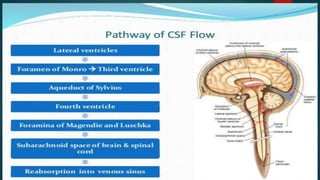
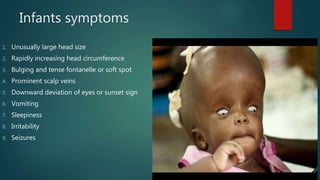
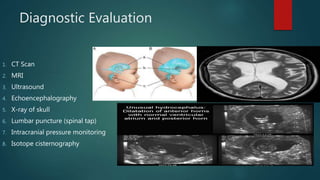
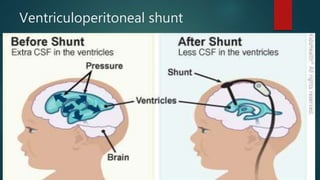
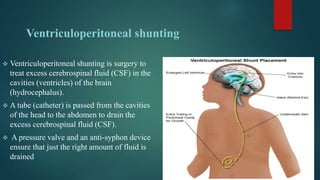
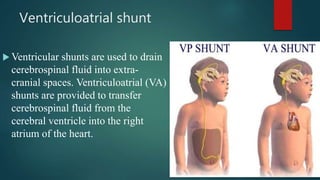
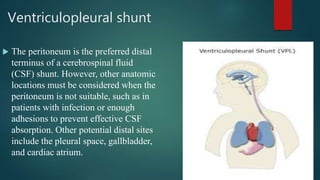
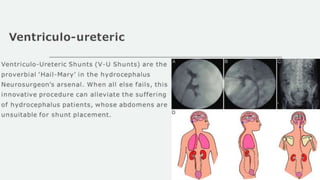
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain, leading to increased intracranial pressure and various symptoms, including rapid head growth in infants and headaches in adults. The condition can be congenital or acquired and is classified into communicating and non-communicating types, with management typically involving surgical intervention like shunt placement. Effective nursing care includes monitoring vital signs, daily head circumference measurement, and providing preoperative and postoperative support.