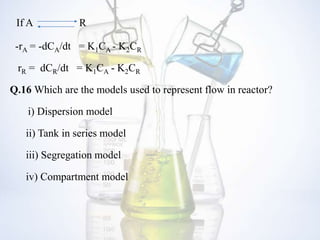
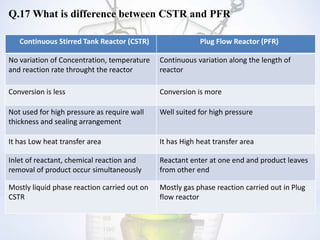
This document contains a FAQ on chemical reaction engineering. It provides answers to 19 questions covering topics such as the rate of reaction, types of reactors, orders of reaction, catalysts, feasibility of reactions based on Gibbs free energy, and models used to represent flow in reactors. Key differences between CSTR and PFR reactors are also summarized.