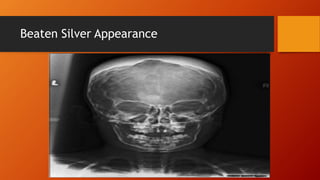
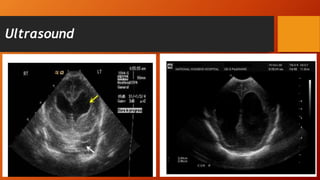
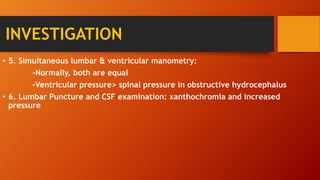
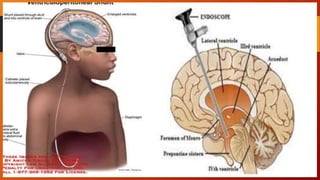
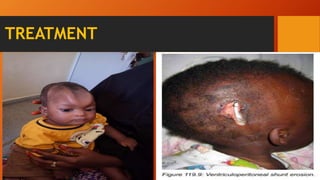
Hydrocephalus is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the ventricles of the brain that results in enlarged ventricles and increased intracranial pressure. It can be caused by obstruction of CSF flow, overproduction of CSF, or impaired absorption of CSF. Common symptoms include an enlarged head size, vomiting, and headaches. Treatment options include the use of shunts to divert CSF from the brain to the abdominal cavity or endoscopic procedures. Prognosis depends on severity but can include long-term neurological and developmental issues if not treated effectively.