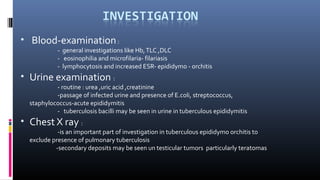
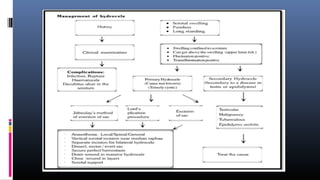
This document discusses the management and treatment of hydrocele. It outlines the necessary investigations which may include blood tests, urine tests, and chest x-rays. Ultrasound is helpful for determining testis position and abnormalities. Fluid aspiration can indicate different conditions. Surgical procedures like lord's plication and Jaboulay's operation are described for fixing different types of hydroceles. Post-operative care and potential complications are also covered. The document provides an overview of evaluating and treating hydroceles.