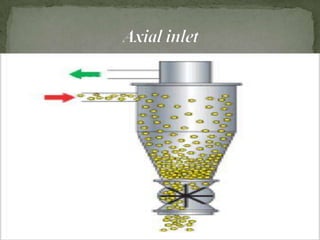
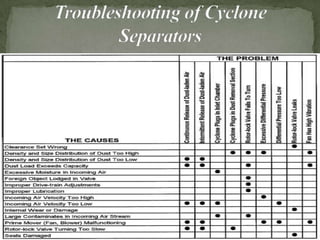
A cyclone separator uses centrifugal force to separate particles from gas streams. It has a tangential inlet that spins the gas into a vortex. Larger, heavier particles are thrown outward against the wall and collected while smaller particles pass through. Key parameters that affect its performance include gas velocity, particle properties, and diameter-to-length ratio. It has advantages such as being dry, low cost, and requiring little maintenance. However, it is less efficient for small particles and has higher pressure drops than some other separators. Cyclone separators are commonly used in industries like mining, manufacturing, and energy production. Regular inspection and maintenance helps optimize its operation.