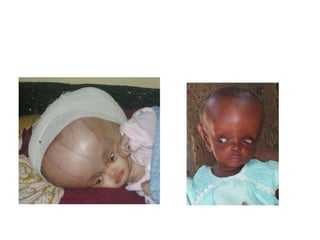
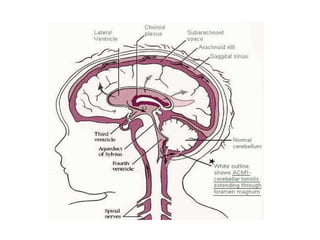
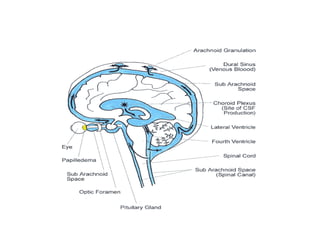
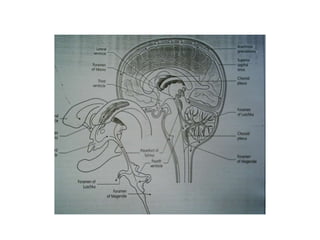
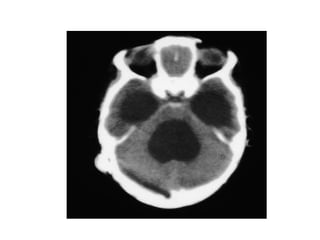
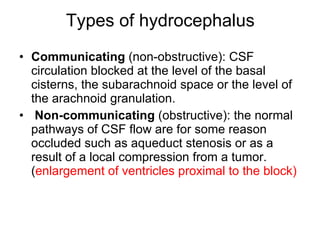
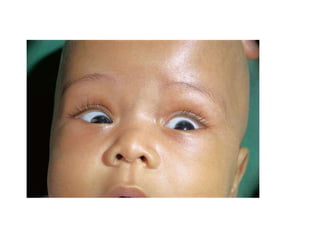
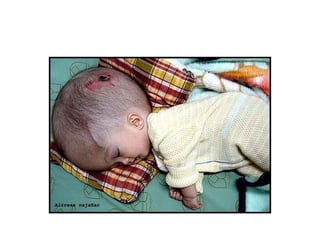
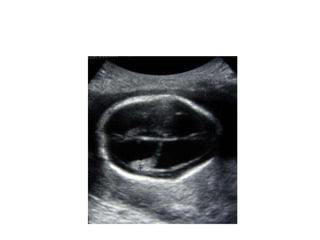
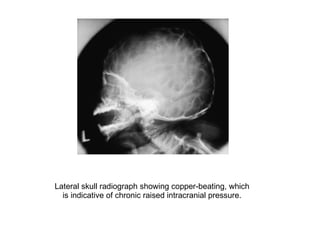
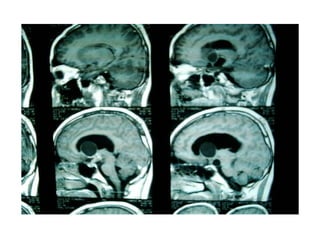
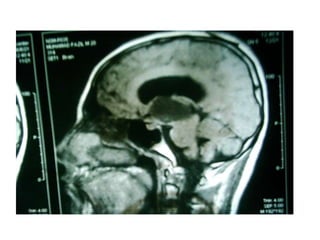
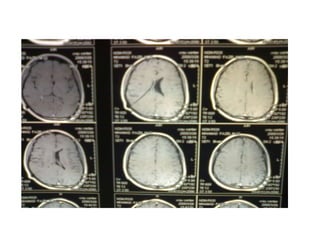
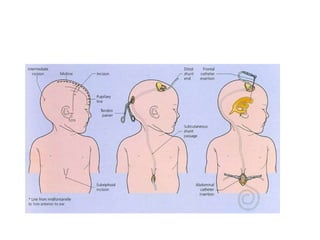
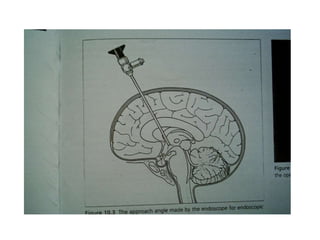
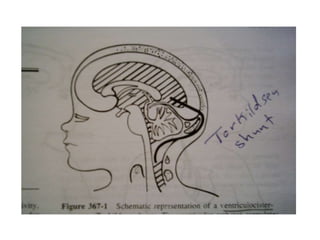
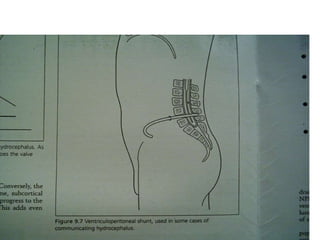
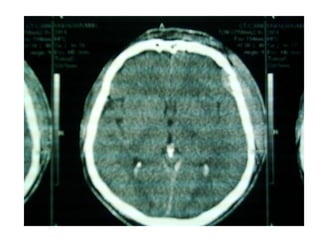
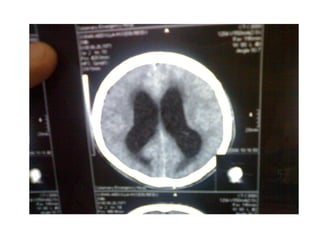
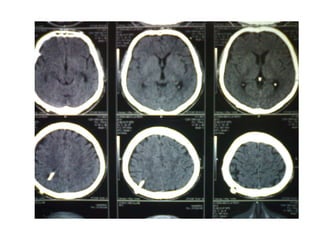
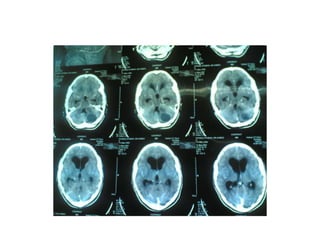
This document discusses hydrocephalus, including its definition, types, causes, clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Hydrocephalus is an increase in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the cranium, usually associated with increased intracranial pressure. It can be communicating or non-communicating depending on whether CSF flow is blocked. Causes include congenital defects, infections, hemorrhages, and masses. Clinical features vary depending on age but include head enlargement, vomiting, headaches, and vision problems. Diagnosis involves imaging like ultrasound, CT, or MRI. Management includes medical treatment, surgical procedures to bypass blockages or drain CSF, and shunt placement. Complications can arise from shunts