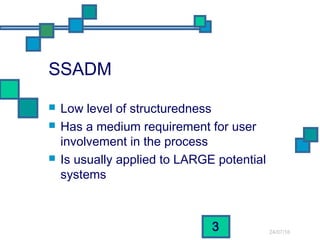
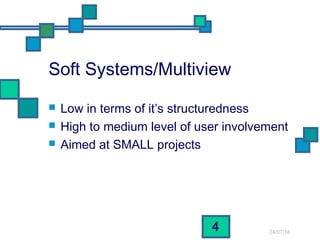
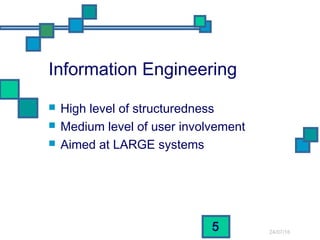
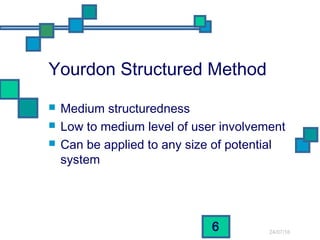
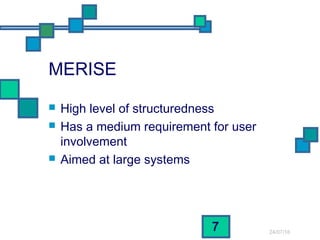
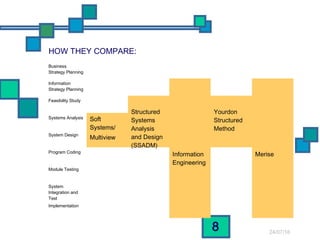
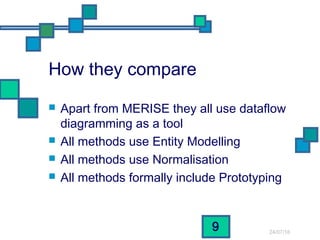
The document discusses and compares several systems analysis methodologies: SSADM, Soft Systems/Multiview, Information Engineering, Yourdon Structured Method, MERISE, RAD, and UML. It provides information on the level of structuredness, required user involvement, and typical project size for each methodology. RAD relies on prototypes and iterative refinement. UML can be used with different methodologies to model the results of analysis and design through structural diagrams.