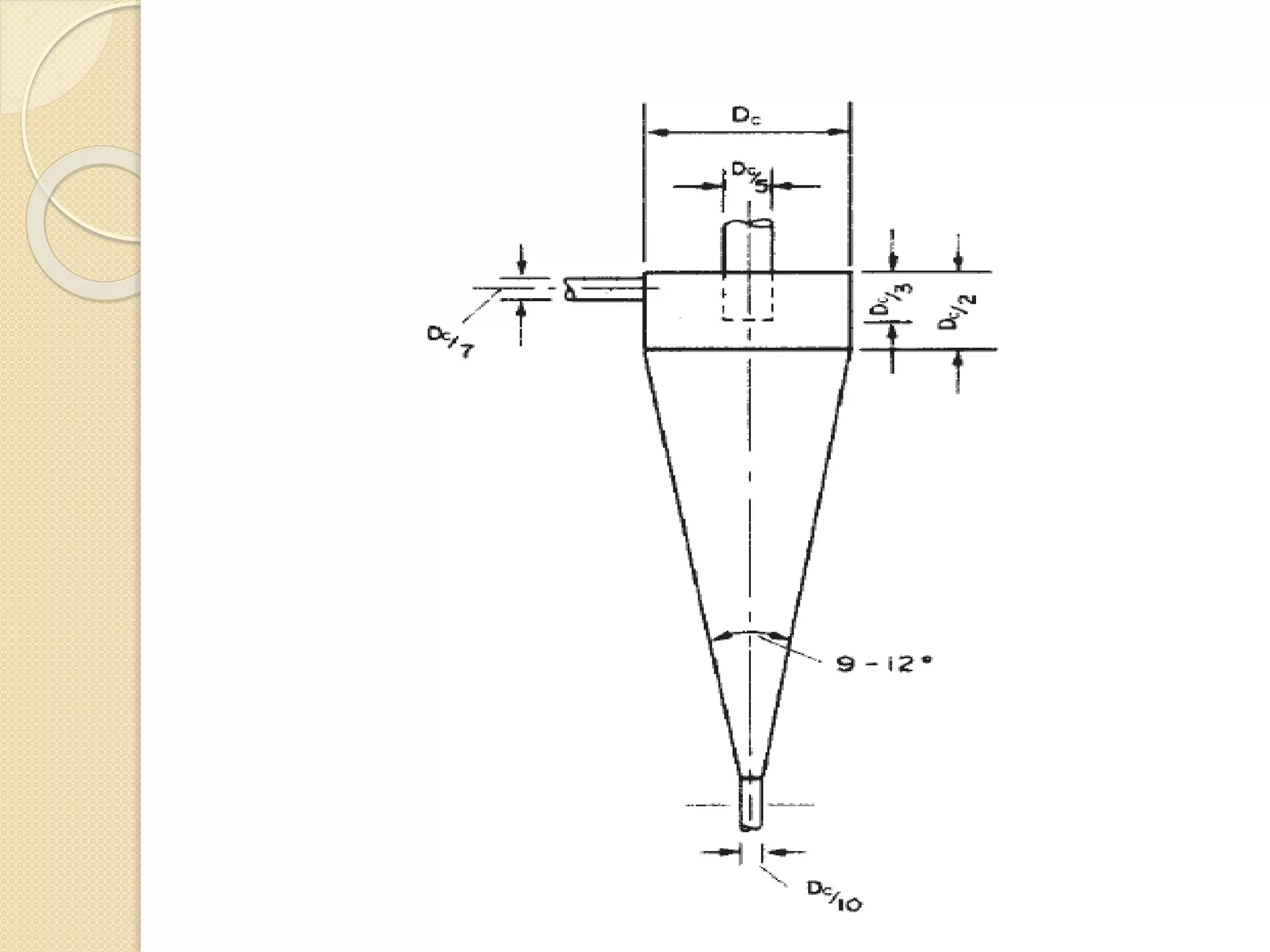
The hydrocyclone is a crucial device in the separation industry, utilizing centrifugal forces to effectively separate heavy components from lighter ones without any moving parts. It is commonly used for solid-liquid separation in various industries, including alumina, pulp and paper, and wastewater treatment. Factors such as vortex finder diameter, pressure drop, and particle size significantly influence the performance of hydrocyclones.