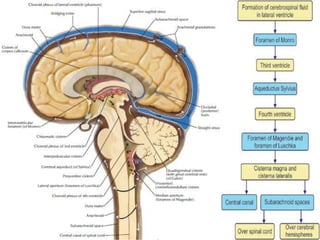
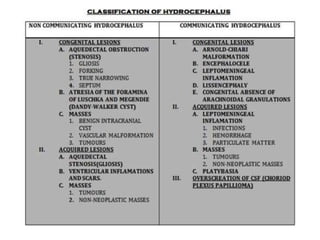
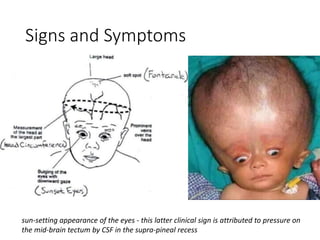
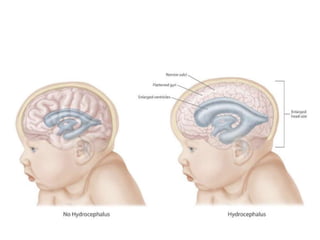
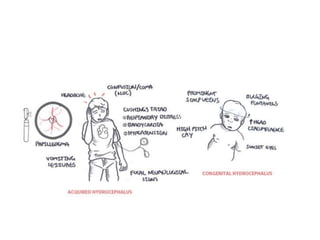
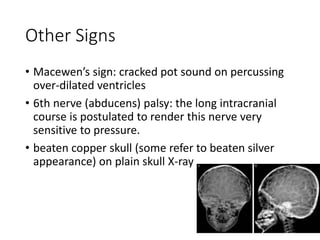
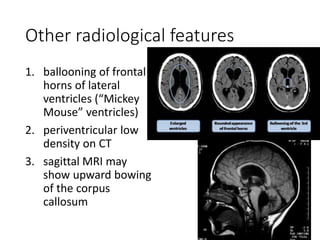
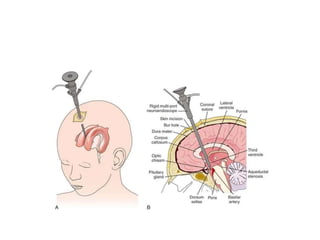
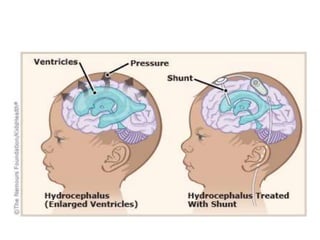
Hydrocephalus is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain's ventricles, primarily caused by subnormal CSF reabsorption, affecting 1-1.5% of the population. Key symptoms include a 'sun-setting' eye appearance, head growth in children, and other subtle signs like irritability and delayed milestones. Management typically requires surgical intervention, such as shunting or ventriculostomy, with a focus on maintaining optimal neurological function and cerebrospinal fluid pressure.